Abstract
Brentuximab vedotin (BV) and the PD-1 inhibitors have dramatically expanded options and improved outcomes for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). For patients with disease progression following BV, PD-1 inhibitors, and autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT), treatment options are limited. Additional classes of drugs have been found to be effective for HL, including drugs that target the PI3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, as well as immune modulatory agents. These agents target both the Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells as well as the tumor microenvironment. While these targeted drugs are options for patients who have progressed after BV or PD-1 inhibitors, there is good rationale for combining some of these agents with either BV or PD-1 inhibitors to improve response rates or durability. Such combinations are under investigation in clinical trials. Emerging therapies for HL include the anti-CD25 antibody drug conjugate, camidanlumab, as well as other therapies that target CD30 such as anti-CD30 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells and the bispecific antibody, AFM-13. Newer targeted agents, emerging therapies, as well as studies evaluating novel combinations will be reviewed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
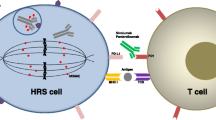
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutton A, Reynolds GM, Dawson CW, Young LS, Murray PG (2005) Constitutive activation of phosphatidyl-inositide 3 kinase contributes to the survival of Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells through a mechanism involving Akt kinase and mTOR. J Pathol 205:498–506
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ, Mills GB, Younes A (2006) Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt promotes G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol 132:503–511
Johnston PB, Pinter-Brown LC, Warsi G, White K, Ramchandren R (2018) Phase 2 study of everolimus for relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Exp Hematol Oncol 7:12
Meadows SA, Vega F, Kashishian A et al (2012) PI3Kdelta inhibitor, GS-1101 (CAL-101), attenuates pathway signaling, induces apoptosis, and overcomes signals from the microenvironment in cellular models of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 119:1897–1900
Gopal AK, Fanale MA, Moskowitz CH et al (2017) Phase II study of idelalisib, a selective inhibitor of PI3Kdelta, for relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Oncol 28:1057–1063
Lemoine M, Derenzini E, Buglio D et al (2012) The pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat induces cell death and synergizes with everolimus in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Blood 119:4017–4025
Oki Y, Buglio D, Fanale M et al (2013) Phase I study of Panobinostat plus Everolimus in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:6882–6890
Ali K, Soond DR, Pineiro R et al (2014) Inactivation of PI(3)K p110delta breaks regulatory T-cell-mediated immune tolerance to cancer. Nature 510:407–411
Marshall NA, Galvin KC, Corcoran AM, Boon L, Higgs R, Mills KH (2012) Immunotherapy with PI3K inhibitor and toll-like receptor agonist induces IFN-gamma+IL-17+ polyfunctional T cells that mediate rejection of murine tumors. Cancer Res 72:581–591
Buglio D, Georgakis GV, Hanabuchi S et al (2008) Vorinostat inhibits STAT6-mediated TH2 cytokine and TARC production and induces cell death in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Blood 112:1424–1433
Buglio D, Khaskhely NM, Voo KS, Martinez-Valdez H, Liu YJ, Younes A (2011) HDAC11 plays an essential role in regulating OX40 ligand expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 117:2910–2917
Kirschbaum MH, Goldman BH, Zain JM et al (2007) Vorinostat (Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic acid) in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: SWOG 0517. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 110:2574
Younes A, Sureda A, Ben-Yehuda D et al (2012) Panobinostat in patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma after autologous stem-cell transplantation: results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30:2197–2203
Younes A, Oki Y, Bociek RG et al (2011) Mocetinostat for relapsed classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 12:1222–1228
Batlevi CL, Kasamon Y, Bociek RG et al (2016) ENGAGE- 501: phase II study of entinostat (SNDX-275) in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica 101:968–975
Skov S, Pedersen MT, Andresen L, Straten PT, Woetmann A, Odum N (2005) Cancer cells become susceptible to natural killer cell killing after exposure to histone deacetylase inhibitors due to glycogen synthase Kinase-3–dependent expression of MHC class I–related chain a and B. Cancer Res 65:11136–11145
Kotla V, Goel S, Nischal S et al (2009) Mechanism of action of lenalidomide in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol 2:36
Gribben JG, Fowler N, Morschhauser F (2015) Mechanisms of action of Lenalidomide in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 33:2803–2811
Boll B, Borchmann P, Topp MS et al (2010) Lenalidomide in patients with refractory or multiple relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol 148:480–482
Fehniger TA, Larson S, Trinkaus K et al (2011) A phase 2 multicenter study of lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 118:5119–5125
Maly JJ, Christian BA, Zhu X et al (2017) A phase I/II trial of Panobinostat in combination with Lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 17:347–353
Padrnos L, Ernst B, Dueck AC et al (2018) A novel combination of the mTORC1 inhibitor everolimus and the immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide produces durable responses in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 18:664–672.e2
Ramos CA, Ballard B, Zhang H et al (2017) Clinical and immunological responses after CD30-specific chimeric antigen receptor-redirected lymphocytes. J Clin Invest 127:3462–3471
Ramos CA, Rouce R, Robertson CS et al (2018) In vivo fate and activity of second- versus third-generation CD19-specific CAR-T cells in B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Mol Ther 26:2727–2737
Ramos CA, Bilgi M, Gerken CP et al (2018) CD30-chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for therapy of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). Blood 132:680
Grover NS, Park SI, Ivanova A et al (2018) Clinical responses to CAR.CD30-T cells in patients with CD30+ lymphomas relapsed after multiple treatments including Brentuximab Vedotin. Blood 132:681
Rothe A, Sasse S, Topp MS et al (2015) A phase 1 study of the bispecific anti-CD30/CD16A antibody construct AFM13 in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 125:4024–4031
Bartlett NL, Chen RW, Domingo-Domenech E et al (2018) A phase 1b study investigating the combination of the tetravalent bispecific NK cell engager AFM13 and Pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma after Brentuximab Vedotin failure: updated safety and efficacy data. Blood 132:1620
Hamadani M, Collins GP, Samaniego F et al (2018) Phase 1 study of Adct-301 (Camidanlumab Tesirine), a novel Pyrrolobenzodiazepine-based antibody drug conjugate, in relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 132:928
Spina V, Bruscaggin A, Cuccaro A et al (2018) Circulating tumor DNA reveals genetics, clonal evolution, and residual disease in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 131:2413–2425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Moskowitz, A.J., Younes, A. (2020). Other New Agents for Hodgkin Lymphoma. In: Engert, A., Younes, A. (eds) Hodgkin Lymphoma. Hematologic Malignancies. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32482-7_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32482-7_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-32481-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-32482-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)