Abstract
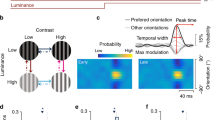
The traditional approach to characterization of orientation maps as they were expounded by Hubel and Wiesel treats them as static representations. Only the magnitude of a neuron’s firing response to orientation is considered and the neuron with the highest response is said to be “tuned” to that response. But the neuronal response to orientation is a time-varying spike train and, if the response of an entire cortical area that potentially responds to orientations in a given part of the visual field is considered, the response must be considered as a spatio-temporal wave. We propose a neural field model consisting of FitzHugh-Nagumo neurons, that generates such a wave. Reflecting the dynamics of a single FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron, the neural field also exhibits excitatory and oscillatory regimes as an offset parameter is increased. We consider the question of the manner in which the input orientation is coded in the response of the neural field and discovered that two different codes − Amplitude Modulation and Phase Modulation − are present. Whereas for smaller offset values, when the model is in excitatory regime the orientation is coded in terms of amplitude, for larger offset values when the model is in the oscillatory regime, the orientation is coded in terms of phase.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Başar, E., Başar-Eroglu, C., Karakaş, S., Schürmann, M.: Gamma, alpha, delta, and theta oscillations govern cognitive processes. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 39(2–3), 241–248 (2001)
Bonhoeffer, T., Grinvald, A.: Iso-orientation domains in cat visual cortex are arranged in pinwheel-like patterns. Nature 353(6343), 429 (1991)
Bosman, C.A., et al.: Attentional stimulus selection through selective synchronization between monkey visual areas. Neuron 75(5), 875–888 (2012)
Buzsaki, G.: Rhythms of the Brain. Oxford University Press, New York (2006)
Christopher deCharms, R., Merzenich, M.M.: Primary cortical representation of sounds by the coordination of action-potential timing. Nature 381(6583), 610 (1996)
Colgin, L.L., et al.: Frequency of gamma oscillations routes flow of information in the hippocampus. Nature 462(7271), 353 (2009)
Einevoll, G.T., Kayser, C., Logothetis, N.K., Panzeri, S.: Modelling and analysis of local field potentials for studying the function of cortical circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14(11), 770 (2013)
Engel, A.K., König, P., Singer, W.: Temporal coding in the visual cortex: new vistas on integration in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 15(6), 218–226 (1992)
Freeman, W.J., Schneider, W.: Changes in spatial patterns of rabbit olfactory eeg with conditioning to odors. Psychophysiology 19(1), 44–56 (1982)
Fries, P.: Neuronal gamma-band synchronization as a fundamental process in cortical computation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 209–224 (2009)
Georgopoulos, A.P., Schwartz, A.B., Kettner, R.E.: Neuronal population coding of movement direction. Science 233(4771), 1416–1419 (1986)
Gray, C.M., Singer, W.: Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 86(5), 1698–1702 (1989)
Grossberg, S., Olsen, S.J.: Rules for the cortical map of ocular dominance and orientation columns. Technical report. Boston University Center for Adaptive Systems and Department of Cognitive and Neural Systems (1994)
Hubel, D.H., Wiesel, T.N.: Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat’s striate cortex. J. Physiol. 148(3), 574–591 (1959)
Katzner, S., et al.: Local origin of field potentials in visual cortex. Neuron 61(1), 35–41 (2009)
Klimesch, W.: Memory processes, brain oscillations and eeg synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 24(1–2), 61–100 (1996)
Klimesch, W., Fellinger, R., Freunberger, R.: Alpha oscillations and early stages of visual encoding. Front. Psychol. 2, 118 (2011)
Kohonen, T.: Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 43(1), 59–69 (1982)
Lee, C., Rohrer, W.H., Sparks, D.L.: Population coding of saccadic eye movements by neurons in the superior colliculus. Nature 332(6162), 357 (1988)
Liu, J., Newsome, W.T.: Local field potential in cortical area mt: stimulus tuning and behavioral correlations. J. Neurosci. 26(30), 7779–7790 (2006)
Miikkulainen, R., Bednar, J.A., Choe, Y., Sirosh, J.: Self-organization, plasticity, and low-level visual phenomena in a laterally connected map model of the primary visual cortex. In: Psychology of Learning and Motivation. volume 36: Perceptual Learning, pp. 257–308. Academic Press, San Diego CA (1997)
Miikkulainen, R., Bednar, J.A., Choe, Y., Sirosh, J.: Computational maps in the visual cortex. Springer, New York (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-28806-6
Miller, K.D., Keller, J.B., Stryker, M.P.: Ocular dominance column development: analysis and simulation. Science 245(4918), 605–615 (1989)
Milner, P.M.: A model for visual shape recognition. Psychol. Rev. 81(6), 521 (1974)
Mitzdorf, U.: Current source-density method and application in cat cerebral cortex: investigation of evoked potentials and eeg phenomena. Physiol. Rev. 65(1), 37–100 (1985)
Niebur, E., Wörgötter, F.: Orientation columns from first principles. In: Eeckman, F.H., Bower, J.M. (eds.) Computation and Neural Systems, pp. 409–413. Springer, Boston (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3254-5_62
Obermayer, K., Ritter, H., Schulten, K.: A principle for the formation of the spatial structure of cortical feature maps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 87(21), 8345–8349 (1990)
Pasupathy, A., Connor, C.E.: Population coding of shape in area v4. Nat. Neurosci. 5(12), 1332 (2002)
Singer, W.: Synchronization of cortical activity and its putative role in information processing and learning. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55(1), 349–374 (1993)
Singer, W., Gray, C.M.: Visual feature integration and the temporal correlation hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 18(1), 555–586 (1995)
Sirota, A., Montgomery, S., Fujisawa, S., Isomura, Y., Zugaro, M., Buzsáki, G.: Entrainment of neocortical neurons and gamma oscillations by the hippocampal theta rhythm. Neuron 60(4), 683–697 (2008)
Tanaka, S.: Theory of self-organization of cortical maps: mathematical framework. Neural Netw. 3(6), 625–640 (1990)
Tort, A.B., Komorowski, R.W., Manns, J.R., Kopell, N.J., Eichenbaum, H.: Theta-gamma coupling increases during the learning of item-context associations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(49), 20942–20947 (2009)
Van Der Meer, M.A., Redish, A.D.: Low and high gamma oscillations in rat ventral striatum have distinct relationships to behavior, reward, and spiking activity on a learned spatial decision task. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 3, 9 (2009)
Womelsdorf, T., Fries, P., Mitra, P.P., Desimone, R.: Gamma-band synchronization in visual cortex predicts speed of change detection. Nature 439(7077), 733 (2006)
Yuille, A., Kammen, D., Cohen, D.: Quadrature and the development of orientation selective cortical cells by hebb rules. Biol. Cybern. 61(3), 183–194 (1989)
Zold, C.L., Shuler, M.G.H.: Theta oscillations in visual cortex emerge with experience to convey expected reward time and experienced reward rate. J. Neurosci. 35(26), 9603–9614 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, B.S., Kori, A., Elango, S., Chakravarthy, V.S. (2018). Phase and Amplitude Modulation in a Neural Oscillatory Model of the Orientation Map. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A., Ozawa, S. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11302. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04179-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04179-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04178-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04179-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)