Abstract
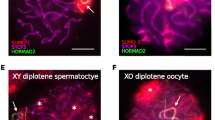
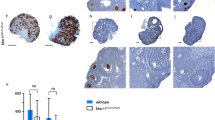
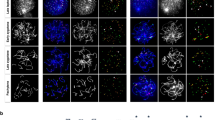
Meiosis is the specialized cell division in sexually reproducing organisms in which haploid gametes are produced. Meiotic prophase I is the defining stage of meiosis, when pairing and synapsis occur between homologous chromosomes, concurrent with reciprocal recombination (or crossing over) events that arise between them. Any disruption of these events during prophase I can lead to improper segregation of homologous chromosomes which can cause severe birth defects in the resulting progeny, and this occurs with alarming frequency in human oocytes. Thus, while the pathways that regulate these events in prophase I are highly conserved in both males and females, the stringency with which these events are monitored and/or controlled appears to be dramatically lower in females. These observations underscore the need to examine and compare meiotic mechanisms across the sexes. However, the study of female meiosis is impeded by the early start of meiosis during fetal development and the very limited amount of ovarian tissue available for meiotic analyses. Here we describe three different techniques which are useful for meiotic prophase I analysis in mouse/human oocytes, ranging from early prophase I events through until the resolution of crossing over at the first and second meiotic divisions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hassold T, Hunt P (2001) To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet 2:280–291
Hunt PA, Hassold TJ (2008) Human female meiosis: what makes a good egg go bad? Trends Genet 24:86–93
Page SL, Hawley RS (2004) The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:525–558
Morelli MA, Cohen PE (2005) Not all germ cells are created equal: aspects of sexual dimorphism in mammalian meiosis. Reproduction 130:761–781
Hassold T, Hall H, Hunt P (2007) The origin of human aneuploidy: where we have been, where we are going. Hum Mol Genet 16 Spec No. 2: R203–R208
Cohen PE, Holloway JK (2010) Predicting gene networks in human oocyte meiosis. Biol Reprod 82:469–472
Hulten MA, Patel S, Jonasson J, Iwarsson E (2010) On the origin of the maternal age effect in trisomy 21 Down syndrome: the Oocyte Mosaicism Selection model. Reproduction 139:1–9
Lenzi ML, Smith J, Snowden T, Kim M, Fishel R, Poulos BK, Cohen PE (2005) Extreme heterogeneity in the molecular events leading to the establishment of chiasmata during meiosis I in human oocytes. Am J Hum Genet 76:112–127
Yuan L, Liu JG, Zhao J, Brundell E, Daneholt B, Hoog C (2000) The murine SCP3 gene is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, chromosome synapsis, and male fertility. Mol Cell 5:73–83
Yuan L, Liu JG, Hoja MR, Wilbertz J, Nordqvist K, Hoog C (2002) Female germ cell aneuploidy and embryo death in mice lacking the meiosis-specific protein SCP3. Science 296:1115–1118
Hamer G, Novak I, Kouznetsova A, Hoog C (2008) Disruption of pairing and synapsis of chromosomes causes stage-specific apoptosis of male meiotic cells. Theriogenology 69:333–339
Pelttari J, Hoja MR, Yuan L, Liu JG, Brundell E, Moens P, Santucci-Darmanin S, Jessberger R, Barbero JL, Heyting C, Hoog C (2001) A meiotic chromosomal core consisting of cohesin complex proteins recruits DNA recombination proteins and promotes synapsis in the absence of an axial element in mammalian meiotic cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:5667–5677
Borum K (1961) Oogenesis in the mouse. Exp Cell Res 24:495–507
Evans CW, Robb DI, Tuckett F, Chanlloner S (1982) Regulation of meiosis in the foetal mouse gonad. J Embryol Exp Morphol 68:59–67
Kan R, Sun X, Kolas NK, Avdievich E, Kneitz B, Edelmann W, Cohen PE (2008) Comparative analysis of meiotic progression in female mice bearing mutations in genes of the DNA mismatch repair pathway. Biol Reprod 78:462–471
Kolas NK, Svetlanov A, Lenzi ML, Macaluso FP, Lipkin SM, Liskay RM, Greally J, Edelmann W, Cohen PE (2005) Localization of MMR proteins on meiotic chromosomes in mice indicates distinct functions during prophase I. J Cell Biol 171:447–458
Wojtasz L, Daniel K, Roig I, Bolcun-Filas E, Xu H, Boonsanay V, Eckmann CR, Cooke HJ, Jasin M, Keeney S, McKay MJ, Toth A (2009) Mouse HORMAD1 and HORMAD2, two conserved meiotic chromosomal proteins, are depleted from synapsed chromosome axes with the help of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase. PLoS Genet 5:e1000702
Bolcun-Filas E, Bannister LA, Barash A, Schimenti KJ, Hartford SA, Eppig JJ, Handel MA, Shen L, Schimenti JC (2011) A-MYB (MYBL1) transcription factor is a master regulator of male meiosis. Development 138:3319–3330
Williams DL, Lafferty DA, Webb SL (1970) An air drying method for the preparation of dictyotene chromosomes from ovaries of Chinese hamsters. Stain Technol 45:133–135
Tarkowski AK (1966) An air-drying method for chromosome preparations from mouse eggs. Cytogenetics 5:394–400
Woods LM, Hodges CA, Baart E, Baker SM, Liskay RM, Hunt PA (1999) Chromosomal influence on meiotic spindle assembly: abnormal meiosis I in female Mlh1 mutant mice. J Cell Biol 145:1395–1406
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding from the NICHD to P.E.C. (HD041012) and by a student fellowship from the Cornell Center for Vertebrate Genomics to X.S. We thank members of the Cohen lab for their helpful comments and suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Sun, X., Cohen, P.E. (2013). Studying Recombination in Mouse Oocytes. In: Homer, H. (eds) Mammalian Oocyte Regulation. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 957. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-191-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-191-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-190-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-191-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols