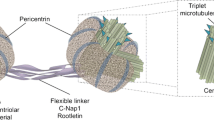
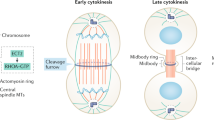
Abstract
Understanding how the genomic instability that accompanies tumour development arises has been an important question for more than a century. One potential cause of such instability is defective chromosome segregation during mitosis. A cause of mitotic defects may lie in the acquisition of multiple mitotic spindle poles, through an increase in the number of centrosomes. Cancer cells frequently possess multiple centrosomes. DNA damaging treatments, or mutations in key DNA repair genes, also lead to centrosome amplification. Here, we review current models for how cells may lose the normal controls on centrosome duplication and acquire more than the normal number of these organelles. We also discuss how genotoxic stresses may contribute to the dysregulation of centrosome duplication and how this process may be a contributory factor in cellular transformation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adon AM, Zeng X, Harrison MK, Sannem S, Kiyokawa H, Kaldis P, Saavedra HI (2010) Cdk2 and Cdk4 regulate the centrosome cycle and are critical mediators of centrosome amplification in p53-null cells. Mol Cell Biol 30(3):694–710
Balczon R, Bao L, Zimmer WE, Brown K, Zinkowski RP, Brinkley BR (1995) Dissociation of centrosome replication events from cycles of DNA synthesis and mitotic division in hydroxyurea-arrested Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol 130(1):105–115
Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, Orntoft T, Lukas J, Bartek J (2005) DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 434(7035):864–870
Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Tort F, Fugger K, Johansson F, Sehested M, Andersen CL, Dyrskjot L, Orntoft T, Lukas J, Kittas C, Helleday T, Halazonetis TD, Bartek J, Gorgoulis VG (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444(7119):633–637
Basto R, Brunk K, Vinadogrova T, Peel N, Franz A, Khodjakov A, Raff JW (2008) Centrosome amplification can initiate tumorigenesis in flies. Cell 133(6):1032–1042
Bertrand P, Lambert S, Joubert C, Lopez BS (2003) Overexpression of mammalian Rad51 does not stimulate tumorigenesis while a dominant-negative Rad51 affects centrosome fragmentation, ploidy and stimulates tumorigenesis, in p53-defective CHO cells. Oncogene 22(48):7587–7592
Bettencourt-Dias M, Rodrigues-Martins A, Carpenter L, Riparbelli M, Lehmann L, Gatt MK, Carmo N, Balloux F, Callaini G, Glover DM (2005) SAK/PLK4 is required for centriole duplication and flagella development. Curr Biol 15(24):2199–2207
Blagosklonny MV (2007) Mitotic arrest and cell fate. Cell Cycle 6(1):e1–e5
Bourke E, Brown JA, Takeda S, Hochegger H, Morrison CG (2010) DNA damage induces Chk1-dependent threonine-160 phosphorylation and activation of Cdk2. Oncogene 29(4):616–624
Bourke E, Dodson H, Merdes A, Cuffe L, Zachos G, Walker M, Gillespie D, Morrison CG (2007) DNA damage induces Chk1-dependent centrosome amplification. EMBO Report 8(6):603–609
Boveri T (2008) Concerning the origin of malignant tumours by Theodor Boveri. Translated and annotated by Henry Harris. J Cell Sci 121(Suppl 1):1–84
Braig M, Lee S, Loddenkemper C, Rudolph C, Peters AH, Schlegelberger B, Stein H, Dorken B, Jenuwein T, Schmitt CA (2005) Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature 436(7051):660–665
Cahill DP, Lengauer C, Yu J, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz SD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1998) Mutations of mitotic checkpoint genes in human cancers. Nature 392(6673):300–303
Carvalho-Santos Z, Machado P, Branco P, Tavares-Cadete F, Rodrigues-Martins A, Pereira-Leal JB, Bettencourt-Dias M (2010) Stepwise evolution of the centriole-assembly pathway. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 9):1414–1426
Castellanos E, Dominguez P, Gonzalez C (2008) Centrosome dysfunction in Drosophila neural stem cells causes tumors that are not due to genome instability. Curr Biol 18(16):1209–1214
Chandhok NS, Pellman D (2009) A little CIN may cost a lot: revisiting aneuploidy and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19(1):74–81
Chen Z, Indjeian VB, McManus M, Wang L, Dynlacht BD (2002) CP110, a cell cycle-dependent CDK substrate, regulates centrosome duplication in human cells. Dev Cell 3(3):339–350
Cimini D, Cameron LA, Salmon ED (2004) Anaphase spindle mechanics prevent mis-segregation of merotelically oriented chromosomes. Curr Biol 14(23):2149–2155
Cimini D, Fioravanti D, Salmon ED, Degrassi F (2002) Merotelic kinetochore orientation versus chromosome mono-orientation in the origin of lagging chromosomes in human primary cells. J Cell Sci 115(Pt 3):507–515
Cimini D, Howell B, Maddox P, Khodjakov A, Degrassi F, Salmon ED (2001) Merotelic kinetochore orientation is a major mechanism of aneuploidy in mitotic mammalian tissue cells. J Cell Biol 153(3):517–527
D’Assoro AB, Barrett SL, Folk C, Negron VC, Boeneman K, Busby R, Whitehead C, Stivala F, Lingle WL, Salisbury JL (2002a) Amplified centrosomes in breast cancer: a potential indicator of tumor aggressiveness. Breast Cancer Res Treat 75(1):25–34
D’Assoro AB, Lingle WL, Salisbury JL (2002b) Centrosome amplification and the development of cancer. Oncogene 21(40):6146–6153
Dai W, Wang Q, Liu T, Swamy M, Fang Y, **e S, Mahmood R, Yang YM, Xu M, Rao CV (2004) Slippage of mitotic arrest and enhanced tumor development in mice with BubR1 haploinsufficiency. Cancer Res 64(2):440–445
Daniels MJ, Wang Y, Lee M, Venkitaraman AR (2004) Abnormal cytokinesis in cells deficient in the breast cancer susceptibility protein BRCA2. Science 306(5697):876–879
Delattre M, Gonczy P (2004) The arithmetic of centrosome biogenesis. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 9):1619–1630
Dodson H, Bourke E, Jeffers LJ, Vagnarelli P, Sonoda E, Takeda S, Earnshaw WC, Merdes A, Morrison C (2004) Centrosome amplification induced by DNA damage occurs during a prolonged G2 phase and involves ATM. EMBO J 23(19):3864–3873
Dodson H, Wheatley SP, Morrison CG (2007) Involvement of centrosome amplification in radiation-induced mitotic catastrophe. Cell Cycle 6(3):364–370
Duensing A, Liu Y, Perdreau SA, Kleylein-Sohn J, Nigg EA, Duensing S (2007) Centriole overduplication through the concurrent formation of multiple daughter centrioles at single maternal templates. Oncogene 26(43):6280–6288
Duensing A, Liu Y, Tseng M, Malumbres M, Barbacid M, Duensing S (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is dispensable for normal centrosome duplication but required for oncogene-induced centrosome overduplication. Oncogene 25(20):2943–2949
Duensing S, Duensing A, Crum CP, Munger K (2001) Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein-induced abnormal centrosome synthesis is an early event in the evolving malignant phenotype. Cancer Res 61(6):2356–2360
Duensing S, Lee LY, Duensing A, Basile J, Piboonniyom S, Gonzalez S, Crum CP, Munger K (2000) The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperate to induce mitotic defects and genomic instability by uncoupling centrosome duplication from the cell division cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(18):10002–10007
Duensing S, Munger K (2002) The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins independently induce numerical and structural chromosome instability. Cancer Res 62(23):7075–7082
Duensing S, Munger K (2003) Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein can induce abnormal centrosome duplication through a mechanism independent of inactivation of retinoblastoma protein family members. J Virol 77(22):12331–12335
Dzhindzhev NS, Yu QD, Weiskopf K, Tzolovsky G, Cunha-Ferreira I, Riparbelli M, Rodrigues-Martins A, Bettencourt-Dias M, Callaini G, Glover DM (2010) Asterless is a scaffold for the onset of centriole assembly. Nature 467(7316):714–718
Fisk HA, Winey M (2001) The mouse Mps1p-like kinase regulates centrosome duplication. Cell 106(1):95–104
Fletcher L, Cerniglia GJ, Nigg EA, Yend TJ, Muschel RJ (2004) Inhibition of centrosome separation after DNA damage: a role for Nek2. Radiat Res 162(2):128–135
Fukasawa K (2005) Centrosome amplification, chromosome instability and cancer development. Cancer Lett 230(1):6–19
Fukasawa K (2008) P53, cyclin-dependent kinase and abnormal amplification of centrosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1786(1):15–23
Fukasawa K, Choi T, Kuriyama R, Rulong S, Vande Woude GF (1996) Abnormal centrosome amplification in the absence of p53. Science 271(5256):1744–1747
Ganem NJ, Godinho SA, Pellman D (2009) A mechanism linking extra centrosomes to chromosomal instability. Nature 460(7252):278–282
Gergely F, Basto R (2008) Multiple centrosomes: together they stand, divided they fall. Genes Dev 22(17):2291–2296
Ghadimi BM, Sackett DL, Difilippantonio MJ, Schrock E, Neumann T, Jauho A, Auer G, Ried T (2000) Centrosome amplification and instability occurs exclusively in aneuploid, but not in diploid colorectal cancer cell lines, and correlates with numerical chromosomal aberrations. Genes Chromosom Cancer 27(2):183–190
Gisselsson D, Palsson E, Yu C, Mertens F, Mandahl N (2004) Mitotic instability associated with late genomic changes in bone and soft tissue tumours. Cancer Lett 206(1):69–76
Godinho SA, Kwon M, Pellman D (2009) Centrosomes and cancer: how cancer cells divide with too many centrosomes. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):85–98
Goepfert TM, Adigun YE, Zhong L, Gay J, Medina D, Brinkley WR (2002) Centrosome amplification and overexpression of aurora A are early events in rat mammary carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 62(14):4115–4122
Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Venere M, Ditullio RA Jr, Kastrinakis NG, Levy B, Kletsas D, Yoneta A, Herlyn M, Kittas C, Halazonetis TD (2005) Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature 434(7035):907–913
Gregan J, Polakova S, Zhang L, Tolić-Nørrelykke IM, Cimini D (2011) Merotelic kinetochore attachment: causes and effects. Trends Cell Biol 21(6):374–381
Griffin CS, Simpson PJ, Wilson CR, Thacker J (2000) Mammalian recombination-repair genes XRCC2 and XRCC3 promote correct chromosome segregation. Nat Cell Biol 2(10):757–761
Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA (2005) The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell 16(3):1095–1107
Guernsey DL, Jiang H, Hussin J, Arnold M, Bouyakdan K, Perry S, Babineau-Sturk T, Beis J, Dumas N, Evans SC, Ferguson M, Matsuoka M, Macgillivray C, Nightingale M, Patry L, Rideout AL, Thomas A, Orr A, Hoffmann I, Michaud JL, Awadalla P, Meek DC, Ludman M, Samuels ME (2010) Mutations in centrosomal protein CEP152 in primary microcephaly families linked to MCPH4. Am J Hum Genet 87(1):40–51
Guiducci C, Cerone MA, Bacchetti S (2001) Expression of mutant telomerase in immortal telomerase-negative human cells results in cell cycle deregulation, nuclear and chromosomal abnormalities and rapid loss of viability. Oncogene 20(6):714–725
Gustafson LM, Gleich LL, Fukasawa K, Chadwell J, Miller MA, Stambrook PJ, Gluckman JL (2000) Centrosome hyperamplification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential phenotypic marker of tumor aggressiveness. Laryngoscope 110(11):1798–1801
Habedanck R, Stierhof YD, Wilkinson CJ, Nigg EA (2005) The Polo kinase Plk4 functions in centriole duplication. Nat Cell Biol 7(11):1140–1146
Hanashiro K, Brancaccio M, Fukasawa K (2011) Activated ROCK II by-passes the requirement of the CDK2 activity for centrosome duplication and amplification. Oncogene 30(19):2188–2197
Hanks S, Coleman K, Reid S, Plaja A, Firth H, Fitzpatrick D, Kidd A, Mehes K, Nash R, Robin N, Shannon N, Tolmie J, Swansbury J, Irrthum A, Douglas J, Rahman N (2004) Constitutional aneuploidy and cancer predisposition caused by biallelic mutations in BUB1B. Nat Genet 36(11):1159–1161
Hatch EM, Kulukian A, Holland AJ, Cleveland DW, Stearns T (2010) Cep152 interacts with Plk4 and is required for centriole duplication. J Cell Biol 191(4):721–729
Hergovich A, Lamla S, Nigg EA, Hemmings BA (2007) Centrosome-associated NDR kinase regulates centrosome duplication. Mol Cell 25(4):625–634
Hinchcliffe EH, Li C, Thompson EA, Maller JL, Sluder G (1999) Requirement of Cdk2-cyclin E activity for repeated centrosome reproduction in Xenopus egg extracts. Science 283(5403):851–854
Hinchcliffe EH, Miller FJ, Cham M, Khodjakov A, Sluder G (2001) Requirement of a centrosomal activity for cell cycle progression through G1 into S phase. Science 291(5508):1547–1550
Hinchcliffe EH, Sluder G (2001) “It takes two to tango”: understanding how centrosome duplication is regulated throughout the cell cycle. Genes Dev 15(10):1167–1181
Hochegger H, Dejsuphong D, Sonoda E, Saberi A, Rajendra E, Kirk J, Hunt T, Takeda S (2007) An essential role for Cdk1 in S phase control is revealed via chemical genetics in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol 178(2):257–268
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW (2009) Boveri revisited: chromosomal instability, aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(7):478–487
Hut HM, Lemstra W, Blaauw EH, Van Cappellen GW, Kam**a HH, Sibon OC (2003) Centrosomes split in the presence of impaired DNA integrity during mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 14(5):1993–2004
Inanc B, Dodson H, Morrison CG (2010) A centrosome-autonomous signal that involves centriole disengagement permits centrosome duplication in G2 phase after DNA damage. Mol Biol Cell 21(22):3866–3877
Johnson PA, Clements P, Hudson K, Caldecott KW (1999) A mitotic spindle requirement for DNA damage-induced apoptosis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res 59(11):2696–2700
Jonathan EC, Bernhard EJ, McKenna WG (1999) How does radiation kill cells? Curr Opin Chem Biol 3(1):77–83
Kalitsis P, Earle E, Fowler KJ, Choo KH (2000) Bub3 gene disruption in mice reveals essential mitotic spindle checkpoint function during early embryogenesis. Genes Dev 14(18):2277–2282
Kawamura K, Izumi H, Ma Z, Ikeda R, Moriyama M, Tanaka T, Nojima T, Levin LS, Fujikawa-Yamamoto K, Suzuki K, Fukasawa K (2004) Induction of centrosome amplification and chromosome instability in human bladder cancer cells by p53 mutation and cyclin E overexpression. Cancer Res 64(14):4800–4809
Kawamura K, Morita N, Domiki C, Fujikawa-Yamamoto K, Hashimoto M, Iwabuchi K, Suzuki K (2006) Induction of centrosome amplification in p53 siRNA-treated human fibroblast cells by radiation exposure. Cancer Sci 97(4):252–258
Kemp CA, Kopish KR, Zipperlen P, Ahringer J, O’Connell KF (2004) Centrosome maturation and duplication in C. elegans require the coiled-coil protein SPD-2. Dev Cell 6(4):511–523
Keryer G, Ris H, Borisy GG (1984) Centriole distribution during tripolar mitosis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol 98(6):2222–2229
Khodjakov A, Cole RW, McEwen BF, Buttle KF, Rieder CL (1997) Chromosome fragments possessing only one kinetochore can congress to the spindle equator. J Cell Biol 136(2):229–240
Khodjakov A, Cole RW, Oakley BR, Rieder CL (2000) Centrosome-independent mitotic spindle formation in vertebrates. Curr Biol 10(2):59–67
Khodjakov A, Rieder CL (2001) Centrosomes enhance the fidelity of cytokinesis in vertebrates and are required for cell cycle progression. J Cell Biol 153(1):237–242
Khodjakov A, Rieder CL, Sluder G, Cassels G, Sibon O, Wang CL (2002) De novo formation of centrosomes in vertebrate cells arrested during S phase. J Cell Biol 158(7):1171–1181
Kirkham M, Muller-Reichert T, Oegema K, Grill S, Hyman AA (2003) SAS-4 is a C. elegans centriolar protein that controls centrosome size. Cell 112(4):575–587
Kleylein-Sohn J, Westendorf J, Le Clech M, Habedanck R, Stierhof YD, Nigg EA (2007) Plk4-induced centriole biogenesis in human cells. Dev Cell 13(2):190–202
Kohlmaier G, Loncarek J, Meng X, McEwen BF, Mogensen MM, Spektor A, Dynlacht BD, Khodjakov A, Gonczy P (2009) Overly long centrioles and defective cell division upon excess of the SAS-4-related protein CPAP. Curr Biol 19(12):1012–1018
Kops GJ, Foltz DR, Cleveland DW (2004) Lethality to human cancer cells through massive chromosome loss by inhibition of the mitotic checkpoint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(23):8699–8704
Kops GJ, Weaver BA, Cleveland DW (2005) On the road to cancer: aneuploidy and the mitotic checkpoint. Nat Rev Cancer 5(10):773–785
Kraakman-van der Zwet M, Overkamp WJ, van Lange RE, Essers J, van Duijn-Goedhart A, Wiggers I, Swaminathan S, van Buul PP, Errami A, Tan RT, Jaspers NG, Sharan SK, Kanaar R, Zdzienicka MZ (2002) Brca2 (XRCC11) deficiency results in radioresistant DNA synthesis and a higher frequency of spontaneous deletions. Mol Cell Biol 22(2):669–679
Kramer A, Schweizer S, Neben K, Giesecke C, Kalla J, Katzenberger T, Benner A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Ho AD, Ott G (2003) Centrosome aberrations as a possible mechanism for chromosomal instability in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia 17(11):2207–2213
Kuo KK, Sato N, Mizumoto K, Maehara N, Yonemasu H, Ker CG, Sheen PC, Tanaka M (2000) Centrosome abnormalities in human carcinomas of the gallbladder and intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. Hepatology 31(1):59–64
Kuriyama R, Terada Y, Lee KS, Wang CL (2007) Centrosome replication in hydroxyurea-arrested CHO cells expressing GFP-tagged centrin2. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 14):2444–2453
La Terra S, English CN, Hergert P, McEwen BF, Sluder G, Khodjakov A (2005) The de novo centriole assembly pathway in HeLa cells: cell cycle progression and centriole assembly/maturation. J Cell Biol 168(5):713–722
Lacey KR, Jackson PK, Stearns T (1999) Cyclin-dependent kinase control of centrosome duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(6):2817–2822
Leidel S, Delattre M, Cerutti L, Baumer K, Gonczy P (2005) SAS-6 defines a protein family required for centrosome duplication in C. elegans and in human cells. Nat Cell Biol 7(2):115–125
Leidel S, Gonczy P (2003) SAS-4 is essential for centrosome duplication in C elegans and is recruited to daughter centrioles once per cell cycle. Dev Cell 4(3):431–439
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1998) Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature 396(6712):643–649
Li GQ, Li H, Zhang HF (2003) Mad2 and p53 expression profiles in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 9(9):1972–1975
Lingle WL, Barrett SL, Negron VC, D’Assoro AB, Boeneman K, Liu W, Whitehead CM, Reynolds C, Salisbury JL (2002) Centrosome amplification drives chromosomal instability in breast tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(4):1978–1983
Lingle WL, Lutz WH, Ingle JN, Maihle NJ, Salisbury JL (1998) Centrosome hypertrophy in human breast tumors: implications for genomic stability and cell polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(6):2950–2955
Lingle WL, Salisbury JL (2001) Methods for the analysis of centrosome reproduction in cancer cells. Methods Cell Biol 67:325–336
Loffler H, Lukas J, Bartek J, Kramer A (2006) Structure meets function–centrosomes, genome maintenance and the DNA damage response. Exp Cell Res 312(14):2633–2640
Loncarek J, Hergert P, Magidson V, Khodjakov A (2008) Control of daughter centriole formation by the pericentriolar material. Nat Cell Biol 10(3):322–328
Loncarek J, Khodjakov A (2009) Ab ovo or de novo? Mechanisms of centriole duplication. Mol Cells 27(2):135–142
Maniotis A, Schliwa M (1991) Microsurgical removal of centrosomes blocks cell reproduction and centriole generation in BSC-1 cells. Cell 67(3):495–504
Mantel C, Braun SE, Reid S, Henegariu O, Liu L, Hangoc G, Broxmeyer HE (1999) p21(cip-1/waf-1) deficiency causes deformed nuclear architecture, centriole overduplication, polyploidy, and relaxed microtubule damage checkpoints in human hematopoietic cells. Blood 93(4):1390–1398
Marshall WF, Vucica Y, Rosenbaum JL (2001) Kinetics and regulation of de novo centriole assembly. Implications for the mechanism of centriole duplication. Curr Biol 11(5):308–317
Matsumoto Y, Hayashi K, Nishida E (1999) Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) is required for centrosome duplication in mammalian cells. Curr Biol 9(8):429–432
McDermott KM, Zhang J, Holst CR, Kozakiewicz BK, Singla V, Tlsty TD (2006) p16(INK4a) prevents centrosome dysfunction and genomic instability in primary cells. PLoS Biol 4(3):e51
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA (2002) Aurora-A overexpression reveals tetraploidization as a major route to centrosome amplification in p53-/- cells. EMBO J 21(4):483–492
Meraldi P, Lukas J, Fry AM, Bartek J, Nigg EA (1999) Centrosome duplication in mammalian somatic cells requires E2F and Cdk2-cyclin A. Nat Cell Biol 1(2):88–93
Mikhailov A, Cole RW, Rieder CL (2002) DNA damage during mitosis in human cells delays the metaphase/anaphase transition via the spindle-assembly checkpoint. Curr Biol 12(21):1797–1806
Mikule K, Delaval B, Kaldis P, Jurcyzk A, Hergert P, Doxsey S (2007) Loss of centrosome integrity induces p38-p53-p21-dependent G1-S arrest. Nat Cell Biol 9(2):160–170
Musacchio A, Salmon ED (2007) The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(5):379–393
Mussman JG, Horn HF, Carroll PE, Okuda M, Tarapore P, Donehower LA, Fukasawa K (2000) Synergistic induction of centrosome hyperamplification by loss of p53 and cyclin E overexpression. Oncogene 19(13):1635–1646
Nigg EA (2002) Centrosome aberrations: cause or consequence of cancer progression? Nat Rev Cancer 2(11):815–825
Nigg EA (2007) Centrosome duplication: of rules and licenses. Trends Cell Biol 17(5):215–221
Nitta M, Kobayashi O, Honda S, Hirota T, Kuninaka S, Marumoto T, Ushio Y, Saya H (2004) Spindle checkpoint function is required for mitotic catastrophe induced by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 23(39):6548–6558
Nitta T, Kanai M, Sugihara E, Tanaka M, Sun B, Nagasawa T, Sonoda S, Saya H, Miwa M (2006) Centrosome amplification in adult T-cell leukemia and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax-induced human T cells. Cancer Sci 97(9):836–841
O’Connell KF, Caron C, Kopish KR, Hurd DD, Kemphues KJ, Li Y, White JG (2001) The C. elegans zyg-1 gene encodes a regulator of centrosome duplication with distinct maternal and paternal roles in the embryo. Cell 105(4):547–558
Okada H, Mak TW (2004) Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 4(8):592–603
Okuda M, Horn HF, Tarapore P, Tokuyama Y, Smulian AG, Chan PK, Knudsen ES, Hofmann IA, Snyder JD, Bove KE, Fukasawa K (2000) Nucleophosmin/B23 is a target of CDK2/cyclin E in centrosome duplication. Cell 103(1):127–140
Oricchio E, Saladino C, Iacovelli S, Soddu S, Cundari E (2006) ATM is activated by default in mitosis, localizes at centrosomes and monitors mitotic spindle integrity. Cell Cycle 5(1):88–92
Peel N, Stevens NR, Basto R, Raff JW (2007) Overexpressing centriole-replication proteins in vivo induces centriole overduplication and de novo formation. Curr Biol 17(10):834–843
Pelletier L, O’Toole E, Schwager A, Hyman AA, Muller-Reichert T (2006) Centriole assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 444(7119):619–623
Pelletier L, Ozlu N, Hannak E, Cowan C, Habermann B, Ruer M, Muller-Reichert T, Hyman AA (2004) The Caenorhabditis elegans centrosomal protein SPD-2 is required for both pericentriolar material recruitment and centriole duplication. Curr Biol 14(10):863–873
Pihan GA, Purohit A, Wallace J, Knecht H, Woda B, Quesenberry P, Doxsey SJ (1998) Centrosome defects and genetic instability in malignant tumors. Cancer Res 58(17):3974–3985
Pihan GA, Purohit A, Wallace J, Malhotra R, Liotta L, Doxsey SJ (2001) Centrosome defects can account for cellular and genetic changes that characterize prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res 61(5):2212–2219
Prosser SL, Straatman KR, Fry AM (2009) Molecular dissection of the centrosome overduplication pathway in S-phase arrested cells. Mol Cell Biol&&&AQ
Quintyne NJ, Reing JE, Hoffelder DR, Gollin SM, Saunders WS (2005) Spindle multipolarity is prevented by centrosomal clustering. Science 307(5706):127–129
Ring D, Hubble R, Kirschner M (1982) Mitosis in a cell with multiple centrioles. J Cell Biol 94(3):549–556
Robinson HM, Bratlie-Thoresen S, Brown R, Gillespie DA (2007) Chk1 is required for G2/M checkpoint response induced by the catalytic topoisomerase II inhibitor ICRF-193. Cell Cycle 6(10):1265–1267
Rodrigues-Martins A, Bettencourt-Dias M, Riparbelli M, Ferreira C, Ferreira I, Callaini G, Glover DM (2007a) DSAS-6 organizes a tube-like centriole precursor, and its absence suggests modularity in centriole assembly. Curr Biol 17(17):1465–1472
Rodrigues-Martins A, Riparbelli M, Callaini G, Glover DM, Bettencourt-Dias M (2007b) Revisiting the role of the mother centriole in centriole biogenesis. Science 316(5827):1046–1050
Roninson IB, Broude EV, Chang BD (2001) If not apoptosis, then what? Treatment-induced senescence and mitotic catastrophe in tumor cells. Drug Resist Updat 4(5):303–313
Saladino C (2010) The impact of DNA damage on centrosomes. PhD Thesis, Biochemistry, National University of Ireland Galway, Galway
Saladino C, Bourke E, Conroy PC, Morrison CG (2009) Centriole separation in DNA damage-induced centrosome amplification. Environ Mol Mutagen 50(8):725–732
Salmon ED, Cimini D, Cameron LA, DeLuca JG (2005) Merotelic kinetochores in mammalian tissue cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360(1455):553–568
Sato C, Kuriyama R, Nishizawa K (1983) Microtubule-organizing centers abnormal in number, structure, and nucleating activity in X-irradiated mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 96(3):776–782
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Nakamura K, Kusumoto M, Niiyama H, Ogawa T, Tanaka M (1999) Centrosome abnormalities in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 5(5):963–970
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Tanaka M (2000a) Radiation-induced centrosome overduplication and multiple mitotic spindles in human tumor cells. Exp Cell Res 255(2):321–326
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Ueno H, Minamishima YA, Farber JL, Tanaka M (2000b) A possible role for centrosome overduplication in radiation-induced cell death. Oncogene 19(46):5281–5290
Shin HJ, Baek KH, Jeon AH, Park MT, Lee SJ, Kang CM, Lee HS, Yoo SH, Chung DH, Sung YC, McKeon F, Lee CW (2003) Dual roles of human BubR1, a mitotic checkpoint kinase, in the monitoring of chromosomal instability. Cancer Cell 4(6):483–497
Shono M, Sato N, Mizumoto K, Maehara N, Nakamura M, Nagai E, Tanaka M (2001) Stepwise progression of centrosome defects associated with local tumor growth and metastatic process of human pancreatic carcinoma cells transplanted orthotopically into nude mice. Lab Invest 81(7):945–952
Sibon OC, Kelkar A, Lemstra W, Theurkauf WE (2000) DNA-replication/DNA-damage-dependent centrosome inactivation in Drosophila embryos. Nat Cell Biol 2(2):90–95
Silkworth WT, Nardi IK, Scholl LM, Cimini D (2009) Multipolar spindle pole coalescence is a major source of kinetochore mis-attachment and chromosome mis-segregation in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6564
Sluder G, Rieder CL (1985) Centriole number and the reproductive capacity of spindle poles. J Cell Biol 100(3):887–896
Smits VA, Klompmaker R, Arnaud L, Rijksen G, Nigg EA, Medema RH (2000) Polo-like kinase-1 is a target of the DNA damage checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 2(9):672–676
Sotillo R, Hernando E, Diaz-Rodriguez E, Teruya-Feldstein J, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Benezra R (2007) Mad2 overexpression promotes aneuploidy and tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Cell 11(1):9–23
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI (1999) Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature 401(6750):297–300
Srsen V, Gnadt N, Dammermann A, Merdes A (2006) Inhibition of centrosome protein assembly leads to p53-dependent exit from the cell cycle. J Cell Biol 174(5):625–630
Stevens NR, Dobbelaere J, Brunk K, Franz A, Raff JW (2010) Drosophila Ana2 is a conserved centriole duplication factor. J Cell Biol 188(3):313–323
Strnad P, Leidel S, Vinogradova T, Euteneuer U, Khodjakov A, Gonczy P (2007) Regulated HsSAS-6 levels ensure formation of a single procentriole per centriole during the centrosome duplication cycle. Dev Cell 13(2):203–213
Swanton C, Marani M, Pardo O, Warne PH, Kelly G, Sahai E, Elustondo F, Chang J, Temple J, Ahmed AA, Brenton JD, Downward J, Nicke B (2007) Regulators of mitotic arrest and ceramide metabolism are determinants of sensitivity to paclitaxel and other chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Cell 11(6):498–512
Tachibana KE, Gonzalez MA, Guarguaglini G, Nigg EA, Laskey RA (2005) Depletion of licensing inhibitor geminin causes centrosome overduplication and mitotic defects. EMBO Report 6(11):1052–1057
Thompson SL, Compton DA (2008) Examining the link between chromosomal instability and aneuploidy in human cells. J Cell Biol 180(4):665–672
Tsou MF, Stearns T (2006) Mechanism limiting centrosome duplication to once per cell cycle. Nature 442(7105):947–951
Tsou MF, Wang WJ, George KA, Uryu K, Stearns T, Jallepalli PV (2009) Polo kinase and separase regulate the mitotic licensing of centriole duplication in human cells. Dev Cell 17(3):344–354
Tutt AN, van Oostrom CT, Ross GM, van Steeg H, Ashworth A (2002) Disruption of Brca2 increases the spontaneous mutation rate in vivo: synergism with ionizing radiation. EMBO Report 3(3):255–260
Uetake Y, Loncarek J, Nordberg JJ, English CN, La Terra S, Khodjakov A, Sluder G (2007) Cell cycle progression and de novo centriole assembly after centrosomal removal in untransformed human cells. J Cell Biol 176(2):173–182
Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M, Zhivotovsky B (2008) Death through a tragedy: mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Differ 15(7):1153–1162
van Vugt MA, Smits VA, Klompmaker R, Medema RH (2001) Inhibition of Polo-like kinase-1 by DNA damage occurs in an ATM- or ATR-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem 276(45):41656–41660
Varmark H, Llamazares S, Rebollo E, Lange B, Reina J, Schwarz H, Gonzalez C (2007) Asterless is a centriolar protein required for centrosome function and embryo development in Drosophila. Curr Biol 17(20):1735–1745
Vogel C, Kienitz A, Muller R, Bastians H (2005) The mitotic spindle checkpoint is a critical determinant for topoisomerase-based chemotherapy. J Biol Chem 280(6):4025–4028
Watanabe N, Yamaguchi T, Akimoto Y, Rattner JB, Hirano H, Nakauchi H (2000) Induction of M-phase arrest and apoptosis after HIV-1 Vpr expression through uncoupling of nuclear and centrosomal cycle in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res 258(2):261–269
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW (2006) Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol 18(6):658–667
Weber RG, Bridger JM, Benner A, Weisenberger D, Ehemann V, Reifenberger G, Lichter P (1998) Centrosome amplification as a possible mechanism for numerical chromosome aberrations in cerebral primitive neuroectodermal tumors with TP53 mutations. Cytogenet Cell Genet 83(3–4):266–269
Williams BR, Prabhu VR, Hunter KE, Glazier CM, Whittaker CA, Housman DE, Amon A (2008) Aneuploidy affects proliferation and spontaneous immortalization in mammalian cells. Science 322(5902):703–709
Wong C, Stearns T (2003) Centrosome number is controlled by a centrosome-intrinsic block to reduplication. Nat Cell Biol 5(6):539–544
Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Sonoda E, Sasaki MS, Morrison C, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Yamashita YM, Yagi T, Takata M, Price C, Kakazu N, Takeda S (1999) Mre11 is essential for the maintenance of chromosomal DNA in vertebrate cells. EMBO J 18(23):6619–6629
Yoon HS, Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Hisamuddin IM, Dalton WB, Yang VW (2005) Kruppel-like factor 4 prevents centrosome amplification following gamma-irradiation-induced DNA damage. Oncogene 24(25):4017–4025
Zhang W, Fletcher L, Muschel RJ (2005) The role of Polo-like kinase 1 in the inhibition of centrosome separation after ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 280(52):42994–42999
Zhu F, Lawo S, Bird A, Pinchev D, Ralph A, Richter C, Muller-Reichert T, Kittler R, Hyman AA, Pelletier L (2008) The mammalian SPD-2 ortholog Cep192 regulates centrosome biogenesis. Curr Biol 18(2):136–141
Zou C, Li J, Bai Y, Gunning WT, Wazer DE, Band V, Gao Q (2005) Centrobin: a novel daughter centriole-associated protein that is required for centriole duplication. J Cell Biol 171(3):437–445
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Saladino, C., Bourke, E., Morrison, C.G. (2012). Centrosomes, DNA Damage and Aneuploidy. In: Schatten, H. (eds) The Centrosome. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-035-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-035-9_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-034-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-035-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)