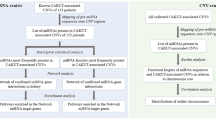
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and copy number variations (CNVs) are two extensively studied genomic components in the field of modern biology—as they have been found to be associated with many disorders such as cancer, Alzheimer, pancreatitis, HIV susceptibility, beta-thalassemia, and glomerulonephritis. Several studies suggested that an alteration in CNV–miRNA interaction could result in some human diseases such as cancer. Therefore, the possible miRNA-binding site information within the CNV genes opens new avenues in understanding such disorders. In this chapter, we present a schematic approach for collecting the information on CNV–miRNA interactions using miRWalk and TargetScan databases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hastings PJ, Ira G, Lupski JR (2009) A microhomology-mediated break-induced replication model for the origin of human copy number variation. PLoS Genet 5:e1000327
Zaman MS, Shahryari V, Deng G et al (2012) Up-regulation of microRNA-21 correlates with lower kidney cancer survival. PLoS One 7:e31060
Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G et al (2006) APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nat Genet 38:24–26
Cheng C, Li W, Zhang Z et al (2013) MicroRNA-144 is regulated by activator protein-1 (AP-1) and decreases expression of Alzheimer disease-related a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 (ADAM10). J Biol Chem 288:13748–13761
Le Marechal C, Masson E, Chen JM et al (2006) Hereditary pancreatitis caused by triplication of the trypsinogen locus. Nat Genet 38:1372–1374
Li A, Yu J, Kim H et al (2013) MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin Cancer Res 19:3600–3610
Townson JR, Barcellos LF, Nibbs RJ (2002) Gene copy number regulates the production of the human chemokine CCL3-L1. Eur J Immunol 32:3016–3026
Narayanan A, Iordanskiy S, Das R et al (2013) Exosomes derived from HIV-1-infected cells contain trans-activation response element RNA. J Biol Chem 288:20014–20033
Aitman TJ, Dong R, Vyse TJ et al (2006) Copy number polymorphism in Fcgr3 predisposes to glomerulonephritis in rats and humans. Nature 439:851–855
Papagregoriou G, Erguler K, Dweep H et al (2012) A miR-1207-5p binding site polymorphism abolishes regulation of HBEGF and is associated with disease severity in CFHR5 nephropathy. PLoS One 7:e31021
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Kim DH, Saetrom P, Snove O Jr et al (2008) MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16230–16235
Lai EC (2002) Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′ UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation. Nat Genet 30:363–364
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2011) miRBase: integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 39: D152–157
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R et al (2010) Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 464: 704–712
Iafrate AJ, Feuk L, Rivera MN et al (2004) Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat Genet 36:949–951
Dear PH (2009) Copy-number variation: the end of the human genome? Trends Biotechnol 27:448–454
Henrichsen CN, Chaignat E, Reymond A (2009) Copy number variants, diseases and gene expression. Hum Mol Genet 18:R1–8
Nozawa M, Kawahara Y, Nei M (2007) Genomic drift and copy number variation of sensory receptor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:20421–20426
Schuster-Bockler B, Conrad D, Bateman A (2010) Dosage sensitivity shapes the evolution of copy-number varied regions. PLoS One 5:e9474
Felekkis K, Voskarides K, Dweep H et al (2011) Increased number of microRNA target sites in genes encoded in CNV regions. Evidence for an evolutionary genomic interaction. Mol Biol Evol 28:2421–2424
Woodwark C, Bateman A (2011) The characterisation of three types of genes that overlie copy number variable regions. PLoS One 6: e14814
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P et al (2011) miRWalk - database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by “walking” the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform 44: 839–837
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Dweep H, Sticht C, Gretz N (2013) In-silico algorithms for the screening of possible microRNA binding sites and their interactions. Curr Genomics 14:127–136
Dweep H, Sticht C, Kharkar A et al (2013) Parallel analysis of mRNA and microRNA microarray profiles to explore functional regulatory patterns in polycystic kidney disease: using PKD/Mhm rat model. PLoS One 8:e53780
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Research Council through Graduiertenkolleg 886 and by the German Federal Ministry of Research and Education through the National Genome Research Network (NGFN-2, Grant no. 01GR 0450).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Dweep, H., Gretz, N., Felekkis, K. (2014). A Schematic Workflow for Collecting Information About the Interaction Between Copy Number Variants and MicroRNAs Using Existing Resources. In: Alvarez, M., Nourbakhsh, M. (eds) RNA Map**. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1182. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1062-5_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1062-5_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-1061-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-1062-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols