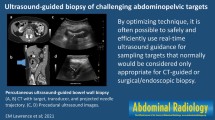
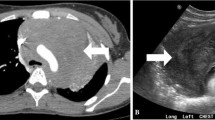
Abstract
Access route planning for image-guided biopsy of deep pelvic masses is challenging because vital structures such as the bowel, bladder, uterus, adnexa, iliac vessels, and osseous structures can intervene in the projected needle path. Thus, a thorough understanding of the cross-sectional anatomy of the pelvis is needed, and the best approach and techniques to use for each patient will depend on the characteristics and exact location of the patient’s lesion. In this article we provide an overview of the relevant anatomy of the pelvic region and discuss the various types of imaging (computed tomography [CT], ultrasound, CT fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, and magnetic field-based electronic guidance system), needles (aspiration and small- and large-caliber cutting needles; single or coaxial), and approaches (anterior or anterolateral transabdominal, transgluteal, anterolateral extraperitoneal, transosseous, transvaginal, and transrectal) that can be used in image-guided pelvic biopsy, along with the advantages and limitations of each technique.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta S, Nguyen HL, Morello Jr FA, et al. Various approaches for CT-guided percutaneous biopsy of deep pelvic lesions: anatomic and technical considerations. Radiographics. 2004;24(1):175–89.
Bodne DJ, Carrasco CH, Richli WR. Transosseous air contrast CT-guided needle biopsy of a cystic neoplasm. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1993;16(2):122–3.
Butch RJ, Mueller PR, Ferrucci Jr JT, et al. Drainage of pelvic abscesses through the greater sciatic foramen. Radiology. 1986;158(2):487–91.
Carlson P, Crummy AB, Wojtowycz M, McDermott JC. A safe route for deep pelvic biopsy with distention of the iliacus muscle. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1991;2(2):277–8.
Guo Z, Kurtycz DF, De Las Casas LE, Hoerl HD. Radiologically guided percutaneous fine-needle aspiration biopsy of pelvic and retroperitoneal masses: a retrospective study of 68 cases. Diagn Cytopathol. 2001;25(1):43–9.
Harisinghani MG, Gervais DA, Hahn PF, et al. CT-guided transgluteal drainage of deep pelvic abscesses: indications, technique, procedure-related complications, and clinical outcome. Radiographics. 2002;22(6):1353–67.
Pardes JG, Schneider M, Koizumi J, Engel IA, Auh YH, Rubenstein W. Percutaneous needle biopsy of deep pelvic masses: a posterior approach. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1986;9(2):65–8.
Phillips VM, Bernardino M. The parallel iliac approach: a safe and accurate technique for deep pelvic node biopsy. J Comput Tomogr. 1984;8(3):237–8.
Rapport 2nd RL, Ferguson GS. Dorsal approach to presacral biopsy: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 1997;40(5):1087–8.
Triller J, Maddern G, Kraft P, Heidar A, Vock P. CT-guided biopsy of pelvic masses. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1991;14(1):63–8.
Gupta S, Ahrar K, Morello Jr FA, Wallace MJ, Madoff DC, Hicks ME. Using a coaxial technique with a curved inner needle for CT-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179(1):109–12.
Schweiger GD, Yip VY, Brown BP. CT fluoroscopic guidance for percutaneous needle placement into abdominopelvic lesions with difficult access routes. Abdom Imaging. 2000;25(6):633–7.
Yueh N, Halvorsen Jr RA, Letourneau JG, Crass JR. Gantry tilt technique for CT-guided biopsy and drainage. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989;13(1):182–4.
Gupta S, Madoff DC, Ahrar K, et al. CT-guided needle biopsy of deep pelvic lesions by extraperitoneal approach through iliopsoas muscle. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003;26(6):534–8.
Fischerova D, Cibula D, Dundr P, et al. Ultrasound-guided tru-cut biopsy in the management of advanced abdomino-pelvic tumors. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2008;18(4):833–7.
Scanlan KA, Propeck PA, Lee Jr FT. Invasive procedures in the female pelvis: value of transabdominal, endovaginal, and endorectal US guidance. Radiographics. 2001;21(2):491–506.
O'Neill MJ, Rafferty EA, Lee SI, et al. Transvaginal interventional procedures: aspiration, biopsy, and catheter drainage. Radiographics. 2001;21(3):657–72.
Rinnab L, Kufer R, Hautmann RE, Gottfried HW. Use of transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy in the diagnosis of pelvic malignancies. J Clin Ultrasound. 2006;34(9):440–5.
Roy D, Kulkarni A, Kulkarni S, Thakur MH, Maheshwari A, Tongaonkar HB. Transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy of recurrent cervical carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2008;81(971):902–6.
Oyen RH, Van Poppel HP, Ameye FE, Van de Voorde WA, Baert AL, Baert LV. Lymph node staging of localized prostatic carcinoma with CT and CT-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: prospective study of 285 patients. Radiology. 1994;190(2):315–22.
Welch TJ, Sheedy 2nd PF, Johnson CD, Johnson CM, Stephens DH. CT-guided biopsy: prospective analysis of 1,000 procedures. Radiology. 1989;171(2):493–6.
Yarram SG, Nghiem HV, Higgins E, Fox G, Nan B, Francis IR. Evaluation of imaging-guided core biopsy of pelvic masses. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(5):1208–11.
Griffin N, Grant LA, Freeman SJ, et al. Image-guided biopsy in patients with suspected ovarian carcinoma: a safe and effective technique? Eur Radiol. 2009;19(1):230–5.
Zanetta G, Brenna A, Pittelli M, Lissoni A, Trio D, Riotta S. Transvaginal ultrasound-guided fine needle sampling of deep cancer recurrences in the pelvis: usefulness and limitations. Gynecol Oncol. 1994;54(1):59–63.
Zanetta G, Lissoni A, Franchi D, Pittelli MR, Cormio G, Trio D. Safety of transvaginal fine needle puncture of gynecologic masses: a report after 500 consecutive procedures. J Ultrasound Med. 1996;15(5):401–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ozkan, E., Gupta, S. (2014). Biopsy of Pelvic Lesions. In: Ahrar, K., Gupta, S. (eds) Percutaneous Image-Guided Biopsy. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8217-8_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8217-8_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-8216-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-8217-8
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)