Abstract
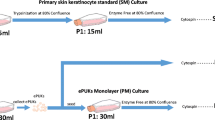
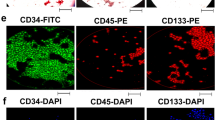
Stem cells are found in niches around the body, including the epidermis of the skin, and can be distinguished from their more committed progeny by their high long-term proliferative capacity in vitro. Here we describe a technique used to isolate three main epidermal cell fractions from human neonatal foreskin termed early differentiating (ED), transient amplifying (TA) and keratinocyte stem cells (KSC) based on their differential expression of two cell surface markers: CD49f and CD71. These three fractions were cultivated in parallel in a serial proliferation assay to determine their long-term proliferative output. This assay demonstrates that the KSC fraction had the highest proliferative output (total cell yield) over a long experimental timeframe of 2–3 months, as well as a higher proliferative rate compared to the other two fractions (P > 0.05). This assay can be utilized under similar conditions to determine the proliferative capacity of other putative stem cells using novel stem cell markers for epidermal or other stem cell populations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dulak J et al (2015) Adult stem cells: hopes and hypes of regenerative medicine. Acta Biochim Pol 62(3):329–337
Jackson CJ, Tønseth KA, Utheim TP (2017) Cultured epidermal stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther 8(1):155–155
Bacakova L et al (2018) Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells—a review. Biotechnol Adv 36(4):1111–1126
Li A, Simmons PJ, Kaur P (1998) Identification and isolation of candidate human keratinocyte stem cells based on cell surface phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(7):3902–3907
Gangatirkar P et al (2007) Establishment of 3D organotypic cultures using human neonatal epidermal cells. Nat Protoc 2(1):178–186
Schlüter H et al (2011) Functional characterization of quiescent keratinocyte stem cells and their progeny reveals a hierarchical organization in human skin epidermis. Stem Cells 29(8):1256–1268
Rheinwatd JG, Green H (1975) Seria cultivation of strains of human epidemal keratinocytes: the formation keratinizin colonies from single cell is. Cell 6(3):331–343
Stenn KS et al (1989) Dispase, a neutral protease from bacillus Polymyxa, is a powerful Fibronectinase and type IV collagenase. J Investig Dermatol 93(2):287–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Pieterse, Z., Kaur, P. (2022). Assaying Candidate Human Skin Keratinocyte Stem Cells by Determining Their Long-Term Serial Proliferative Output in Culture. In: Kannan, N., Beer, P. (eds) Stem Cell Assays. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2429. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1979-7_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1979-7_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1978-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1979-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols