Abstract
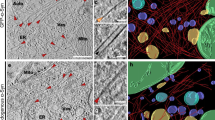
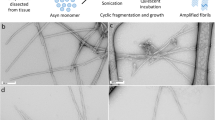
α-Synuclein (α-syn) is a major component of abnormal protein deposits observed in the brains of patients with synucleinopathies, including Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy (MSA). The synaptic protein α-syn is water-soluble under normal physiological conditions, but in these patients’ brains, we see accumulation of insoluble amyloid-like α-syn fibrils with prion-like properties. Intracerebral accumulation of these fibrils is correlated with disease onset and progression. Recombinant α-syn protein also forms amyloid-like fibrils that are structurally akin to those extracted from patients’ brains. Recent cryo-electron microscopic studies have identified the core structures of synthetic α-syn fibrils and α-syn fibrils extracted from the brains of patients with MSA at the atomic level. In this chapter, we describe negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy protocols for ultrastructural characterization of synthetic α-syn fibrils and pathological α-syn fibrils.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goedert M (2001) Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(7):492–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/35081564
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) Alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(11):6469–6473. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.11.6469
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251(3):205–208
Tarutani A, Arai T, Murayama S, Hisanaga SI, Hasegawa M (2018) Potent prion-like behaviors of pathogenic alpha-synuclein and evaluation of inactivation methods. Acta Neuropathol Commun 6(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-018-0532-2
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) Alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4(2):160–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb748
Hasegawa M, Fujiwara H, Nonaka T, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Mann D, Iwatsubo T (2002) Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein is ubiquitinated in alpha-synucleinopathy lesions. J Biol Chem 277(50):49071–49076. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208046200
Nussbaum RL (2018) Genetics of Synucleinopathies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8(6):a024109. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a024109
Maroteaux L, Campanelli JT, Scheller RH (1988) Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci 8(8):2804–2815
Crowther RA, Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Goedert M (1998) Synthetic filaments assembled from C-terminally truncated alpha-synuclein. FEBS Lett 436(3):309–312
Serpell LC, Berriman J, Jakes R, Goedert M, Crowther RA (2000) Fiber diffraction of synthetic alpha-synuclein filaments shows amyloid-like cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(9):4897–4902. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.9.4897
Tarutani A, Hasegawa M (2019) Prion-like propagation of alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 168:323–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.07.005
El-Agnaf OM, Jakes R, Curran MD, Wallace A (1998) Effects of the mutations Ala30 to Pro and Ala53 to Thr on the physical and morphological properties of alpha-synuclein protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett 440(1–2):67–70
Bousset L, Pieri L, Ruiz-Arlandis G, Gath J, Jensen PH, Habenstein B, Madiona K, Olieric V, Bockmann A, Meier BH, Melki R (2013) Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat Commun 4:2575. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3575
Suzuki G, Imura S, Hosokawa M, Katsumata R, Nonaka T, Hisanaga SI, Saeki Y, Hasegawa M (2020) Alpha-synuclein strains that cause distinct pathologies differentially inhibit proteasome. Elife 9:e56825. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.56825
Schweighauser M, Shi Y, Tarutani A, Kametani F, Murzin AG, Ghetti B, Matsubara T, Tomita T, Ando T, Hasegawa K, Murayama S, Yoshida M, Hasegawa M, Scheres SHW, Goedert M (2020) Structures of alpha-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Nature 585(7825):464–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2317-6
Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, Moskalyuk A, Pulizzi R, Giugliano M, Van den Haute C, Melki R, Baekelandt V (2015) Alpha-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 522(7556):340–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14547
Peng C, Gathagan RJ, Covell DJ, Medellin C, Stieber A, Robinson JL, Zhang B, Pitkin RM, Olufemi MF, Luk KC, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2018) Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological alpha-synuclein strains in alpha-synucleinopathies. Nature 557(7706):558–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0104-4
Shahnawaz M, Mukherjee A, Pritzkow S, Mendez N, Rabadia P, Liu XG, Hu B, Schmeichel A, Singer W, Wu G, Tsai AL, Shirani H, Nilsson KPR, Low PA, Soto C (2020) Discriminating alpha-synuclein strains in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 578(7794):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1984-7
Tarutani A, Suzuki G, Shimozawa A, Nonaka T, Akiyama H, Hisanaga S, Hasegawa M (2016) The effect of fragmented pathogenic alpha-Synuclein seeds on prion-like propagation. J Biol Chem 291(36):18675–18688. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.734707
Taniguchi-Watanabe S, Arai T, Kametani F, Nonaka T, Masuda-Suzukake M, Tarutani A, Murayama S, Saito Y, Arima K, Yoshida M, Akiyama H, Robinson A, Mann DMA, Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M (2016) Biochemical classification of tauopathies by immunoblot, protein sequence and mass spectrometric analyses of sarkosyl-insoluble and trypsin-resistant tau. Acta Neuropathol 131(2):267–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1503-3
Wenborn A, Terry C, Gros N, Joiner S, D'Castro L, Panico S, Sells J, Cronier S, Linehan JM, Brandner S, Saibil HR, Collinge J, Wadsworth JD (2015) A novel and rapid method for obtaining high titre intact prion strains from mammalian brain. Sci Rep 5:10062. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Tarutani, A., Hasegawa, M. (2021). Electron Microscopic Analysis of α-Synuclein Fibrils. In: Imai, Y. (eds) Experimental Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2322. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1495-2_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1495-2_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1494-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1495-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols