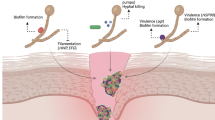
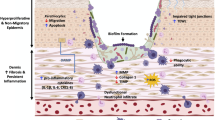
Abstract
Chronic wounds including vascular ulcers, diabetic ulcers, pressure ulcers, and burn wounds show delayed progress through the healing process. Some of their common features are prolonged inflammation, persistent infection, and presence of biofilms resistant to antimicrobials and host immune response. Biofilm formation by opportunistic pathogens is a major problem in chronic wound management. Some of the commonly and traditionally used chronic wound management techniques are physical debridement and cleansing. In recent years, novel techniques based on anti-biofilm agents are explored to prevent biofilm-associated infections and facilitate wound healing. In this chapter, the role of biofilms formed by the ESKAPE pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Candida species in delayed wound healing have been discussed. The current and emerging techniques in the detection of biofilms for the management of wounds have been focused. The limitations of the existing therapeutics and novel wound management strategies have been deliberated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abootaleb M, Mohammadi Bandari N, Arbab Soleimani N (2021) Interference of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum with Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the infected burns in Wistar rats. J Burn Care Res 34893853
Akiyama H, Kanzaki H, Tada J, Arata J (1996) Staphylocococcus aureus infection on cut wounds in the mouse skin: experimental staphylococcal botyomycosis. J Dermatol Sci 11:234
Akiyama H, Oono T, Saito M, Iwatsuki K (2004) Assessment of cadexomer iodine against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vivo and in vitro using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Dermatol 31(7):529–534
Alves PJ, Barreto RT, Barrois BM, Gryson LG, Meaume S, Monstrey SJ (2021) Update on the role of antiseptics in the management of chronic wounds with critical colonisation and/or biofilm. Int Wound J 18(3):342–358
Anju V, Dyavaiah M, Siddhardha B (2021) Wound healing research. Springer, Berlin, pp 643–659
Argenta A, Satish L, Gallo P, Liu F, Kathju S (2016) Local application of probiotic bacteria prophylaxes against sepsis and death resulting from burn wound infection. PLoS One 25(10):e0165294
Babushkina IV, Mamontova IA, Gladkova EV (2015) Metal nanoparticles reduce bacterial contamination of experimental purulent wounds. Bull Exp Biol Med 158(5):692–694
Banin E, Brady KM, Greenberg EP (2006) Chelator-induced dispersal and killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells in a biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3):2064–2069
Barki KG, Das A, Dixith S, Ghatak PD, Mathew-Steiner S, Schwab E, Khanna S, Wozniak DJ, Roy S, Sen CK (2019) Electric field based dressing disrupts mixed-species bacterial biofilm infection and restores functional wound healing. Ann Surg 269(4):756–766
Bauer J, Siala W, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F (2013) A combined pharmacodynamic quantitative and qualitative model reveals the potent activity of daptomycin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(6):2726–2737
Bjarnsholt T, Kirketerp-Møller K, Jensen PØ (2008) Why chronic wounds will not heal: a el hypothesis. Wound Repair Regen 16:2
Bjarnsholt T, Ciofu O, Molin S, Givskov M, Hoiby N (2013) Applying insights from biofilm biology to drug development – can a new approach be developed? Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:791–808
Borges EL, Frison SS, Honorato-Sampaio K, Guedes ACM, Lima VLAN, Oliveira OMM, Ferraz AF, Tyrone AC (2018) Effect of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide solution on bacterial load and biofilm in venous leg ulcers: a randomized controlled trial. J Wound Ostomy Cont Nurs 45(5):425–431
Brachkova MI, Ques P, Rocha J, Sepodes B, Duarte MA, Pinto JF (2011) Alginate films containing lactobacillus plantarum as wound dressing for prevention of burn infection. J Hosp Infect 79(4):375–377
Brandenburg KS, Weaver AJ Jr, Karna SLR, You T, Chen P, Stryk SV, Qian L, Pineda U, Abercrombie JJ, Leung KP (2011) Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in full-thickness scald burn wounds in rats. Sci Rep 9(1):13627
Bruno M, Trucchi B, Burlando B, Ranzato E, Martinotti S, Akkol EK, Süntar I, Keleş H, Verotta L (2013) (+)-Usnic acid enamines with remarkable cicatrizing properties. Bioorg Med Chem 21(7):1834–1843
Castro J, França A, Bradwell KR, Serrano MG, Jefferson KK, Cerca N (2017) Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Gardnerella vaginalis biofilms vs. planktonic cultures using RNA-seq. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 3:3
Cerqueira L, Azevedo NF, Almeida C, Jardim T, Keevil CW, Vieira MJ (2008) DNA mimics for the rapid identification of microorganisms by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Int J Mol Sci 9(10):1944–1960
Chaney SB, Ganesh K, Mathew-Steiner S, Stromberg P, Roy S, Sen CK, Wozniak DJ (2017) Histopathological comparisons of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa experimental infected porcine burn wounds. Wound Repair Regen 25(3):541–549
Ciani I, Schulze H, Corrigan DK, Henihan G, Giraud G, Terry JG, Walton AJ, Pethig R, Ghazal P, Crain J, Campbell CJ, Bachmann TT, Mount AR (2012) Development of immunosensors for direct detection of three wound infection biomarkers at point of care using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):413–418
Daghdari SG, Ahmadi M, Dastmalchi Saei H, Tehrani AA (2017) The effect of ZnO nanoparticles on bacterial load of experimental infectious wounds contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Nanomed J 4(4):232–236
Dai T, Gupta A, Huang YY, Yin R, Murray CK, Vrahas MS, Sherwood ME, Tegos GP, Hamblin MR (2013) Blue light rescues mice from potentially fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infection: efficacy, safety, and mechanism of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(3):1238–1245
Davies CE, Hill KE, Wilson MJ, Stephens P, Hill CM, Harding KG, Thomas DW (2004) Use of 16S ribosomal DNA PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis for analysis of the microfloras of healing and nonhealing chronic venous leg ulcers. J Clin Microbiol 42(8):3549–3557
Davis SC, Ricotti C, Cazzaniga A, Welsh E, Eaglstein WH, Mertz PM (2008) Microscopic and physiologic evidence for biofilm-associated wound colonization in vivo. Wound Repair Regen 16:23
Davis SC, Harding A, Gil J, Parajon F, Valdes J, Solis M, Higa A (2017) Effectiveness of a polyhexanide irrigation solution on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in a porcine wound model. Int Wound J 14(6):937–944
Donelli G, Vuotto C (2014) Biofilm-based infections in long-term care facilities. Future Microbiol 9(2):175–188
Donelli G, Francolini I, Romoli D, Guaglianone E, Piozzi A, Ragunath C, Kaplan JB (2007) Synergistic activity of dispersin B and cefamandole nafate in inhibition of staphylococcal biofilm growth on polyurethanes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:2733–2740
Dowd SE, Sun Y, Wolcott RD, Domingo A, Carroll JA (2008) Bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP) for microbiome studies: bacterial diversity in the ileum of newly weaned Salmonellainfected pigs. Foodborne Pathog Dis 5(4):459–472
Drago L, Signori V, De Vecchi E, Vassena C, Palazzi E, Cappelletti L, Romanò D, Romanò CL (2013) Use of dithiothreitol to improve the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections. J Orthop Res 31(11):1694–1699
Fazli M, Bjarnsholt T, Kirketerp-Møller K, Jørgensen B, Andersen AS, Krogfelt KA, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2009) Nonrandom distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in chronic wounds. J Clin Microbiol 47(12):4084–4089
Fazli M, Bjarnsholt T, Kirketerp-Møller K, Jørgensen A, Andersen CB, Givskov M (2011) Quantitative analysis of the cellular inflammatory response against biofilm bacteria in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 19:387
Fitzgerald DJ, Renick PJ, Forrest EC, Tetens SP, Earnest DN, McMillan J, Kiedaisch BM, Shi L, Roche ED (2017) Cadexomer iodine provides superior efficacy against bacterial wound biofilms in vitro and in vivo. Wound Repair Regen 25(1):13–24
Francolini I, Piozzi A, Donelli G (2019) Usnic acid: potential role in management of wound infections. Adv Exp Med Biol 1214:31–41
Frykberg RG, Banks J (2015) Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv Wound Care. (New Rochelle) 4(9):560–582
Garalde DR, Snell EA, Jachimowicz D, Sipos B, Lloyd JH, Bruce M, Pantic N, Admassu T, James P, Warland A, Jordan M, Ciccone J, Serra S, Keenan J, Martin S, McNeill L, Wallace EJ, Jayasinghe L, Wright C, Blasco J, Young S, Brocklebank D, Juul S, Clarke J, Heron AJ, Turner DJ (2018) Highly parallel direct RNA sequencing on an array of nanopores. Nat Methods 15(3):201–206
Gurjala AN, Geringer MR, Seth AK (2011) Development of highly quantitative in vivo model for the study of biofilm-impaired cutaneous wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 19:400
Han A, Zenilman JM, Melendez JH, Shirtliff ME, Agostinho A, James GA (2011) The importance of a multifaceted approach to characterizing the microbial flora of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 19:532
Hassan A, Usman J, Kaleem F, Omair M, Khalid A, Iqbal M (2011) Evaluation of different detection methods of biofilm formation in the clinical isolates. Braz J Infect Dis 15(4):305–311
Higgins PG, Poirel L, Lehmann M, Nordmann P, Seifert H (2009) OXA-143, a novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D beta-lactamase in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(12):5035–5038
James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, Pulcini E, Secor P, Sestrich J (2008) Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 16:37
Jault P, Leclerc T, Jennes S, Pirnay JP, Que YA, Resch G, Rousseau AF, Ravat F, Carsin H, Le Floch R, Schaal JV, Soler C, Fevre C, Arnaud I, Bretaudeau L, Gabard J (2018) Efficacy and tolerability of a cocktail of bacteriophages to treat burn wounds infected by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PhagoBurn): a randomised, controlled, double-blind phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 19(1):35–45
Johani K, Malone M, Jensen SO, Dickson HG, Gosbell IB, Hu H, Yang Q, Schultz G, Vickery K (2018) Evaluation of short exposure times of antimicrobial wound solutions against microbial biofilms: from in vitro to in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother 73(2):494–502
Johnson EN, Burns TC, Hayda RA, Hospenthal DR, Murray CK (2007) Infectious complications of open type III tibial fractures among combat casualties. Clin Infect Dis 45(4):409–415
Kanno E, Toriyabe S, Zhang L, Imai Y, Tachi M (2010) Biofilm formation on rat skin wounds by Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying the green fluorescent protein gene. Exp Dermatol 19:154
Kanno E, Tanno H, Suzuki A, Kamimatsuno R, Tachi M (2016) Reconsideration of iodine in wound irrigation: the effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. J Wound Care 25(6):335–339
Keen EF 3rd, Robinson BJ, Hospenthal DR, Aldous WK, Wolf SE, Chung KK, Murray CK (2010) Incidence and bacteriology of burn infections at a military burn center. Burns 36(4):461–468
Kennedy P, Brammah S, Wills E (2010) Burns, biofilm and a new appraisal of burn wound sepsis. Burns 36:49
Kim D, Namen Ii W, Moore J, Buchanan M, Hayes V, Myntti MF, Hakaim A (2018) Clinical assessment of a biofilm-disrupting agent for the Management of Chronic Wounds Compared with Standard of care: a therapeutic approach. Wounds 30(5):120–130
Kim JH, Yang B, Tedesco A, Lebig EGD, Ruegger PM, Xu K, Borneman J, Tins-Green M (2019) High levels of oxidative stress and skin microbiome are critical for initiation and development of chronic wounds in diabetic mice. Sci Rep 9(1):19318
Kim JH, Ruegger PR, Lebig EG, VanSchalkwyk S, Jeske DR, Hsiao A, Borneman J, Tins-Green M (2020) High levels of oxidative stress create a microenvironment that significantly increases the diversity of the microbiota in diabetic chronic wounds and promotes biofilm formation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:259
Kirketerp-Møller K, Jenson PO, Fazli M, Madsen KG, Pedersen J, Moser C (2008) Distribution, organization, and ecology of bacteria in chronic wounds. J Clin Microbiol 46:2712
Kitamura A, Nakagami G, Yoshida M, Noguchi H, Nishijima Y, Minematsu T, Naito A, Sugawara J, Shibayama H, Takahashi K, Hakuta A, Umemoto J, Terada N, Segawa R, Mori T, Sanada H (2014) Visualization of tumor necrosis factor-α distributions within pressure ulcer tissue using the wound blotting method: a case report and discussion. Wounds 26(11):323–329
Kumari S, Harjai K, Chhibber S (2011) Bacteriophage versus antimicrobial agents for the treatment of murine burn wound infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055. J Med Microbiol 60:205–210
Lee CR, Lee JH, Park KS, Jeon JH, Kim YB, Cha CJ, Jeong BC, Lee SH (2017) Antimicrobial resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology, Hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 21(7):483
Lenseilink E, Andriessen A (2011) A cohort study on the efficacy of a polyhexanide-containing biocellulose dressing in the treatment of biofilms in wounds. J Wound Care 534:536–539
Li L, Mendis N, Trigui H, Oliver JD, Faucher SP (2014) The importance of the viable but non-culturable state in human bacterial pathogens. Front Microbiol 5:258
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, Beldavs ZG, Dumyati G, Kainer MA, Lynfield R, Maloney M, McAllister-Hollod L, Nadle J, Ray SM, Thompson DL, Wilson LE, Fridkin SK (2014) Emerging infections program healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use prevalence survey team. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N Engl J Med 370(13):1198–1208. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2022 16;386(24):2348
Malic S, Hill KE, Hayes A, Percival SL, Thomas DW, Williams DW (2009) Detection and identification of specific bacteria in wound biofilms using peptide nucleic acid fluorescent in situ hybridization (PNA FISH). Microbiology 155:2603–2611
Malone M, Johani K, Jensen SO, Gosbell IB, Dickson HG, McLennan S, Hu H, Vickery K (2017) Effect of cadexomer iodine on the microbial load and diversity of chronic non-healing diabetic foot ulcers complicated by biofilm in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:2093–2101
Malone M, Schwarzer S, Radzieta M, Jeffries T, Walsh A, Dickson HG, Micali G, Jensen SO (2019) Effect on total microbial load and community composition with two vs six-week topical Cadexomer iodine for treating chronic biofilm infections in diabetic foot ulcers. Int Wound J 16:1477–1486
Malone M, Radzieta M, Schwarzer S, Jensen SO, Lavery LA (2021) Efficacy of a topical concentrated surfactant gel on microbial communities in non-healing diabetic foot ulcers with chronic biofilm infections: a proof-of-concept study. Int Wound J 18(4):457–466
Martineau L, Dosch HM (2007a) Biofilm reduction by a new burn gel that targets nociception. J Appl Microbiol 103:297–304
Martineau L, Dosch HM (2007b) Management of bioburden with a burn gel that targets nociceptors. J Wound Care 16:157–164
Maslova E, Eisaiankhongi L, Sjöberg F, McCarthy RR (2021) Burns and biofilms: priority pathogens and in vivo models. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 7(1):73
Mendes JJ, Leandro C, Corte-Real S, Barbosa R, Cavaco-Silva P, Melo-Cristino J, Górski A, Garcia M (2013) Wound healing potential of topical bacteriophage therapy on diabetic cutaneous wounds. Wound Repair Regen 21(4):595–603
Mekkawy AI, El-Mokhtar MA, Nafady NA, Yousef N, Hamad MA, El-Shanawany SM, Ibrahim EH, Elsabahy M (2017) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles for topical applications: effect of surface coating and loading into hydrogels. Int J Nanomedicine 12:759–777
Minematsu T, Nakagami G, Yamamoto Y, Kanazawa T, Huang L, Koyanagi H, Sasaki S, Uchida G, Fujita H, Haga N, Yoshimura K, Nagase T, Sanada H (2013) Wound blotting: a convenient biochemical assessment tool for protein components in exudate of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 21(2):329–334
Mota FA, Pereira SA, Araújo AR, Passos ML, Saraiva ML (2021) Biomarkers in the diagnosis of wounds infection: an analytical perspective. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 143:116405
Nakagami G, Schultz G, Gibson DJ, Phillips P, Kitamura A, Minematsu T, Miyagaki T, Hayashi A, Sasaki S, Sugama J, Sanada H (2017) Biofilm detection by wound blotting can predict slough development in pressure ulcers: a prospective observational study. Wound Repair Regen 25(1):131–138
Neut D, Tijdens-Creusen EJ, Bulstra SK, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2011) Biofilms in chronic diabetic foot ulcers – a study of 2 cases. Acta Orthop 82:383
Ngernpimai S, Geng Y, Makabenta JM, Landis RF, Keshri P, Gupta A, Li CH, Chompoosor A, Rotello VM (2019) Rapid identification of biofilms using a robust multichannel polymer sensor Array. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(12):11202–11208
Nguyen KT, Seth AK, Hong SJ (2013) Deficient cytokine expression and neutrophil oxidative burst contribute to impaired cutaneous wound healing in diabetic, biofilm-containing chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 21:833–841
Pastar I, Nusbaum AG, Gil J, Patel SB, Chen J, Valdes J (2013) Interactions of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in polymicrobial wound infection. PLoS One 8:e56846
Percival SL, McCarty SM (2015) Silver and alginates: role in wound healing and biofilm control. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4(7):407–414
Percival SL, Bowler P, Parson D (2005) Antimicrobial composition. US/WO patent is http://www.google.com.bz/patents/WO2007068938A2?cl=en
Percival SL, Suleman L, Francolini I, Donelli G (2014) The effectiveness of photodynamic therapy on planktonic cells and biofilms and its role in wound healing. Future Microbiol 9(9):1083–1094
Percival SL, McCarty SM, Lipsky B (2015a) Biofilms and wounds: an overview of the evidence. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 4(7):373–381
Percival SL, Suleman L, Vuotto C, Donelli G (2015b) Healthcare-associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: risk, tolerance and control. J Med Microbiol 64(Pt 4):323–334
Percival SL, Vuotto C, Donelli G, Lipsky BA (2015c) Biofilms and wounds: an identification algorithm and potential treatment options. Adv Wound Care 4(7):389–397
Percival SL, Francolini I, Donelli G (2015d) Low-level laser therapy as an antimicrobial and antibiofilm technology and its relevance to wound healing. Future Microbiol 10(2):255–272
Percival SL, Finnegan S, Donelli G, Vuotto C, Rimmer S, Lipsky BA (2016) Antiseptics for treating infected wounds: efficacy on biofilms and effect of pH. Crit Rev Microbiol 42(2):293–309
Perez F, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, Decker BK, Rather PN, Bonomo RA (2007) Global challenge of multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(10):3471–3484
Phillips PL, Yang Q, Schultz GS (2013) The effect of negative pressure wound therapy with periodic instillation using antimicrobial solutions on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm on porcine skin explants. Int Wound J 12:48–55
Phillips PL, Yang Q, Davis S, Sampson EM, Azeke JI, Hamad A, Schultz GS (2015) Antimicrobial dressing efficacy against mature Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm on porcine skin explants. Int Wound J 12(4):469–483
Poma N, Vivaldi F, Bonini A, Salvo P, Kirchhain A, Melai B, Bottai D, Tavanti A, Di Francesco F (2020) A graphenic and potentiometric sensor for monitoring the growth of bacterial biofilms. Sensors Actuators B Chem 323:128662
Pozzi C, Waters EM, Rudkin JK, Schaeffer CR, Lohan AJ, Tong P, Loftus BJ, Pier GB, Fey PD, Massey RC, O’Gara JP (2012) Methicillin resistance alters the biofilm phenotype and attenuates virulence in Staphylococcus aureus device-associated infections. PLoS Pathog 8(4):e1002626
Rhoads DD, Wolcott RD, Sun Y, Dowd SE (2012) Comparison of culture and molecular identification of bacteria in chronic wounds. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):2535–2550
Roche ED, Renick PJ, Tetens SP, Carson DL (2012a) A model for evaluating topical antimicrobial efficacy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in superficial murine wounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:4508
Roche ED, Renick PJ, Tetens SP, Ramsay SJ, Daniels EQ, Carson DL (2012b) Increasing the presence of biofilm and healing delay in a porcine model of MRSA-infected wounds. Wound Repair Regen 20:537
Roche ED, Woodmansey EJ, Yang Q, Gibson DJ, Zhang H, Schultz GS (2019) Cadexomer iodine effectively reduces bacterial biofilm in porcine wounds ex vivo and in vivo. Int Wound J 16(3):674–683
Roy S, Elgharably H, Sinha M, Ganesh K, Chaney S, Mann E, Miller C, Khanna S, Bergdall VK, Powell HM, Cook CH, Gordillo GM, Wozniak DJ, Sen CK (2014) Mixed-species biofilm compromises wound healing by disrupting epidermal barrier function. J Pathol 233(4):331–343
Rumbaugh KP, Griswold JA, Hamood AN (1999) Contribution of the regulatory gene lasR to the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of burned mice. J Burn Care Rehabil 20:42
Sanford NE, Wilkinson JE, Nguyen H, Diaz G, Wolcott R (2018) Efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in bacterial biofilm eradication. J Wound Care 27(Sup1):S20–S28
Schaber JA, Triffo WJ, Suh SJ, Oliver JW, Hastert MC, Griswold JA (2007) Pseudomonas aeruginosa forms biofilms in acute infection independent of cell-to-cell signalling. Infect Immun 75:3715
Schierle CF, De la Garza M, Mustoe TA, Galiano RD (2009) Staphylococcal biofilms impair wound healing by delaying reepithelialization in a murine cutaneous wound model. Wound Repair Regen 17:354
Schultz G, Bjarnsholt T, James GA, Leaper DJ, McBain AJ, Malone M, Stoodley P, Swanson T, Tachi M, Wolcott RD (2017) Global wound biofilm expert panel. Consensus guidelines for the identification and treatment of biofilms in chronic nonhealing wounds. Wound Repair Regen 25(5):744–757
Serralta VW, Harrison-Balestra C, Cazzaniga AL (2001) Lifestyles of bacteria in wounds: presence of biofilms? Wounds 13:29
Seth AK, Geringer MR, Galiano RD, Leung KP, Mustoe TA, Hong SJ (2012a) Quantitative comparison and analysis of species-specific wound biofilm virulence using an in vivo, rabbit ear model. J Am Coll Surg 215:388
Seth AK, Geringer MR, Hong SJ, Leung KP, Galiano RD, Mustoe TA (2012b) Comparative analysis of single-species and polybacterial wound biofilms using a quantitative, in vivo, rabbit ear model. PLoS One 7:e42897
Shivaswamy VC, Kalasuramath SB, Sadanand CK, Basavaraju AK, Ginnavaram V, Bille S, Ukken SS, Pushparaj UN (2015) Ability of bacteriophage in resolving wound infection caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in uncontrolled diabetic rats. Microb Drug Resist 21(2):171–177
Su S, Shi X, Xu W, Li Y, Chen X, Jia S, Sun S (2020) Antifungal activity and potential mechanism of Panobinostat in combination with fluconazole against Candida albicans. Front Microbiol 11:1584
Tan X, Qin N, Wu C, Sheng J, Yang R, Zheng B, Ma Z, Liu L, Peng X, Jia A (2015) Transcriptome analysis of the biofilm formed by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 7(5):11997
Thompson MG, Black CC, Pavlicek RL (2014) Validation of a murine wound model of Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:1332
Thurlow LR, Hanke ML, Fritz T, Angle A, Aldrich A, Williams SH, Engebretsen IL, Bayles KW, Horswill AR, Kielian T (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms prevent macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate inflammation in vivo. J Immunol 186(11):6585–6596
Tipton CD, Mathew ME, Wolcott RA, Wolcott RD, Kingston T, Phillips CD (2017) Temporal dynamics of relative abundances and bacterial succession in chronic wound communities. Wound Repair Regen 25(4):673–679
Tipton CD, Wolcott RD, Sanford NE, Miller C, Pathak G, Silzer TK, Sun J, Fleming D, Rumbaugh KP, Little TD, Phillips N, Phillips CD (2020) Patient genetics is linked to chronic wound microbiome composition and healing. PLoS Pathog 16(6):e1008511
Trampuz A, Piper KE, Jacobson MJ, Hanssen AD, Unni KK, Osmon DR, Mandrekar JN, Cockerill FR, Steckelberg JM, Greenleaf JF, Patel R (2007) Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N Engl J Med 357(7):654–663
Trostrup H, Thomsen K, Christophersen LJ (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm aggravates skin inflammatory response in BALB/c mice in chronic wound model. Wound Repair Regen 21:292
Trostrup H, Lerche CJ, Christophersen LJ, Thomsen K, Jensen PØ, Hougen HP, Høiby N, Moser C (2017) Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infection impairs murine S100A8/A9 and neutrophil effector cytokines-implications for delayed wound closure? Pathog Dis 29(7)
Trostrup H, Lerche CJ, Christophersen LJ, Thomsen K, Jensen PØ, Hougen HP, Høiby N, Moser C (2018) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm hampers murine central wound healing by suppression of vascular epithelial growth factor. Int Wound J 15(1):123–132
Vagesjo E, Öhnstedt E, Mortier A, Lofton H, Huss F, Proost P, Roos S, Phillipson M (2018) Accelerated wound healing in mice by on-site production and delivery of CXCL12 by transformed lactic acid bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(8):1895–1900
Valdez JC, Peral MC, Rachid M, Santana M, Perdigón G (2005) Interference of lactobacillus plantarum with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in infected burns: the potential use of probiotics in wound treatment. Clin Microbiol Infect 11(6):472–479
Vanegas JM, Higuita LF, Vargas CA, Cienfuegos AV, Rodríguez ÉA, Roncancio GE, Jiménez JN (2015) Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing osteomyelitis and infections of skin and soft tissues in hospitals of Medellín. Colomb Biomedica 35(4):522–530
Velasco C, Dunn C, Sturdy C, Izda V, Tin J, Rivas A, McNaughton J, Jeffries MA (2021) Ear wound healing in MRL/MpJ mice is associated with gut microbiome composition and is transferable to non-healer mice via microbiome transplantation. PLoS One 16(7):e0248322
Vuotto C, Donelli G (2015) Anaerobes in biofilm-based healthcare-associated infections. Adv Exp Med Biol 830:97–112
Wang Y, Wu X, Chen J, Amin R, Lu M, Bhayana B, Zhao J, Murray CK, Hamblin MR, Hooper DC, Dai T (2016) Antimicrobial blue light inactivation of gram-negative pathogens in biofilms: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Infect Dis 213(9):1380–1387
Wang G, Li Z, Li T, Wang S, Zhang L, Zhang L, Tang P (2018) Negative-pressure wound therapy in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection model. Biomed Res Int 9496183
Watters C, DeLeon K, Trivedi U, Griswold JA, Lyte M, Hampel KJ (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms perturb wound resolution and antibiotic tolerance in diabetic mice. Med Microbiol Immunol 202:131
Wei Q, Zhang Z, Luo J, Kong J, Ding Y, Chen Y, Wang K (2019) Insulin treatment enhances pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by increasing intracellular cyclic di-GMP levels, leading to chronic wound infection and delayed wound healing. Am J Transl Res 11(6):3261–3279. Erratum in: Am J Transl Res. 2020 15;12(12):8259-8261
Wintachai P, Surachat K, Singkhamanan K (2022) Isolation and characterization of a el Autographiviridae phage and its combined effect with Tigecycline in controlling multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-associated skin and soft tissue infections. Viruses 14(2):194
Wolcott R (2015) Disrupting the biofilm matrix improves wound healing outcomes. J Wound Care 24(8):366–371
Xu Z, Fang X, Wood TK, Huang ZJ (2013) A systems-level approach for investigating Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. PLoS One 8(2):e57050
Yang Q, Larose C, Della Porta AC, Schultz GS, Gibson DJ (2017) A surfactant-based wound dressing can reduce bacterial biofilms in a porcine skin explant model. Int Wound J 14(2):408–413
Yasuda H, Ajiki Y, Koga T, Kawada H, Yokota T (1993) Interaction between biofilms formed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and clarithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37(9):1749–1755
Zhao T, Liu Y (2010) N-acetylcysteine inhibit biofilms produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol 12(10):140
Zhao G, Hochwalt PC, Usui ML (2010) Delayed wound healing in diabetic (db/db) mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm challenge: a model for the study of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 18:467
Zhao G, Usui ML, Underwood RA (2012) Time course study of delayed wound healing in a biofilm-challenged diabetic mouse model. Wound Repair Regen 20:342
Zmuda HM, Mohamed A, Raval YS, Call DR, Schuetz AN, Patel R, Beyenal H (2020) Hypochlorous acidgenerating electrochemical scaffold eliminates Candida albicans biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 129(4):776–786
Zolb C, Cech JD (2016) Efficacy of a new multifunctional surfactant-based biomaterial dressing with 1% silver sulphadiazine in chronic wounds. Int Wound J 13(5):738–743
Zurawski DV, Black CC, Alamneh YA, Biggemann L, Banerjee J, Thompson MG, Wise MC, Honnold CL, Kim RK, Paranavitana C, Shearer JP, Tyner SD, Demons ST (2019) A porcine wound model of Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Adv Wound Care 8(1):14–27
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of Special Interest Group on Biofilms in Clinical Settings and their Control, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, Mysore.
Author’s Contribution
JBA, PR, and SHM drafted the manuscript. The manuscript was conceived, reviewed, and supervised by JBA, SGS, and RRV. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Aswathanarayan, J.B., Rao, P., HM, S., GS, S., Rai, R.V. (2022). Biofilm-Associated Infections in Chronic Wounds and Their Management. In: Donelli, G. (eds) Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology(), vol 1434. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/5584_2022_738
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/5584_2022_738
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-34177-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-34178-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)