Search
Search Results
-
Neuronal DSCAM regulates the peri-synaptic localization of GLAST in Bergmann glia for functional synapse formation
In the central nervous system, astrocytes enable appropriate synapse function through glutamate clearance from the synaptic cleft; however, it...

-
Progesterone modulates the DSCAM-AS1/miR-130a/ESR1 axis to suppress cell invasion and migration in breast cancer
BackgroundA preoperative-progesterone intervention increases disease-free survival in patients with breast cancer, with an unknown underlying...
-
DSCAM is differentially patterned along the optic axon pathway in the develo** Xenopus visual system and guides axon termination at the target
BackgroundThe Xenopus retinotectal circuit is organized topographically, where the dorsal–ventral axis of the retina maps respectively on to the...

-
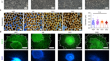
Migration deficits of the neural crest caused by CXADR triplication in a human Down syndrome stem cell model
Down syndrome (DS) is the most common chromosomal abnormality in live-born infants and is caused by trisomy of chromosome 21. Most individuals with...
-
Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule like-1 (DSCAML1) links the GABA system and seizure susceptibility
The Ihara epileptic rat (IER) is a mutant model with limbic-like seizures whose pathology and causative gene remain elusive. In this report, via...

-
Down Syndrome: Historical, Genetic, Clinical, and Ethical Perspectives
This chapter explores the fascinating history of Down syndrome screening, beginning with John Langdon Down’s journey from a grocery store attendant...
-
Understanding the genetic mechanisms and cognitive impairments in Down syndrome: towards a holistic approach
The most common genetic cause of intellectual disability is Down syndrome (DS), trisomy 21. It commonly results from three copies of human chromosome...

-
Dysfunction of NMDA receptors in neuronal models of an autism spectrum disorder patient with a DSCAM mutation and in Dscam-knockout mice
Heterogeneity in the etiopathology of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) limits the development of generic remedies, requires individualistic and...

-
Pharmacological Inhibition of p-21 Activated Kinase (PAK) Restores Impaired Neurite Outgrowth and Remodeling in a Cellular Model of Down Syndrome
Down syndrome (DS) is characterized by the trisomy of chromosome 21 and by cognitive deficits that have been related to neuronal morphological...

-
Shaking up the silence: consequences of HMGN1 antagonizing PRC2 in the Down syndrome brain
Intellectual disability is a well-known hallmark of Down Syndrome (DS) that results from the triplication of the critical region of human chromosome...

-
Epigenomic signature of major congenital heart defects in newborns with Down syndrome
BackgroundCongenital heart defects (CHDs) affect approximately half of individuals with Down syndrome (DS), but the molecular reasons for incomplete...

-
Structural basis for the self-recognition of sDSCAM in Chelicerata
To create a functional neural circuit, neurons develop a molecular identity to discriminate self from non-self. The invertebrate Dscam family and...

-
Shrimp Immune System and Immune Responses
Shrimp, being an invertebrate, lack a vertebrate-like adaptive immune system. However, an efficient innate immune system, consisting of physical...
-
Differential microRNA expression profile in blood of children with Down syndrome suggests a role in immunological dysfunction
Down syndrome (DS), caused by trisomy of chromosome 21 (HSA21), results in a broad range of phenotypes. However, the determinants contributing to the...

-
The clinical significance of circulating DSCAM-AS1 in patients with ER-positive breast cancer and construction of its competitive endogenous RNA network
AbstractLong Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs), with diagnostic and therapeutic applications in malignancies, are newly described tumour-related molecules....

-
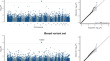
Exome-wide analysis implicates rare protein-altering variants in human handedness
Handedness is a manifestation of brain hemispheric specialization. Left-handedness occurs at increased rates in neurodevelopmental disorders....
-
Secreted immunoglobulin domain effector molecules of invertebrates and management of gut microbial ecology
The origins of a “pass-through” gut in early bilaterians facilitated the exploration of new habitats, motivated the innovation of feeding styles and...

-
Large-scale bioreactor production of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells for treatment of acute radiation syndrome
BackgroundHematopoietic acute radiation syndrome (H-ARS) occurring after exposure to ionizing radiation damages bone marrow causing cytopenias,...

-
Cell type diversity in a develo** octopus brain
Octopuses are mollusks that have evolved intricate neural systems comparable with vertebrates in terms of cell number, complexity and size. The brain...

