Search
Search Results
-
Advances in tumor vascular growth inhibition
Tumor growth and metastasis require neovascularization, which is dependent on a complex array of factors, such as the production of various...
-
LIMK2 promotes melanoma tumor growth and metastasis through G3BP1-ESM1 pathway-mediated apoptosis inhibition
Melanoma is the leading cause of skin cancer-related deaths, and current melanoma therapies, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies,...

-
Potent anti-tumor immune response and tumor growth inhibition induced by HER2 subdomain fusion protein in a mouse tumor model
PurposeSeveral approaches have so far been employed to establish anti-tumor immunity by targeting HER2 protein. Active immunization with recombinant...

-
External validation of a tumor growth inhibition-overall survival model in non-small-cell lung cancer based on atezolizumab studies using alectinib data
BackgroundA modeling framework was previously developed to simulate overall survival (OS) using tumor growth inhibition (TGI) data from six...

-
The long non-coding RNA OTX2-AS1 promotes tumor growth and predicts response to BCL-2 inhibition in medulloblastoma
PurposePrimary brain tumors are a leading cause of cancer-related death in children, and medulloblastoma is the most common malignant pediatric brain...

-
MiR-210-3p enhances intermittent hypoxia-induced tumor progression via inhibition of E2F3
PurposeIntermittent hypoxia (IH) is a hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which is related to tumorigenesis and progression. Although...

-
Tumor cell integrin β4 and tumor stroma E-/P-selectin cooperatively regulate tumor growth in vivo
BackgroundThe immunological composition of the tumor microenvironment has a decisive influence on the biological course of cancer and is therefore of...

-
Dual function of activated PPARγ by ligands on tumor growth and immunotherapy
As one of the peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) members, PPARγ is a ligand binding and activated nuclear hormone receptor, which is...

-
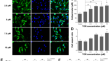
The adverse effect of anticancer drug toremifene on vascular smooth muscle cells is an important aspect of its tumor growth inhibition
PurposeToremifene (TOR) is widely used as an antineoplastic drug and has an inhibitory effect on angiogenesis in mesenteric desmoid tumors and...
-
Pan-PI3K inhibition with copanlisib overcomes Treg- and M2-TAM-mediated immune suppression and promotes anti-tumor immune responses
The PI3K pathway is one of the most frequently altered signaling pathways in human cancer. In addition to its function in cancer cells, PI3K plays a...

-
Inhibition of the epigenetically activated miR-483-5p/IGF-2 pathway results in rapid loss of meningioma tumor cell viability
PurposeMeningioma is the most common primary central nervous system tumor often causing serious complications, and presently no medical treatment is...

-
Aurora Kinase A inhibition enhances DNA damage and tumor cell death with 131I-MIBG therapy in high-risk neuroblastoma
BackgroundNeuroblastoma is the most common extra-cranial pediatric solid tumor. 131 I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) is a targeted...

-
Modelling the impact of liver regeneration on hepatoblastoma patient-derived-xenograft tumor growth
BackgroundTwenty percent of children with hepatoblastoma (HB) have lung metastasis at diagnosis. Treatment protocols recommend surgical removal of...

-
IKKα promotes lung adenocarcinoma growth through ERK signaling activation via DARPP-32-mediated inhibition of PP1 activity
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80–85% cases of lung cancer cases. Diagnosis at advanced stages is common, after which...

-
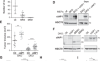
cIAP1/TRAF2 interplay promotes tumor growth through the activation of STAT3
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-1 (cIAP1) is a signaling regulator with oncogenic properties. It is involved in the regulation of signaling pathways...
-
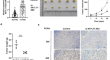
LncRNA XXYLT1-AS2 promotes tumor progression via autophagy inhibition through ubiquitinated degradation of TFEB in hepatocellular carcinoma
PurposeThere is compelling evidence that long-stranded non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an important role in the progression of hepatocellular...
-
Inhibition of BRD4 enhanced the tumor suppression effect of dasatinib in gastric cancer
BRD4, a member of the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) family, is elevated in multiple cancer tissues, including gastric cancer (GC). Targeted...

-
E3 ligase MG53 suppresses tumor growth by degrading cyclin D1
Due to the essential role of cyclin D1 in regulating transition from G1 to S phase in cell cycle, aberrant cyclin D1 expression is a major oncogenic...

-
Fibroblast growth factor inhibition by molecular-targeted agents mitigates immunosuppressive tissue microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
Background & aimsCombination immunotherapy refers to the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) and molecular-targeted agents (MTA), which have...

-
Fibroblast activation protein targeted radiotherapy induces an immunogenic tumor microenvironment and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibition
PurposeFAP is a membrane-bound protease under investigation as a pan-cancer target, given its high levels in tumors but limited expression in normal...

