Search
Search Results
-
FLI1 induces erythroleukemia through opposing effects on UBASH3A and UBASH3B expression
BackgroundFLI1 is an oncogenic transcription factor that promotes diverse malignancies through mechanisms that are not fully understood. Herein, FLI1...

-
FLI1 regulates radiotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through TIE1-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
BackgroundRadiotherapy resistance is the main cause of treatment failure in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), which leads to poor prognosis. It is...

-
The transcription factor Fli1 restricts the formation of memory precursor NK cells during viral infection
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that possess traits of adaptive immunity, such as memory formation. However, the molecular...

-
Single-cell RNA profiling identifies diverse cellular responses to EWSR1/FLI1 downregulation in Ewing sarcoma cells
BackgroundThe EWSR1/FLI1 gene fusion is the most common rearrangement leading to cell transformation in Ewing sarcoma (ES). Previous studies have...

-
ASB2 is a direct target of FLI1 that sustains NF-κB pathway activation in germinal center-derived diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
BackgroundDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) comprises at least two main biologically distinct entities: germinal center B-cell (GCB) and...

-
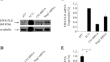
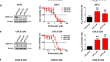
Loss of Stag2 cooperates with EWS-FLI1 to transform murine Mesenchymal stem cells
BackgroundEwing sarcoma is a malignancy of primitive cells, possibly of mesenchymal origin. It is probable that genetic perturbations other than EWS-FLI1...
-
Hypoxia and HIFs in Ewing sarcoma: new perspectives on a multi-facetted relationship
Hypoxia develops during the growth of solid tumors and influences tumoral activity in multiple ways. Low oxygen tension is also present in the bone...

-
Colorectal cancer detected by liquid biopsy 2 years prior to clinical diagnosis in the HUNT study
BackgroundColorectal cancer (CRC) is often diagnosed in advanced stages. Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) has been proposed as an early diagnostic...

-
Genetically Engineered Mouse Model in Ewing Sarcoma
Modeling Ewing sarcoma is challenging, since overexpression of EWS-FLI1 induces apoptosis and is not sufficient for tumor induction. It is therefore...
-
EWS-FLI1-mediated tenascin-C expression promotes tumour progression by targeting MALAT1 through integrin α5β1-mediated YAP activation in Ewing sarcoma
BackgroundThe extracellular matrix has been critically associated with the tumorigenesis and progression of Ewing sarcoma (ES). However, the...

-
Targeted inhibition of histone deacetylase leads to suppression of Ewing sarcoma tumor growth through an unappreciated EWS-FLI1/HDAC3/HSP90 signaling axis
AbstractEwing sarcoma (ES) are aggressive pediatric bone and soft tissue tumors driven by EWS-ETS fusion oncogenes, most commonly EWS-FLI1 ....
-
Epigenetic Analysis in Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a highly malignant tumor characterized by a chromosomal translocation that modifies the activity of an ETS family transcription...
-
Patients with Chromosome 11q Deletions Are Characterized by Inborn Errors of Immunity Involving both B and T Lymphocytes
Disorders of the long arm of chromosome 11 (11q) are rare and involve various chromosomal regions. Patients with 11q disorders, including Jacobsen...
-
Systems Biology Analysis for Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma (EwS) is a highly aggressive pediatric bone cancer that is defined by a somatic fusion between the EWSR1 gene and an ETS family member,...
-
Genetic Assessment of Projected Residual Feed Consumption and Expression of Significant Candidate Genes in Duroc Pigs and Second-Generation Commercial Blends
Residual feed intake (RFI) is one of the basic and complex feed characteristics that is economically important for livestock production. However, the...

-
Class I histone deacetylases (HDAC) critically contribute to Ewing sarcoma pathogenesis
BackgroundHistone acetylation and deacetylation seem processes involved in the pathogenesis of Ewing sarcoma (EwS). Here histone deacetylases (HDAC)...

-
Molecular Approaches to Diagnosis in Ewing Sarcoma: RT-PCR
Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive tumor that affects children and young adults. Ewing sarcomas are characterized by specific chromosomal...
-
Neomorphic DNA-binding enables tumor-specific therapeutic gene expression in fusion-addicted childhood sarcoma
Chimeric fusion transcription factors are oncogenic hallmarks of several devastating cancer entities including pediatric sarcomas, such as Ewing...

-
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Followed by Next-Generation Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) Analysis in Ewing Sarcoma
ChIP-seq is the method of choice for profiling protein–DNA interactions, and notably for characterizing the landscape of transcription factor binding...
-
Extracellular vesicle-associated IGF2BP3 tunes Ewing sarcoma cell migration and affects PI3K/Akt pathway in neighboring cells
Ewing sarcoma (EWS) is a challenging pediatric cancer characterized by vast intra-tumor heterogeneity. We evaluated the RNA-binding protein IGF2BP3,...

