Search
Search Results
-
Expression of Dystrophin Dp71 Splice Variants Is Temporally Regulated During Rodent Brain Development
Dystrophin Dp71 is the major product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy ( DMD ) gene in the brain, and its loss in DMD patients and mouse models leads...

-
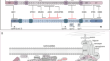
Dystrophin- and Utrophin-Based Therapeutic Approaches for Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Comparative Review
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a devastating disease that leads to progressive muscle loss and premature death. While medical management focuses...
-
Trichinella spiralis (Owen, 1835) Induces Increased Dystrophin Expression in Invaded Cross-striated Muscle
PurposeDystrophin and the dystrophin glycoprotein complex serve as a cytoskeletal integrator, critical for muscle membrane stability. The aim of the...

-
Dystrophin Short Product, Dp71, Interacts with AQP4 and Kir4.1 Channels in the Mouse Cerebellar Glial Cells in Contrast to Dp427 at Inhibitory Postsynapses in the Purkinje Neurons
Dystrophin is the causative gene for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy (DMD/BMD), and it produces full-length and short dystrophin, Dp427 and...

-
Evaluation of the dystrophin carboxy-terminal domain for micro-dystrophin gene therapy in cardiac and skeletal muscles in the DMDmdx rat model
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a muscle wasting disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding dystrophin. Gene therapy using...

-
Brain magnetic resonance imaging in the DE50-MD dog model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy reveals regional reductions in cerebral gray matter
BackgroundDuchenne muscular dystrophy is a X-linked disease characterized by severe and progressive muscle weakness, alongside cognitive impairment...

-
Identification of Dp140 and α1-syntrophin as novel molecular interactors of the neuronal CaV2.1 channel
The primary function of dystrophin is to form a link between the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. In addition to this crucial structural...

-
Complexity of skeletal muscle degeneration: multi-systems pathophysiology and organ crosstalk in dystrophinopathy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a highly progressive muscle wasting disorder due to primary abnormalities in one of the largest genes in the human...

-
Dystrophin Dp71 and the Neuropathophysiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by frameshift mutations in the DMD gene that prevent the body-wide translation of its protein product,...

-
Specific Dystrophins Selectively Associate with Inhibitory and Excitatory Synapses of the Mouse Cerebellum and their Loss Alters Expression of P2X7 Purinoceptors and Pro-Inflammatory Mediators
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients, having mutations of the DMD gene, present with a range of neuropsychiatric disorders, in addition to the...

-
Therapeutic approaches for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a monogenic muscle-wasting disorder and a priority candidate for molecular and cellular therapeutics. Although...

-
Severe cardiac involvement with preserved truncated dystrophin expression in Becker muscular dystrophy by +1G>A DMD splice-site mutation: a case report
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) is caused by specific mutations in the DMD gene that causes progressive muscle weakness and primarily affects...

-
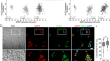
Plectin plays a role in the migration and volume regulation of astrocytes: a potential biomarker of glioblastoma
BackgroundThe expression of aquaporin 4 (AQP4) and intermediate filament (IF) proteins is altered in malignant glioblastoma (GBM), yet the expression...
-
Regenerative Rehabilitation for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe, progressive, genetic muscle wasting disorder arising from the absence of the membrane stabilizing...
-
Truncated SCRIB isoform promotes breast cancer metastasis through HNRNP A1 mediated exon 16 skip**
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors with high mortality due to metastases. SCRIB, a scaffold protein mainly distributed in the...

-
The administration of antisense oligonucleotide golodirsen reduces pathological regeneration in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
During the last decade, multiple clinical trials for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) have focused on the induction of dystrophin expression using...

-
Roles and mechanisms of ankyrin-G in neuropsychiatric disorders
Ankyrin proteins act as molecular scaffolds and play an essential role in regulating cellular functions. Recent evidence has implicated the ANK3 ...

-
Cellular pathology of the human heart in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD): lessons learned from in vitro modeling
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder where an X-linked mutation in the DMD gene initiates pathogenic development caused by the absence...

-
Design and Application of a Short (16-mer) Locked Nucleic Acid Splice-Switching Oligonucleotide for Dystrophin Production in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Myotubes
Splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs) have been used to modulate gene expression by interfering with pre-mRNA splicing with the intent to treat...
-
CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Discovery of the CRISPR-Cas (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat, CRISPR-associated) system a decade ago has opened new...

