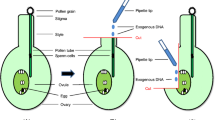
Abstract
Numerous techniques have been developed to transfer genes into plants to create genetically engineered crops that can tolerate environmental stresses, and to improve productivity and quality. The search for easier, more efficient techniques to transfer genes continues because the efficiencies of current techniques are low and recovering fertile transgenic plants is difficult and time consuming with some plant species.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess, D. (1987) Pollen-based techniques in genetic manipulation. Inter. Rev. Cytol. 107, 367–395.
De Wet, J. M. J., Bergquist, R. R., Harlan, J. F., Brink, D. E., Cohen, C. E., Newell, C. A., and De Wet, A.-E. (1985) Exogenous gene transfer in maize (Zea mays) using DNA-treated pollen, in Experimental Manipulation of Ovule Tissues. (Chapman, G. P., Mantell, S. H., and Daniels, R. W., eds.) Longman, London, pp. 197–209.
Ohta, Y. (1986) High-efficiency genetic transformation of maize by a mixture of pollen and exogenous DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 715–719.
Pandey, K. K. (1978) Gametic gene transfer in Nicotiana by means of irradiated pollen. Genetica 49, 53–69.
Pandey, K. K. (1980) Further evidence for egg transformation in Nicotiana. Heredity 45, 15–29.
Sanford, J. C., Skubik, K. A., and Reisch, B. I. (1985) Attempted pollen-mediated plant transformation employing genomic donor DNA. Theor. Appl. Genet. 69, 571–574.
Matousek, J. and Tupy, J. (1983) The release of nucleases from tobacco pollen. Plant Sci. Lett. 30, 83–89.
Roeckel, P., Heizmann, P., Dubois, M., and Dumas, C. (1988) Attempts to transform Zea mays via pollen grains, effect of pollen and stigma nuclease activities. Sex Plant Reprod. 1, 156–163.
Abdul-Baki, A. A., Saunders, J. A., Matthews, B. F., and Pittarelli, G. W. (1990) DNA uptake by electroporation of germinating pollen grains. Plant Sci. 70, 181–190.
Matthews, B. F., Abdul-Baki, A. A., and Saunders, J. A. (1990) Expresston of a foreign gene in electroporated pollen grains of tobacco. Sex Plant Reprod. 3, 147–151.
Smith, C. R., Saunders, J. A., Van Wert, S., Cheng, J., and Matthews, B. F. (1994) Expression of GUS and CAT activities using electrotransformed pollen. Plant Sci. 104, 49–58.
Van Wert, S. L. and Saunders J. A. (1992) Reduction of nuclease activity released from germinating pollen under conditions used for pollen electrotransformation. Plant Sci. 84, 11–16.
Dickinson, D. B. (1968) Rapid starch synthesis associated with increased respiration in germinating lily pollen. Plant Phys. 43, 1–8.
Matousek, J. and Tupy, J. (1984) Purification and properties of extracellular nuclease from tobacco pollen. Bio. Plantarum 26, 62–73.
Saunders, J. A., Lin, C. H., Cheng, J., Tsengwa, N., Lin, J. J., Smith, C. R., McIntosh, M., and Wert, S. V. (1994) Rapid optimization of electroporation conditions for plant cells, protoplasts, and pollen. Mol. Biotechnol. (in press).
Saunders, J. A., Roskos, L. A., Mischke, B. S., Aly, M., and Owens, L. D. (1986) Behavior and viability of tobacco protoplasts in response to electrofusion parameters. Plant Physiol. 80, 117–121.
Abdul-Baki, A. A. (1992) Determination of pollen viability in tomatoes. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 117(3), 473–476.
Fromm, M., Taylor, L. P., and Walbot, V. (1985) Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 5824–5828.
Fromm, M. E., Taylor, L. P., and Walbot, V. (1986) Stable transformation of maize after gene transfer by electroporation. Nature 319, 791–793.
Neumann, E., Schaefer-Ridder, M., Wang, Y., and Hofschneider, P. H. (1982) Inhibition of gene expression in plant cells by expression of antisense RNA. EMBO J. 1, 841–845.
Wong, T. K. and Neumann, E. (1982) Electric field mediated gene transfer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 107, 584–587.
Potter, H., Weir, L., and Leder, P. (1984) Enhancer-dependent expression of human κ immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 7161–7165.
Weber, H., Forester, W., and Jacob, H. E. (1981) Parasexual hybridization of yeasts by electric field stimulated fusion of protoplasts. Curr. Genet. 4, 165,166.
Saunders, J. A., Matthews, B. F., and Van Wert, S. L. (1991) Pollen electrotransformation for gene transfer in plants, in Guide to Electroporation and Electrofusion. (Chang, D. C., Chassy, B. M., Saunders, J. A., and Sowers, A. E., eds.), Academic, San Diego, CA, pp. 227–247.
Saunders, J. A., Matthews, B. F., and Miller, P. D. (1989) Plant gene transfer using electrofusion and electroporation, in Electroporation and Electrofusion in Cell Biology. (Neumann, E., Sowers, A., and Jordan, C., eds.) Plenum, New York, pp. 343–354.
Liang, H., Purucker, W. J., Stenger, D. A., Kubiniec, R. T., and Hui, S. W. (1988) Uptake of fluorescence-labeled dextrans by 10T 1/2 fibroblasts following permeation by rectangular and exponential electric field pulses. BioTechniques 6, 550–558.
Benz, R., Zimmermann, U., and Wecker, E. (1981) High electric fields effects on the cell membranes of Halicystis parvula: a charge-pulse study. Planta 152, 314–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Saunders, J.A., Matthews, B.F. (1995). Pollen Electrotransformation in Tobacco. In: Nickoloff, J.A. (eds) Plant Cell Electroporation and Electrofusion Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 55. Springer, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-328-7:81
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-328-7:81
Publisher Name: Springer, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-0-89603-328-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-59259-542-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols