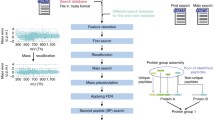
Abstract
This chapter describes how to improve quantitative accuracy and precision in shotgun proteomics by PQPQ (protein quantification by peptide quality control). The method is based on the assumption that the quantitative pattern of peptides derived from one protein will correlate over several samples. Dissonant patterns are assumed to arise either from mismatched peptides or due to the presence of different protein species. PQPQ identifies and excludes outliers and detects the existence of different protein species by correlation analysis. Alternative protein species can then be quantified separately. PQPQ can handle shotgun proteomics data from several MS instruments, data from different kinds of labeling, and label-free data.
We have previously shown that data processing by PQPQ improves the information output from shotgun proteomics by validating the algorithm on seven datasets related to different cancer studies (Forshed et al., Mol Cell Proteomics 10(10):M111.010264, 2011). Data from two labeling procedures and three different instrumental platforms was included in the evaluation. With this unique method using both peptide sequence data and quantitative data, we can improve the quantitative accuracy and precision on the protein level and detect different protein species (Forshed et al., Mol Cell Proteomics 10(10):M111.010264, 2011).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson TJ, Dinan MA, Dewhirst M, Garcia-Blanco MA, Pearson JL (2010) SplicerAV: a tool for mining microarray expression data for changes in RNA processing. BMC Bioinformatics 11(1):108
Duncan MW, Aebersold R, Caprioli RM (2010) The pros and cons of peptide-centric proteomics. Nat Biotechnol 28(7):659–664
Nesvizhskii A, Aebersold R (2005) Interpretation of shotgun proteomic data - The protein inference problem. Mol Cell Proteomics 4(10):1419–1440
Karp NA, Huber W, Sadowski PG, Charles PD, Hester SV, Lilley KS (2010) Addressing accuracy and precision issues in iTRAQ quantitation. Mol Cell Proteomics 9(9):1885–1897
Boehm AM, Pütz S, Altenhöfer D, Sickmann A, Falk M (2007) Precise protein quantification based on peptide quantification using iTRAQ™. BMC Bioinformatics 8(1):214
Lau KW, Jones AR, Swainston N, Siepen JA, Hubbard SJ (2007) Capture and analysis of quantitative proteomic data. Proteomics 7(16):2787–2799
Park SK, Venable JD, Xu T, Yates JR (2008) A quantitative analysis software tool for mass spectrometry–based proteomics. Nat Methods 5:319–322
Mueller LN, Brusniak M-Y, Mani DR, Aebersold R (2008) An assessment of software solutions for the analysis of mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics data. J Proteome Res 7(1):51–61
Panchaud A, Affolter M, Moreillon P, Kussmann M (2008) Experimental and computational approaches to quantitative proteomics: status quo and outlook. J Proteomics 71(1):19–33
D’Ascenzo M, Choe L, Lee KH (2008) iTRAQPak: an R based analysis and visualization package for 8-plex isobaric protein expression data. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 7(2):127–135
Cox J, Mann M (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26(12):1367–1372
Forshed J, Johansson HJ, Pernemalm M, Branca RMM, Sandberg A, Lehtio J (2011) Enhanced information output from shotgun proteomics data by protein quantification and peptide quality control (PQPQ). Mol Cell Proteomics 10(10):M111.010264
Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, Rick J, Kuster B (2007) Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:1017–1031
Song XM, Bandow J, Sherman J, Baker JD, Brown PW, McDowell MT, Molloy MP (2008) iTRAQ experimental design for plasma biomarker discovery. J Proteome Res 7:2952–2958
Reiter L, Claassen M, Schrimpf SP, Jovanovic M, Schmidt A, Buhmann JM et al (2009) Protein identification false discovery rates for very large proteomics data sets generated by tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 8(11):2405–2417
Elias JE, Gygi SP (2007) Target-decoy search strategy for increased confidence in large-scale protein identifications by mass spectrometry. Nat Methods 4(3):207–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Forshed, J. (2013). Protein Quantification by Peptide Quality Control (PQPQ) of Shotgun Proteomics Data. In: Bäckvall, H., Lehtiö, J. (eds) The Low Molecular Weight Proteome. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1023. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7209-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7209-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-7167-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-7209-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols