Abstract
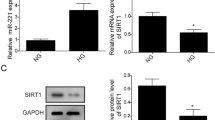
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the main complication of diabetes mellitus (DM). Recent studies have implicated microRNAs dysfunction in human retinal microvascular endothelial cell (HRMEC). In this study, we aim to investigate the apoptotic promotion of miR-29b-3p by blocking SIRT1 in HRMEC for DR situation. To identify the regulating relationship between miR-29b-3p and SIRT1, HRMECs were transfected with miR-29b-3p mimics/inhibitors or their negative controls. Cell viability was assessed with the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and apoptotic cells were stained by one-step TUNEL assay kit. Gene and protein expression were assayed by RT-qPCR and Western blotting separately. Dual-luciferase reporter assay using HEK293T cells was performed to show the direct interaction of miR-29b-3p and the 3′-UTR of SIRT1. HRMECs were identified as >95% positive for CD31 and vWF. Upregulated miR-29b-3p decreased the expression of SIRT1 and increased the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2, while downregulated miR-29b-3p increased the expression of SIRT1 protein and downregulated the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2. Dual-luciferase reporter assay showed the direct interaction of miR-29b-3p and SIRT1. The dysregulation of miR-29b-3p/SIRT1 is a potential mechanism of HRMEC apoptosis in DR. miR-29b-3p/SIRT1 may be a potential therapeutic target for DR.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME (2018) MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(4):1202–1207
O’Kelly F et al (2012) MicroRNAs as putative mediators of treatment response in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 9(7):397–407
Landrier JF et al (2019) MicroRNAs in obesity and related metabolic disorders. Cell 8(8):859
Klieser E et al (2019) The crosstalk of miRNA and oxidative stress in the liver: from physiology to pathology and clinical implications. Int J Mol Sci 20(21):5266
Majidinia M et al (2019) Targeting miRNAs by polyphenols: novel therapeutic strategy for aging. Biochemist Pharmacol 173:113688
Nasr MA et al (2019) Dysregulated MicroRNA fingerprints and methylation patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma, cancer stem cells, and mesenchymal stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:229
Zhao M et al (2019) The regulatory role of non-coding RNAs on programmed cell death four in inflammation and cancer. Front Oncol 9:919
Duan YR et al (2019) Exosomal microRNA-16-5p from human urine-derived stem cells ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through protection of podocyte. J Cell Mol Med 25(23):10798–10813
Khan R et al (2019) Circulatory miR-98-5p levels are deregulated during diabetes and it inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting PPP1R15B in keratinocytes. RNA Biol 17:1–14
Ventriglia G et al (2019) miR-409-3p is reduced in plasma and islet immune infiltrates of NOD diabetic mice and is differentially expressed in people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 63:124
Fu X, Ou B (2019) miR-152/LIN28B axis modulates high-glucose-induced angiogenesis in human retinal endothelial cells via VEGF signaling. J Cell Biochem 121(2):954–962
Ji H et al (2019) Circulating miR-3197 and miR-2116-5p as novel biomarkers for diabetic retinopathy. Clin Chim Acta 501:147–153
Thounaojam MC et al (2019) MicroRNA-34a (miR-34a) mediates retinal endothelial cell premature senescence through mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of antioxidant activities. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(9):328
Balestrieri ML et al (2013) Poor glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes patients reduces endothelial progenitor cell number by influencing SIRT1 signalling via platelet-activating factor receptor activation. Diabetologia 56(1):162–172
Esteves JV et al (2018) Diabetes modulates MicroRNAs 29b-3p, 29c-3p, 199a-5p and 532-3p expression in muscle: possible role in GLUT4 and HK2 repression. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:536
Su T et al (2019) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived Exosomal MiR-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano 13(2):2450–2462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Zeng, Y., Cui, Z., Chen, J., Tang, S. (2023). Investigating the Function of MicroRNAs in Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells of Diabetic Retinopathy. In: Liu, GS., Wang, JH. (eds) Diabetic Retinopathy. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2678. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3255-0_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3255-0_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3254-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3255-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols