Abstract
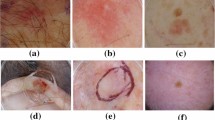
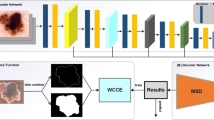
Medical image segmentation separates target structures or tissues within medical images to promote precise diagnoses. Automated image segmentation algorithms can help dermatologists to diagnose skin cancer by identifying skin lesions. Many popular image segmentation algorithms combine UNet and Transformer, but cannot fully utilize the global information between different scales and also have a huge number of parameters. To this end, this paper proposes a lightweight Transformer-based UNet (LTUNet) method for medical image segmentation, which designs an effective approach to extract and fully use multi-scale features. Firstly, the multi-scale feature maps of images are extracted by the inverted residual blocks of lightweight UNet encoder. Then, the feature maps are concatenated as the input of the Transformer’s encoder blocks to compute intra- and inter-scale attention scores, and the scores are used to enhance the feature map of each scale. Finally, we fuse the upsampled results of all scales on UNet to improve the performance of segmentation. Our method achieves 0.9432, 0.8948, 0.9348 for mDice, mIoU and mACC on the ISIC2016 dataset, and 0.9058, 0.8138, 0.8968 on the ISIC2018 dataset respectively, which outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Besides, our network has a smaller number of parameters and converges faster.
This research is supported by Major Program of the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21 &ZD102).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, H., et al.: Swin-Unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds.) Computer Vision-ECCV 2022 Workshops: Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022, Proceedings, Part III, pp. 205–218. Springer, Cham (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25066-8_9
Chen, J., et al.: TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. ar**v:abs/2102.04306 (2021)
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., Adam, H.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 833–851. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
Codella, N., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: a challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). ar**v preprint ar**v:1902.03368 (2019)
Contributors, M.: MMSegmentation: Openmmlab semantic segmentation toolbox and benchmark (2020). https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database, pp. 248–255 (2009)
Diakogiannis, F.I., Waldner, F., Caccetta, P., Wu, C.: ResUNet-a: a deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 162, 94–114 (2020)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16 \(\times \) 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ar**v preprint ar**v:2010.11929 (2020)
Gutman, D., et al.: Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). ar**v preprint ar**v:1605.01397 (2016)
Han, K., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Guo, J., Xu, C., Xu, C.: GhostNet: more features from cheap operations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1580–1589 (2020)
Han, S., Pool, J., Tran, J., Dally, W.: Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hinton, G.E., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. ar**v:abs/1503.02531 (2015)
Howard, A.G., et al.: MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. ar**v preprint ar**v:1704.04861 (2017)
Iandola, F.N., Han, S., Moskewicz, M.W., Ashraf, K., Dally, W.J., Keutzer, K.: SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and \(<\)0.5 MB model size. ar**v preprint ar**v:1602.07360 (2016)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 936–944 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
Marks, R., Staples, M., Giles, G.G.: Trends in non-melanocytic skin cancer treated in Australia: the second national survey. Int. J. Cancer J. Int. Du Cancer 53(4), 585–590 (2010)
Ni, Z.L., et al.: RAUNet: residual attention U-Net for semantic segmentation of cataract surgical instruments. In: Gedeon, T., Wong, K., Lee, M. (eds.) Neural Information Processing: 26th International Conference, ICONIP 2019, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 12–15 December 2019, Proceedings, Part II, pp. 139–149. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36711-4_13
Oktay, O., et al.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. ar**v preprint ar**v:1804.03999 (2018)
Punn, N.S., Agarwal, S.: Inception U-Net architecture for semantic segmentation to identify nuclei in microscopy cell images. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 16(1), 1–15 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Sharma, N., Aggarwal, L.M.: Automated medical image segmentation techniques. J. Med. Phys./Assoc. Med. Physicists India 35(1), 3 (2010)
Strudel, R., Garcia, R., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: Segmenter: transformer for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7262–7272 (2021)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Ullrich, K., Meeds, E., Welling, M.: Soft weight-sharing for neural network compression. ar**v preprint ar**v:1702.04008 (2017)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Wang, R., Lei, T., Cui, R., Zhang, B., Meng, H., Nandi, A.K.: Medical image segmentation using deep learning: a survey. IET Image Process. 16(5), 1243–1267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12419
Yuan, K., Guo, S., Liu, Z., Zhou, A., Yu, F., Wu, W.: Incorporating convolution designs into visual transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 579–588 (2021)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M.M.R., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(6), 1856–1867 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, H., Zhang, H., Li, M., Quan, X. (2024). LTUNet: A Lightweight Transformer-Based UNet with Multi-scale Mechanism for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In: Fang, L., Pei, J., Zhai, G., Wang, R. (eds) Artificial Intelligence. CICAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14474. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9119-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9119-8_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-9118-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-9119-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)