Abstract
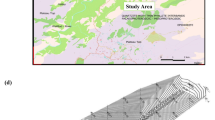
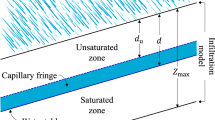
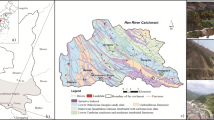
The identification of landslide-triggering rainfall thresholds plays an important role in providing early warning information and implementing emergency remedial actions before landslide occurs. In this study, fully coupled hydro-mechanical model was conducted to establish intensity–duration (I-D) thresholds for shallow landslides upon rainfall. The numerical model was first verified against measurements obtained from a full-scale field test for slope. The simulation result shows good agreement with the experimental results, indicating that the proposed numerical model is appropriate for use in the simulation of unsaturated soil slope behavior subjected to rainfall infiltration. This approach was then used to determine new I-D thresholds for shallow landslides considering the different hydrological conditions. Finally, the critical rainfall threshold curves obtained for the study were compared with shallow landslides historic data. The result revealed that antecedent soil moistures through initial soil suctions is a critical factor affecting the I-D thresholds. The majority of landslide data recorded from literature through case studies located within the proposed thresholds corresponding initial suction of 2–10 kPa. The findings of this study can be implemented into the current activities for predicting the occurrence of shallow landslides in the future in Vietnam.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petley, D. (2012). Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology, 40(10): 927–930.
Guzzetti, F., Peruccacci, S., Rossi, M., Stark, C.P. (2008). The rainfall intensity–duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: an update. Landslides, 5(1): 3–17.
Segoni, S., Piciullo, L., Gariano, S.L. (2018). A review of the recent literature on rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence. Landslides, 15(8): 1483–1501.
Collins, B.D., Znidarcic, D. (2004). Stability analyses of rainfall induced landslides. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 130(4): 362–372.
Yang, K.H., Uzuoka, R., Thuo, J.N., Lin, G.L., Nakai, Y. (2017). Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis of two unstable unsaturated slopes subject to rainfall infiltration. Engineering Geology, 216(13–30.
Caine, N. (1980). The rainfall intensity duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows. Geogr Ann, 62(1-2): 23–27.
Aleotti, P. (2004). A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures. Engineering Geology, 73(3-4): 247–265.
Brinkgreve, R.B.J., Kumarswamy, S., Swolfs, W.M. (2019). PLAXIS 2019 manual. PLAXIS bv, Delft, Netherlands
Ng, C.W.W., Zhan, L.T., Bao, C.G., Fredlund, D.G., Gong, B.W. (2003). Performance of an unsaturated expansive soil slope subjected to artificial rainfall infiltration. Geotechnique, 53(2): 143–157.
Qi, S.C., Vanapalli, S.K. (2018). Simulating hydraulic and mechanical responses of unsaturated expansive soil slope to rainfall: case study. International Journal of Geomechanics, 18(6): 05018002.
Alonso, E.E., Gens, A., Josa, A. (1990). A constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Geotechnique, 40(3): 405–430.
Yang, K.H., Nguyen, T.S., Rahardjo, H., Lin, D.G. (2020). Deformation characteristics of unstable shallow slopes triggered by rainfall infiltration. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 80(1): 317–344.
Cuomo, S., Della Sala, M. (2013). Rainfall-induced infiltration, runoff and failure in steep unsaturated shallow soil deposits. Engineering Geology, 162: 118–127.
Zhan, T.L.T., & Ng, C.W.W. (2006). Shear strength characteristics of an unsaturated expansive clay. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 43(7): 751–763.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National University of Civil Engineering (NUCE), Viet Nam under grant number 18-2021/KHXD-TĐ. The financial supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nguyen, TS., Pham, VA., Nguyen, BV., Yang, KH. (2022). Establishing Thresholds for Rainfall‐Induced Shallow Landslides Using Fully Coupled Hydro-Mechanical Model. In: Ha-Minh, C., Tang, A.M., Bui, T.Q., Vu, X.H., Huynh, D.V.K. (eds) CIGOS 2021, Emerging Technologies and Applications for Green Infrastructure. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 203. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7160-9_105
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7160-9_105
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7159-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7160-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)