Abstract
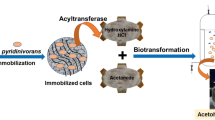
The potential applications of acyltransferases in the synthesis of pharmaceutically significant hydroxamic acids have rendered it substantial industrial importance. Enrichment techniques were used to isolate a thermophilic bacterial strain which is capable of degrading acetamide. This isolate was classified as Bacillus sp. on the basis of morphology, biochemical and physiological tests. Based on the 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing, the isolate was designated as Bacillus megaterium. Its resting cells containing the active acyltransferase enzyme were immobilized in the gel beads of different matrices as sodium alginate, agar, polyacrylamide and polyvinyl alcohol-alginate. The assay of acyltransferase activity of the immobilized beads was done using iron (III) chloride reagents at high temperature of 55 °C. The best performing sodium alginate beads were optimized for various parameters such as substrate concentration, temperature, pH and the type of buffer. This chapter provides insights on acyltransferase enzyme immobilization technique, its operational stability and its significance in hydroxamic acid synthesis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhalla TC et al (2018) Nitrile metabolizing enzymes in biocatalysis and biotransformation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 185(4):925–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2705-7
Bhatia RK et al (2013) Bench scale production of benzohydroxamic acid using acyl transfer activity of amidase from Alcaligenes sp. MTCC 10674. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1206-x
Chand D et al (2004) Treatment of simulated wastewater containing toxic amides by immobilized Rhodococcus rhodochrous NHB-2 using a highly compact 5-stage plug flow reactor. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(7):679–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-2158-8
Choi JM, Han SS, Kim HS (2015) Industrial applications of enzyme biocatalysis: current status and future aspects. Biotechnol Adv 33(7):1443–1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.014
Coffey L et al (2010) Real-time PCR detection of Fe-type nitrile hydratase genes from environmental isolates suggests horizontal gene transfer between multiple genera. Anton Leeuw Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 98(4):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9459-8
D’Oca CDRM et al (2010) Synthesis and antituberculosis activity of new fatty acid amides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(17):5255–5257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.149
Dennett GV, Blamey JM (2016) A new thermophilic nitrilase from an Antarctic hyperthermophilic microorganism. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 4(FEB):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2016.00005
Ep**er E, Stolz A (2019) Conversion of phenylglycinonitrile by recombinant Escherichia coli cells synthesizing variants of the arylacetonitrilase from Pseudomonas fluorescens EBC191. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(16):6737–6746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09957-y
Fu L et al (2014) Purification and characterization of a thermostable aliphatic amidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii CH1. Extremophiles 18(2):429–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0628-y
Gong JS et al (2012) Nitrilases in nitrile biocatalysis: recent progress and forthcoming research. Microb Cell Factories 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-11-142
Jiang Y et al (2019) Reactivity of an unusual amidase may explain colibactin’s DNA cross-linking activity. J Am Chem Soc 141(29):11489–11496. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b02453
Jochems P et al (2011) Enzyme immobilization on/in polymeric membranes: status, challenges and perspectives in biocatalytic membrane reactors (BMRs). Green Chem 13(7):1609–1623. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1gc15178a
Joshi SJ, Abed RMM (2017) Biodegradation of polyacrylamide and its derivatives. Environm Processes 4(2):463–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0224-0
Kumar H et al (2006) Constitutive acetonitrile hydrolysing activity of Nocardia globerula NHB-2: optimization of production and reaction conditions. Indian J Exp Biol 44(3):240–245
Kumar V et al (2015) Purification, characterization and in-silico analysis of nitrilase from Gordonia terrae. Protein Pept Lett 22(1):52–62
Landis W et al (2003) Introduction to environmental toxicology: impacts of chemicals upon ecological systems, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Li T et al (2007) Biodegradation of organonitriles by adapted activated sludge consortium with acetonitrile-degrading microorganisms. Water Res 41(15):3465–3473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.033
Li H et al (2015) Improving the catalytic potential and substrate tolerance of Gibberella intermedia nitrilase by whole-cell immobilization. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38(1):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1258-6
Li C et al (2016) A novel strategy for acetonitrile wastewater treatment by using a recombinant bacterium with biofilm-forming and nitrile-degrading capability. Chemosphere 161:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.019
Mateo C et al (2004) A new, mild cross-linking methodology to prepare cross-linked enzyme aggregates. Biotechnol Bioeng 86(3):273–276. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20033
Mikkelsen SR, Cortï E (2016) Bioanalytical chemistry. Wiley
Mukram I et al (2016) Biodegradation of butyronitrile and demonstration of its mineralization by Rhodococcus sp. MTB5. 3 Biotech 6(2):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0456-0
Nader AM (2012) Directed evolution of cyanide degrading enzymes. Texas A&M University
Offor SJ, Mbagwu HOC, Orisakwe OE (2017) Lead induced hepato-renal damage in male albino rats and effects of activated charcoal. Front Pharmacol 8(MAR):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00107
Pal A, Datta S, Paul AK (2013) Hexavalent chromium reduction by immobilized cells of Bacillus sphaericus and 303. Braz Arch Biol Technol 56(3):505–512. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132013000300019
Pandey D, Singh R, Chand D (2011) An improved bioprocess for synthesis of acetohydroxamic acid using DTT (dithiothreitol) treated resting cells of Bacillus sp. APB-6. Bioresour Technol 102(11):6579–6586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.071
Poli A et al (2013) Halomonas smyrnensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.037036-0
Poonkuzhali K, Palvannan T (2013) Comparison of biopolymers for immobilization of laccase: ecotoxicity assessment of azo dye. Indian J Biotechnol 12(3):395–401
Raj J et al (2010) Bioconversion of acrylonitrile to acrylamide using polyacrylamide entrapped cells of Rhodococcus rhodochrous PA-34. Folia Microbiol 55(5):442–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0074-x
Ramteke PW et al (2013) Nitrile-converting enzymes: an eco-friendly tool for industrial biocatalysis. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 60(5):459–481. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1139
Ruan LT, Zheng RC, Zheng YG (2016) A novel amidase from Brevibacterium epidermidis ZJB-07021: gene cloning, refolding and application in butyrylhydroxamic acid synthesis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(8):1071–1083. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1786-y
Rzeznicka K et al (2010) Cloning and functional expression of a nitrile hydratase (NHase) from Rhodococcus equi TG328-2 in Escherichia coli, its purification and biochemical characterisation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(5):1417–1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2153-y
Santoshkumar M et al (2017) Purification and characterization of amidase from Paracoccus sp. SKG: utilization of amidase-inhibited whole cells for bioconversion of acrylonitrile to acrylamide’. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 10:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.04.001
Schoevaart R et al (2004) Preparation, optimization, and structures, of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Biotechnol Bioeng 87(6):754–762. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20184
Sharma M, Sharma NN, Bhalla TC (2012) Biotransformation of acetamide to acetohydroxamic acid at bench scale using acyl transferase activity of amidase of Geobacillus pallidus BTP-5x MTCC 9225. Indian J Microbiol 52(1):76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0211-5
Siyanbola T et al (2015) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of polyesteramide resin from Moringa oleifera seed oil (Moso) for surface coating application. Can J Pure Appl Sci 9(1):3229–3240
Sogani M et al (2012a) Biotransformation of amide using Bacillus sp.: isolation strategy, strain characteristics and enzyme immobilization. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9(1):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-011-0005-7
Sogani M et al (2012b) Comparison of immobilized whole resting cells in different matrices vis-A-vis free cells of Bacillus megaterium for acyltransferase activity. J Environ Res Dev 6(3):695–701
Sogani M et al (2014) Acetamide hydrolyzing activity of Bacillus megaterium F-8 with bioremediation potential: optimization of production and reaction conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8822–8830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2818-7
Thakur V et al (2015) Decolorization of dye by alginate immobilized laccase from Cercospora SPF-6: using compact 5 stage plug flow reactor. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 4(1):183–200
Uemura T et al (2016) The catalytic mechanism of decarboxylative hydroxylation of salicylate hydroxylase revealed by crystal structure analysis at 2.5 Å resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469(2):158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.087
Ventosa A et al (2014) The Santa Pola saltern as a model for studying the microbiota of hypersaline environments. Extremophiles 18(5):811–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0681-6
Veselá AB et al (2012) Biotransformation of benzonitrile herbicides via the nitrile hydratase-amidase pathway in rhodococci. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39(12):1811–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1184-z
Wu ZM, Zheng RC, Zheng YG (2017) Identification and characterization of a novel amidase signature family amidase from Parvibaculum lavamentivorans ZJB14001. Protein Expr Purif 129:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2016.09.005
Yousefi Kebria D et al (2009) Isolation and characterization of a novel native Bacillus strain capable of degrading diesel fuel. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6(3):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03326082
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Syed, Z., Sogani, M. (2022). Emerging Technique of Enzymatic Biotransformation of Amides to Hydroxamic Acid for Pharmaceutical and Dye Waste Treatment. In: Arora, S., Kumar, A., Ogita, S., Yau, Y.Y. (eds) Innovations in Environmental Biotechnology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4445-0_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4445-0_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-4444-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-4445-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)