Abstract
Entamoeba histolytica is an intestinal protozoan parasite that causes amebic dysentery and liver abscess in millions of inhabitants of endemic areas. E. histolytica trophozoites are exposed to highly toxic reactive oxygen and nitrogen species during tissue invasion. The capacity of E. histolytica trophozoites to survive reactive oxygen and nitrogen species is integral to its pathogenic potential and disease outcome. E. histolytica lacks most of the components of canonical eukaryotic anti-oxidative defense systems including catalase, glutathione, and its metabolic enzymes, and L-cysteine is the major intracellular low molecular mass thiol. However, this parasite possesses a functional thioredoxin system composed of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase, which is critical for maintaining cellular redox balance and antioxidant function. Major enzymes involved in the redox balancing and the antioxidative pathways have been proven to be essential for the pathogen and, therefore, fulfill the prerequisite for a potential drug target. In this chapter, we summarized the currently available knowledge on the oxidative/nitrosative stress during E. histolytica infections, redox regulation and detoxification mechanisms for oxidative and nitrosative species in E. histolytica, and its potential use as a target for drug discovery against amebiasis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E, Petri W (2003) Amebiasis. N Engl J Med 348:1565–1573
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V et al (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 380:2095–2128
Ghasemi E, Rahdar M, Rostami M (2015) Prevalence of Entamoeba histolytica/dispar in drinking water in the city of shush, Khuzestan Province in 2011. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 4:582–588
Jeelani G, Sato D, Nozaki T (2015) Metabolomic analysis of Entamoeba biology. In: Nozaki T, Bhattacharya A (eds) Amebiasis: biology and pathogenesis of Entamoeba. Springer, Tokyo, pp 331–349
Ralston KS, Petri WA Jr (2011) Tissue destruction and invasion by Entamoeba histolytica. Trends Parasitol 27:254–263
Stanley SL Jr (2003) Amoebiasis Lancet 361:1025–1034
Nagaraja S, Ankri S (2018) Utilization of different omic approaches to unravel stress response mechanisms in the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:19
Pineda E, Perdomo D (2017) Entamoeba histolytica under oxidative stress: what countermeasure mechanisms are in place? Cell 6:44
Begum S, Quach J, Chadee K (2015) Immune evasion mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica: progression to disease. Front Microbiol 6:1394
Santi-Rocca J, Smith S, Weber C, Pineda E, Hon CC, Saavedra E, Olivos-Garcia A, Rousseau S, Dillies MA, Coppee JY, Guillen N (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-sensing mechanism is activated in Entamoeba histolytica upon treatment with nitric oxide. PLoS One 7:e31777
Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T (2016) Immune response of amebiasis and immune evasion by Entamoeba histolytica. Front Immunol 7:175
Rastew E, Vicente JB, Singh U (2012) Oxidative stress resistance genes contribute to the pathogenic potential of the anaerobic protozoan parasite, Entamoeba histolytica. Int J Parasitol 42:1007–1015
MacFarlane RC, Singh U (2006) Identification of differentially expressed genes in virulent and nonvirulent Entamoeba species: potential implications for amebic pathogenesis. Infect Immun 74:340–351
Ramos-Martinez E, Olivos-Garcia A, Saavedra E, Nequiz M, Sanchez EC, Tello E, El-Hafidi M, Saralegui A, Pineda E, Delgado J, Montfort I, Perez-Tamayo R (2009) Entamoeba histolytica: oxygen resistance and virulence. Int J Parasitol 39:693–702
Akbar MA, Chatterjee NS, Sen P, Debnath A, Pal A, Bera T, Das P (2004) Genes induced by a high-oxygen environment in Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 133:187–196
Vicente JB, Ehrenkaufer GM, Saraiva LM, Teixeira M, Singh U (2009) Entamoeba histolytica modulates a complex repertoire of novel genes in response to oxidative and nitrosative stresses: implications for amebic pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 11:51–69
Biller L, Schmidt H, Krause E, Gelhaus C, Matthiesen J, Handal G, Lotter H, Janssen O, Tannich E, Bruchhaus I (2009) Comparison of two genetically related Entamoeba histolytica cell lines derived from the same isolate with different pathogenic properties. Proteomics 9:4107–4120
Band RN, Cirrito H (1979) Growth response of axenic Entamoeba histolytica to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and oxygen. J Protozool 26:282–286
Avery SV (2011) Molecular targets of oxidative stress. Biochem J 434:201–210
Loftus B, Anderson I, Davies R, Alsmark UC, Samuelson J et al (2005) The genome of the protist parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nature 433:865–868
Makiuchi T, Mi-ichi F, Nozaki T (2015) Mitosomes in Entamoeba histolytica. In: Nozaki T, Bhattacharya A (eds) Amebiasis: biology and pathogenesis of Entamoeba. Springer, Tokyo, pp 305–327
Jeelani G, Nozaki T (2016) Entamoeba thiol-based redox metabolism: a potential target for drug development. Mol Biochem Parasitol 206:39–45
Fahey RC, Newton GL, Arrick B, Overdank-Bogart T, Aley SB (1984) Entamoeba histolytica: a eukaryote without glutathione metabolism. Science 224:70–72
Arias DG, Gutierrez CE, Iglesias AA, Guerrero SA (2007) Thioredoxin-linked metabolism in Entamoeba histolytica. Free Radic Biol Med 42:1496–1505
Arias DG, Regner EL, Iglesias AA, Guerrero SA (2012) Entamoeba histolytica thioredoxin reductase: molecular and functional characterization of its atypical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:1859–1866
Bruchhaus I, Richter S, Tannich E (1997) Removal of hydrogen peroxide by the 29 kDa protein of Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem J 326:785–789
Maralikova B, Ali V, Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T, van der Giezen M, Henze K, Tovar J (2010) Bacterial-type oxygen detoxification and iron–sulfur cluster assembly in amoebal relict mitochondria. Cell Microbiol 12:331–342
Vicente JB, Tran V, Pinto L, Teixeira M, Singh U (2012) A detoxifying oxygen reductase in the anaerobic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot Cell 11:1112–1118
Bruchhaus I, Richter S, Tannich E (1998) Recombinant expression and biochemical characterization of an NADPH:flavin oxidoreductase from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem J 330:1217–1221
Jeelani G, Husain A, Sato D, Ali V, Suematsu M, Soga T, Nozaki T (2010) Two atypical L-cysteine-regulated NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases involved in redox maintenance, L-cystine and iron reduction, and metronidazole activation in the enteric protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem 285:26889–26899
Andersson JO, Hirt RP, Foster PG, Roger AJ (2006) Evolution of four gene families with patchy phylogenetic distributions: influx of genes into protist genomes. BMC Evol Biol 6:27
Bruchhaus I, Brattig NW, Tannich E (1992) Recombinant expression, purification and biochemical characterization of a superoxide dismutase from Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Med Res 23:27–29
Husain A, Jeelani G, Sato D, Nozaki T (2011) Global analysis of gene expression in response to L-cysteine deprivation in the anaerobic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. BMC Genomics 12:275
Sim S, Yong TS, Park SJ, Im KI, Kong Y, Ryu JS, Min DY, Shin MH (2005) NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of ERK1/2 is required for apoptosis of human neutrophils induced by Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol 174:4279–4288
Reeves RE (1984) Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903. Adv Parasitol 23:105–142
Imlay JA (2006) Iron-Sulphur clusters and the problem with oxygen. Mol Microbiol 59:1073–1082
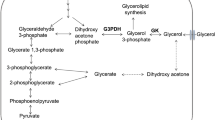
Husain A, Sato D, Jeelani G, Soga T, Nozaki T (2012) Dramatic increase in glycerol biosynthesis upon oxidative stress in the anaerobic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1831
Varet H, Shaulov Y, Sismeiro O, Trebicz-Geffen M, Legendre R, Coppée JY, Ankri S, Guillen N (2018) Enteric bacteria boost defences against oxidative stress in Entamoeba histolytica. Sci Rep 8:9042
Begum S, Quach J, Chadee K (2015) Immune evasion mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica: progression to disease. Front Microbiol 6:1394
Radi R (2013) Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J Biol Chem 288:26464–26472
Ramos E, Olivos-Garcia A, Nequiz M, Saavedra E, Tello E, Saralegui A, Montfort I, Perez Tamayo R (2007) Entamoeba histolytica: apoptosis induced in vitro by nitric oxide species. Exp Parasitol 116:257–265
Hertz R, Tovy A, Kirschenbaum M, Geffen M, Nozaki T, Adir N et al (2014) The Entamoeba histolytica Dnmt2 homolog (Ehmeth) confers resistance to nitrosative stress. Eukaryot Cell 13:494–503
Krauth-Siegel RL, Leroux AE (2012) Low molecular mass antioxidants in parasites. Antioxid Redox Signal 17:583–607
Pearson RJ, Morf L, Singh U (2013) Regulation of H2O2 stress-responsive genes through a novel transcription factor in the protozoan pathogen Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem 288:4462–4474
Lin JY, Chadee K (1992) Macrophage cytotoxicity against Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Immunol 148:3999–4005
Shahi P, Trebicz-Geffen M, Nagaraja S, Hertz R, Baumel-Alterzon S, Methling K, Lalk M, Mazumder M, Samudrala G, Ankri S (2017) Corrigendum: N-acetyl ornithine deacetylase is a moonlighting protein and is involved in the adaptation of Entamoeba histolytica to nitrosative stress. Sci Rep 7:45802
Hertz R, Ben Lulu S, Shahi P, Trebicz-Geffen M, Benhar M, Ankri S (2014) Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in the parasite Entamoeba histolytica by resin-assisted capture: insights into the regulation of the Gal/GalNAc lectin by nitric oxide. PLoS One 9:e91518
Trebicz-Geffen M, Shahi P, Nagaraja S, Vanunu S, Manor S, Avrahami A, Ankri S (2017) Identification of S-Nitrosylated (SNO) proteins in Entamoeba histolytica adapted to nitrosative stress: insights into the role of SNO actin and in vitro virulence. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:192
Jeelani G, Husain A, Sato D, Soga T, Suematsu M, Nozaki T (2013) Biochemical and functional characterization of novel NADH kinase in the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Biochimie 95:309–319
Lillig CH, Holmgren A (2007) Thioredoxin and related molecules from biology to health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:25–47
Mehlotra RK (1996) Antioxidant defense mechanisms in parasitic protozoa. Crit Rev Microbiol 22:295–314
Michelet L, Zaffagnini M, Lemaire SD (2009) Thioredoxins and related proteins. In: Stern DB (ed) The chlamydomonas sourcebook: organellar and metabolic processes, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Kidlington, pp 401–443
Holmgren A, Soderberg BO, Eklund H, Branden CI (1975) Three dimensional structure of Escherichia coli thioredoxin-S2 to 2.8 a resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:2305–2309
Duchene M (2015) Metronidazole and the redox biochemistry of Entamoeba histolytica. In: Nozaki T, Bhattacharya A (eds) Amebiasis: biology and pathogenesis of Entamoeba. Springer, Tokyo, pp 523–541
Arias DG, Carranza PG, Lujan HD, Iglesias AA, Guerrero SA (2008) Immunolocalization and enzymatic functional characterization of the thioredoxin system in Entamoeba histolytica. Free Radic Biol Med 45:32–39
Martínez LI, Piattoni CV, Garay SA, Rodrígues DE, Guerrero SA, Iglesias AA (2011) Redox regulation of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochimie 93:260–268
Cheng Z, Arscott LD, Ballou DP, Williams CH Jr (2007) The relationship of the redox potentials of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Drosophila melanogaster to the enzymatic mechanism: reduced thioredoxin is the reductant of glutathione in Drosophila. Biochemistry 46:7875–7885
Alkhalfioui F, Renard M, Montrichard F (2007) Unique properties of NADP-thioredoxin reductase C in legumes. J Exp Bot 58:969–978
Tachibana H, Cheng XJ (2000) Entamoeba dispar: cloning and characterization of peroxiredoxin genes. Exp Parasitol 94:51–55
Cheng XJ, Yoshihara E, Takeuchi T, Tachibana H (2004) Molecular characterization of peroxiredoxin from Entamoeba moshkovskii and a comparison with Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 138:195–203
Choi MH, Sajed D, Poole L, Hirata K, Herdman S, Torian BE, Reed SL (2005) An unusual surface peroxiredoxin protects invasive Entamoeba histolytica from oxidant attack. Mol Biochem Parasitol 143:80–89
deMare F, Kurtz DM, Nordlund P (1996) The structure of Desulfovibrio vulgaris rubrerythrin reveals a unique combination of rubredoxin-like FeS4 and ferritin-like diiron domains. Nat Struct Biol 3:539–546
Maralikova B, Ali V, Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T, van der Giezen M, Henze K, Tovar J (2010) Bacterial-type oxygen detoxification and iron-sulfur cluster assembly in amoebal relict mitochondria. Cell Microbiol 12:331–342
Mi-ichi F, Abu Yousuf M, Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T (2009) Mitosomes in Entamoeba histolytica contain a sulfate activation pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:21731–21736
Cabeza MS, Guerrero SA, Iglesias AA, Arias DG (2015) New enzymatic pathways for the reduction of reactive oxygen species in Entamoeba histolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:1233–1244
Saraiva LM, Vicente JB, Teixeira M (2004) The role of the flavodiiron proteins in microbial nitric oxide detoxification. Adv Microb Physiol 49:77–129
Gonçalves VL, Vicente JB, Pinto L, Romão CV, Frazão C, Sarti P, Giuffrè A, Teixeira M (2014) Flavodiiron oxygen reductase from Entamoeba histolytica: modulation of substrate preference by tyrosine 271 and lysine 53. J Biol Chem 289:28260–28270
Vicente JB, Tran V, Pinto L, Teixeira M, Singh U (2012) A detoxifying oxygen reductase in the anaerobic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot Cell 11:1112–1118
Kurutas EB (2016) The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state. Nutr J 15:71
Gillin FD, Diamond LS (1981) Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia: growth responses to reducing agents. Exp Parasitol 51:382–391
Nozaki T, Ali V, Tokoro M (2005) Sulfur-containing amino acid metabolism in parasitic protozoa. Adv Parasitol 60:1–99
Jeelani G, Nozaki T (2014) Metabolomic analysis of Entamoeba: applications and implications. Curr Opin Microbiol 20:118–124
Byrne CR, Monroe RS, Ward KA, Kredich NM (1988) DNA sequences of the cysK regions of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli and linkage of the cysK regions to ptsH. J Bacteriol 170:3150–3157
Saito K, Miura N, Yamazaki M, Hirano H, Murakoshi I (1992) Molecular cloning and bacterial expression of cDNA encoding a plant cysteine synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:8078–8082
Jeelani G, Sato D, Soga T, Nozaki T (2017) Genetic, metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of the de novo L-cysteine biosynthetic pathway in the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Sci Rep 7:15649
Hussain S, Ali V, Jeelani G, Nozaki T (2009) Isoform-dependent feedback regulation of serine O-acetyltransferase isoenzymes involved in L- cysteine biosynthesis of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 163:39–47
Husain A, Sato D, Jeelani G, Mi-ichi F, Ali V, Suematsu M, Soga T, Nozaki T (2010) Metabolome analysis revealed increase in S-methylcysteine and phosphatidylisopropanolamine synthesis upon L-cysteine deprivation in the anaerobic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem 285:39160–39170
Rebeille F, Jabrin S, Bligny R, Loizeau K, Gambonnet B, Van Wilder V, Douce R, Ravanel S (2006) Methionine catabolism in Arabidopsis cells is initiated by a gamma-cleavage process and leads to S-methylcysteine and isoleucine syntheses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15687–15692
Mae T, Ohira K, Fujiwara A (1971) Metabolism of S-methylcysteine and its sulfoxide in chinese cabbage, Brassica pekinensis Rupr. Plant Cell Physiol 12:881–887
Park S, Imlay JA (2003) High levels of intracellular cysteine promote oxidative DNA damage by driving the Fenton reaction. J Bacteriol 185:942–950
Jeelani G, Sato D, Soga T, Watanabe H, Nozaki T (2014) Mass spectrometric analysis of L-cysteine metabolism: physiological role and fate of L-cysteine in the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. MBio 5:e01995–e01914
Elthon TE, Stewart CR (1984) Effects of the proline analogue L-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid on proline metabolism. Plant Physiol 74:213–218
Weber HU, Fleming JF, Miquel J (1982) Thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, a physiologic sulfhydryl antioxidant with potential value in geriatric medicine. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 1:299–310
Freeman CD, Klutman NE, Lamp KC (1997) Metronidazole. A therapeutic review and update. Drugs 54:679–708
Cudmore SL, Delgaty KL, Hayward-McClelland SF, Petrin DP, Garber GE (2004) Treatment of infections caused by metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:783–793
Wassmann C, Hellberg A, Tannich E, Bruchhaus I (1999) Metronidazole resistance in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica is associated with increased expression of iron-containing superoxide dismutase and peroxiredoxin and decreased expression of ferredoxin 1 and flavin reductase. J Biol Chem 274:26051–26056
Penuliar GM, Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T (2015) Phenotypic and transcriptional profiling in Entamoeba histolytica reveal costs to fitness and adaptive responses associated with metronidazole resistance. Front Microbiol 6:354
Leitsch D, Kolarich D, Wilson IB, Altmann F, Duchêne M (2007) Nitroimidazole action in Entamoeba histolytica: a central role for thioredoxin reductase. PLoS Biol 5:e211
Muller S, Liebau E, Walter RD, Krauth-Siegel RL (2003) Thiol-based redox metabolism of protozoan parasites. Trends Parasitol 19:320–328
Debnath A, Parsonage D, Andrade RM, He C, Cobo ER, Hirata K, Chen S, García-Rivera G, Orozco E, Martínez MB, Gunatilleke SS, Barrios AM, Arkin MR, Poole LB, McKerrow JH, Reed SL (2012) A high through put drug screen for Entamoeba histolytica identifies a new lead and target. Nat Med 18:956–960
Capparelli EV, Bricker-Ford R, Rogers MJ, McKerrowJH RSL (2016) Phase I clinical trail results of auranofin, a novel antiparasitic agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(1):e01947
Spyrakis F, Singh R, Cozzini P, Campanini B, Salsi E, Felici P, Raboni S, Benedetti P, Cruciani G, Kellogg GE, Cook PF, Mozzarelli A (2013) Isozyme-specific ligands for O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase, a novel antibiotic target. PLoS One 8:e77558
Williams RA, Westrop GD, Coombs GH (2009) Two pathways for cysteine biosynthesis in Leishmania major. Biochem J 420:451–462
Nozaki T, Asai T, Sanchez LB, Kobayashi S, Nakazawa M, Takeuchi T (1999) Characterization of the gene encoding serine acetyltransferase, a regulated enzyme of cysteine biosynthesis from the protist parasites Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar. Regulation and possible function of the cysteine biosynthetic pathway in Entamoeba. J Biol Chem 274:32445–32452
Kumar S, Raj I, Nagpal I, Subbarao N, Gourinath S (2011) Structural and biochemical studies of serine acetyltransferase reveal why the parasite Entamoeba histolytica cannot form a cysteine synthase complex. J Biol Chem 286:12533–12541
Chinthalapudi K, Kumar M, Kumar S, Jain S, Alam N, Gourinath S (2008) Crystal structure of native O-acetyl-serine sulfhydrylase from Entamoeba histolytica and its complex with cysteine: structural evidence for cysteine binding and lack of interactions with serine acetyl transferase. Proteins 72:1222–1232
Agarwal SM, Jain R, Bhattacharya A, Azam A (2008) Inhibitors of Escherichia coli serine acetyltransferase block proliferation of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Int J Parasitol 38:137–141
Nagpal I, Raj I, Subbarao N, Gourinath S (2012) Virtual screening, identification and in vitro testing of novel inhibitors of O-acetyl-L-serine sulfhydrylase of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS One 7:e30305
Mori M, Jeelani G, Masuda Y, Sakai K, Tsukui K, Waluyo D, Tarwadi WY, Nonaka K, Matsumoto A, Ōmura S, Nozaki T, Shiomi K (2015) Identification of natural inhibitors of Entamoeba histolytica cysteine synthase from microbial secondary metabolites. Front Microbiol 6:962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jeelani, G., Nozaki, T. (2019). Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Mechanism in the Human Enteric Protozoan Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. In: Chakraborti, S., Chakraborti, T., Chattopadhyay, D., Shaha, C. (eds) Oxidative Stress in Microbial Diseases. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8763-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8763-0_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8762-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8763-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)