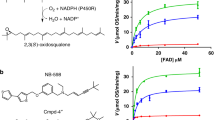
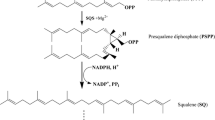
Abstract
Squalene (SQ) is an unsaturated triterpene which is formed by six linked isoprenes, it is a key intermediate product in the metabolic pathway of cholesterol synthesis. The synthetic process of cholesterol is a key step in the biosynthesis of steroids, at the same time this step is a bifurcate point from the isoprenoid central metabolic pathway into the triterpenoid branch biosynthesis. The squalene synthase (SQS) is a key enzyme in isoprenoid synthesis. Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) are catalyzed into a 30-carbon linear squalene molecule. This paper systematically reviews the metabolic mechanism, research achievements of SQS, and broad applications in biosynthetic pathways and human health.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silva AAS, Morais SM, Falcão MJC et al (2014) Activity of cycloartane-type triterpenes and sterols isolated from Musa paradisiaca fruit peel against Leishmania infantum chagasi. Phytomedicine 21(11):1419–1423
Lukić M, Lukić I, Krapac M et al (2013) Sterols and triterpene diols in olive oil as indicators of variety and degree of ripening. Food Chem 136(1):251–258
Batista I, Nunes ML (1992) Characterisation of shark liver oils. Fish Res 14(4):329–334
Hye JC, Taylor W, Timothy P et al (2013) Vibrational spectra and DFT calculations of squalene. J Mol Struct 1032:203–206
Harivardhan LR, Squalene CP (2009) A natural triterpene for use in disease management and therapy. J Adv Drug Delivery Rev 61(15):1412–1426
Kin S, Karadeniz F (2012) Biological importance and application of squalene and squalane. Adv Food Nutr Res 65:223–233
Pragst F, Auwärter V, Kiessling B et al (2004) Wipe-test and patch-test for alcohol misuse based on the concentration ratio of fatty acid ethyl esters and squalene C FAEE/C SQ in skin surface lipids. Forensic Sci Int 143(2):77–86
Rissmann R, Oudshoorn MH, Kocks E et al (2008) Lanolin-derived lipid mixtures mimic closely the lipid composition and organization of vernix caseosa lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Biomembr 1778(10):2350–2360
Preez HD (2008) Squalene-antioxidant of the future. Nat Med 33:106–112
Kelly GS (1999) Squalene and its potential clinical uses. Altern Med Rev 4(1):30–36
Newmark HL (1997) Squalene, olive oil and cancer risk review and hypothesis. Cancer Epidemol 889(1):193–203
Chinthalapally VR, Newmark HL, Bandaru SR (1998) Chemopreventive effect of squalene on colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 19(2):287–290
Desai KN, Wei H, Lamartiniere CA (1996) The preventive and therapeutic of the squalene-containing compound, Roidex on tumor promotion and regression. Cancer Lett 101(1):93–96
Nowicki R, Baraska-Rybak W (2007) Shark liver oil as a supporting therapy in atopic dermatitis. Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski 22(130):312–313
Lewkowicz N, Lewkowicz P, Kurnatowska A et al (2006) Biological action and clinical application of shark liver oil. Polski merkuriusz lekarski: organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego 20(119):598–601
Jennings SM, Tsay YH, Fisch TM et al (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of the yeast gene for squalene synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(16):6038–6042
Tansey TR, Shechter I (2000) Structure and regulation of mammalian squalene synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1529(23):49–62
Liu CI, Jeng WY, Chang WJ et al (2014) Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of human squalene synthase. Acta Crystallogr A 70(2):231–241
Gu P, Ishii Y, Spencer TA et al (1998) Function-structure studies and identification of three enzyme domains involved in the catalytic activity in rat hepatic squalene synthase. J Biol Chem 273(16):12515–12525
Kourounakis AP, Katselou MG, Matralis AN et al (2011) Squalene synthase inhibitors: an update on the search for new antihyperlipidemic and antiatherosclerotic agents. Curt Med Chem 18(2):4418–4439
Paradise EM, Kirby J, Chan R et al (2008) Redirection of flux through the FPP branch-point in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by down-regulating squalene synthase. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(5):371–378
Okazaki H, Tazoe F, Okazaki S et al (2006) Increased cholesterol biosynthesis and hypercholesterolemia in mice overexpressing squalene synthase in the liver. J Lipid Res 47(3):1950–1958
Jarstfer MB, Zhang DL, Poulter CD (2002) Recombinant squalene synthase. Synthesis of non-head-to-tail isoprenoids in the absence of NADPH. J Am Chem Soc 124(11):8834–8845
Lee MH, Jeong JH, Seo JW et al (2004) Enhanced triterpene and phytosterol biosynthesis in Panax ginseng overexpressing squalene synthase gene. Plant Cell Physiol 45(3):976–984
Seo JW, Jeong JH, Shin CG et al (2005) Overexpression of squalene synthase in Eleutherococcus senticosus increases phytosterol and triterpene accumulation. Phytochemistry 66(5):869–877
Kim YS, Cho JH, Park S et al (2011) Gene regulation patterns in tfiterpene biosynthetic pathway driven by overexpression of squalene synthase and methyl jasmonate elicitation in Bupleurum falcatum. Planta 233(13):343–355
Yang Y, Laval S, Yu B (2014) Chemical synthesis of saponins, Chap 2. Adv Carbohydrate Chem Biochem 71:137–226
Zhao R-Y, **ao W, Cheng H-L et al (2010) Cloning and characterization of squalene synthase gene from Fusarium fujikuroi (Saw.) Wr. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37(2):171–1182
Kim YJ, Zhang D, Yang DC (2015) Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of ginsenosides. Biotechnol Adv 33(6):717–735
Nakashima T, Inoue T, Oka A et al (1995) Cloning, expression, and characterization of cDNAs encoding Arabidopsis thaliana squalene synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(7):2328–2332
Blagg BS, Jarstfer MB, Rogers DH, Poulter CD (2002) Recombinant squalene synthase. A mechanism for the rearrangement of presqualene diphosphate to squalene. J Am Chem Soc 124(30):8846–8853
Davidson MH (2007) Squalene synthase inhibition: a novel target for the management of dyslipidemia. Curt Atheroscler Rep 9(2):78–80
Mookhtiar KA, Kalinowski SS, Zhang D et al (1994) Yeast squalene synthase. A mechanism for addition of substrates and activation by NADPH. J Biol Chem 269(21):1201–1207
Lin FY, Liu CL, Liu YL et al (2010) Mechanism of action and inhibition of dehydrosqualene synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(11):21337–21342
Pandit J, Danley DE, Schulte GK et al (2000) Crystal structure of human squalene synthase. A key enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 275(8):30610–30617
Huang D, Yao Y, Zhang H et al (2015) Directed optimization of a newly identified squalene synthase from Mortierella alpine based on sequence truncation and site directed mutagenesis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:1341–1352
Pandit J, Danley DE, Schulte GK et al (2000) Crystal structure of human squalene synthase. A key enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 275:30610–30617
Lee Sungwon, Dale Poulter C (2008) Cloning, solubilization, and characterization of squalene synthase from Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1. J Bacteriol 190(11):3808–3816
Furubayashi M, Li L, Katabami A et al (2014) Construction of carotenoid biosynthetic pathways using squalene synthase. FEBS Lett 588:436–442
Tozawa R, Ishibashi S, Osuga J et al (1999) Embryonic lethality and defective neural tube closure in mice lacking squalene synthase. J Biol Chem 274:30843–30848
Karst F, Lacroute F (1977) Ergosterol biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants deficient in early steps of pathway. Mol Gen Genet 154:269–277
Grover A, Samuel G, Bisaria VS et al (2013) Enhanced withanolide production by overexpression of squalene synthase in Withania somnifera. J Biosci Bioeng 115(6):680–685
Paddon CJ, Westfall PJ, Pitera DJ, Benjamin K et al (2013) High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin. Nature 496:528–532
Rasool A, Zhang G, Li Z et al (2016) Engineering of the terpenoid pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-overproduces squalene and the non-terpenoid compound oleic acid. Chem Eng Sci 152:457–456
Rasool A, Ahmed MS, Li C (2016) Overproduction of squalene synergistically downregulates ethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem Eng Sci 152:370–380
Kim SK, Karadeniz F (2012) Biological importance and applications of squalene and squalane. Adv Food Nutr 65:223–233
Do R, Kiss RS, Gaudet D et al (2009) Squalene synthase: a critical enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Clin Genet 75(5):19–29
Gora1 WM, Wysocka-Kapcinska M et al (2016) Genetic engineering and molecular characterization of yeast strain expressing hybrid human-yeast squalene synthase as a tool for anti-cholesterol drug assessment. J Appl Microbiol 120:877–888
Armitage J (2007) The safety of statins in clinical practice. Lancet 370:1781–1790
Liao JK (2011) Squalene synthase inhibitor lapaquistat acetate: could anything be better than statins. Circulation 123:1925–1928
Shechter I, Klinger E, Rucker ML et al (1992) Solubilization, purification, and characterization of a truncated form of rat hepatic squalene synthetase. J Biol Chem 267(21):8628–8635
Stamellos KD, Shackelford JE, Shechter I et al (1993) Subcellular localization of squalene synthase in rat hepatic cells. Biochemical and immunochemical evidence. J Biol Chem 268(11):12825–12836
Jiang G, McKenzie TL, Conrad DG et al (1993) Transcriptional regulation by lovastatin and 25-hydroxycholesterol in HepG2 cells and molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the human hepatic squalene synthase. J Biol Chem 268(13):12818–12824
Summers C, Kant F, Charles AD (1993) Cloning, expression and characterisation of the cDNA encoding human hepatic squalene synthase, and its relationship to phytoene synthase. Gene 136(9):185–192
Soltis DA, McMahon G, Caplan SL et al (1995) Expression, purification, and characterization of the human squalene synthase: use of yeast and baculoviral systems. Arch Biochem Biophys 316(26):713–723
Uchida H, Yamashita H, Kajikawa M et al (2009) Cloning and characterization of a squalene synthase gene from a petroleum plant. Euphorbia tirucalli L. Planta 229(19):1243–1252
Huang Z, Jiang K, Pi Y et al (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of the yew gene encoding squalene synthase from Taxus cuspidate. J Biochem Mol Biol 40(2): 625–635
Zhao MW, Liang WQ, Zhang DB et al (2007) Cloning and characterization of squalene synthase (SQS) gene from Ganoderma lucidum. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17(2):1106–1112
Lograsso PV, Soltis DA, Boettcher BR (1993) Overexpression, purification, and kinetic characterization of a carboxyl-terminal-truncated yeast squalene synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys 307(12):193–199
Lee S, Pouiter CD (2008) Cloning, solubilization, and characterization of squalene synthase from Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1. J Bacteriol 190(15):3808–3816
Sealey-Cardona M, Cammerer S, Jones S et al (2007) Kinetic characterization of squalene synthase from Trypanosoma cruzi: selective Inhibition by quinuclidine derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(3):2123–2129
Shang N, Li Q, Ko T-P et al (2014) Squalene synthase as a target for Chagas disease therapeutics. PLoS Pathogen 10(5):1178–1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, D. et al. (2018). Research Progress of Squalene Synthase on Function and Application. In: Liu, H., Song, C., Ram, A. (eds) Advances in Applied Biotechnology. ICAB 2016. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 444. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4801-2_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4801-2_78
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-4800-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-4801-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)