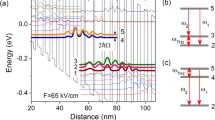
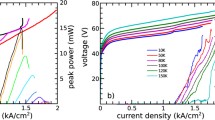
Abstract
We report the development of terahertz frequency quantum cascade lasers for applications as local oscillators. A range of active region designs and waveguide structures have been characterised in order to develop the devices for operation at high temperatures, with high output power and low dissipated power. Quantum cascade lasers based on a LO-phonon bound-to-continuum design emitting at 3.5 THz, suitable for the detection of hydroxyl, were fabricated with a double-metal (gold-gold) waveguide structure. These devices operated in continuous-wave up to 94 K, with an output power of 0.4 mW and dissipated power of 1.7 W at 10 K. A new, mechanically robust packaging and waveguide-integration scheme is also presented for operation outside laboratory environments, which further allows integration of quantum cascade lasers with terahertz waveguides, mixers and other system components. This integration scheme yielded a better beam quality, with a divergence of <20°, compared to standard double-metal devices. Its impacts on the device performance, such as operating temperature range, spectral emission, output power and electrical properties, are presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Dean, A. Valavanis, J. Keeley, K. Bertling, Y. L. Lim, R. Alhathlool, A. D. Burnett, L. H. Li, S. P. Khanna, D. Ind**, T. Taimre, A. D. Rakić, E. H. Linfield, A. G. Davies, Terahertz imaging using quantum cascade lasers – review of systems and applications, J. Phys. D 47, 374008 (2014)
J. Faist, F. Capasso, D. L. Sivco, C. Sirtor, A. L. Hutchinson, A. Y. Cho, Quantum Cascade Laser, Science 264, 553–556 (1994)
R. Köhler, A. Tredicucci, F. Beltram, H. E. Beere, E. H. Linfield, A. G. Davies, D. A. Ritchie, R. C. Iotti, F. Rossi, Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure laser, Nature 417, 156–159 (2002)
L. Li, L. Chen, J. Zhu, J. Freeman, P. Dean, A. Valavanis, A. G. Davies E.H. Linfield, Terahertz quantum cascade lasers with >1 W output powers, Electron Lett. 50, 309–311 (2014)
C. Walther, M. Fischer, G. Scalari, R. Terazzi, N. Hoyler, J. Faist, Quantum cascade lasers operating from 1.2 to 1.6 THz, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 131122 (2007)
C. W. Chan, Q. Hu, J. L. Reno, Ground state terahertz quantum cascade lasers, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 151108 (2012)
J. R. Gao, J. N. Hovenier, Z. Q. Yang, J. J. A. Baselmans, A. Baryshev, M. Hajenius, T. M. Klapwijk, A. J. L. Adam, T. O. Klaassen, B. S. Williams, S. Kumar, Q. Hu, J. L. Reno, Terahertz heterodyne receiver based on a quantum cascade laser and a superconducting bolometer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 244104 (2005)
H. W. Hubers, S. G. Pavlov, A. D. Semenov, R. Köhler, L. Mahler, A. Tredicucci, H. E. Beere D. A. Ritchie, E. H. Linfield, Terahertz quantum cascade laser as local oscillator in a heterodyne receiver, Opt Express 13, 5890–5896 (2005)
R. G. Prinn, J. Huang, R. F. Weiss, D. M. Cunnold, P.J. Fraser, P.G. Simmonds, A. McCulloch, C. Harth, P. Salameh, S. O’Doherty, R.H.J. Wang, L. Porter, B. R. Miller, Evidence for substantial variations of atmospheric hydroxyl radicals in the past two decades, Science 292, 1882–1888, (2001)
R. T. Boreiko1, A. L. Betz1, Heterodyne Spectroscopy of the 63 μm O I Line in M42, The Astrophysical J. Lett. 464, L83 (1996)
A. Valavanis, Y. J. Han, N. Brewster, P. Dean, R. Dong, L. Bushnell, M. Oldfield, J. X. Zhu, L. H. Li, A. G. Davies, B. Ellison, E. H. Linfield, Mechanically robust waveguide-integration and beam sha** of terahertz quantum cascade lasers, Electron. Lett. 51, 919–920 (2015)
B. S. Williams, S. Kumar, H. Callebaut, Qing Hu, J. L. Reno, Terahertz quantum-cascade laser at lambda approximate to 100 mu m using metal waveguide for mode confinement, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2124–2126 (2003)
G. Scalari, L. Ajili, J. Faist, H. Beere, E. H. Linfield, David Ritchie, A. G. Davies, Far-infrared (lambda similar or equal to 87 μm) bound-to-continuum quantum-cascade lasers operating up to 90 K, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3165–3167 (2003)
M. Wienold, L. Schrottke, M. Giehler, R. Hey, W. Anders, H. T. Grahn, Low-voltage terahertz quantum-cascade lasers based on LO-phonon-assisted interminiband transitions, Electron. Lett. 45, 1030–1040 (2009)
S. Fathololoumi, E. Dupont, C. W. Chan, Z. R. Wasilewski, S. R. Laframboise, D. Ban, A. Mátyás, C. Jirauschek, Q. Hu, and H. C. Liu, Terahertz quantum cascade lasers operating up to ~ 200 K with optimized oscillator strength and improved injection tunneling, Opt. Express 20, 3866–3876 (2012)
M. I. Amanti, M. Fischer, G. Scalari, M. Beck, J. Faist, Low-divergence single-mode terahertz quantum cascade laser, Nature Photonics 3, 586–590 (2009)
N. F. Yu, J. Fan, and Q. J. Wang, C. Pflügl, L. Diehl, T. Edamura, M. Yamanishi, H. Kan, F. Capasso, Small-divergence semiconductor lasers by plasmonic collimation, Nature Photonics 2, 564–570 (2008)
M. I. Amanti, M. Fischer, C. Walther, G. Scalari, M. Beck, J. Faist, Horn antennas for terahertz quantum cascade lasers, Electron Lett 43, 573–574 (2007)
A. W. M. Lee, Q. Qin, S. Kumar, B. S. Williams, Q. Hu, J. L. Reno, High-power and high-temperature THz quantum-cascade lasers based on lens-coupled metal-metal waveguides, Opt. Lett. 32, 2840–2842 (2007)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the EPSRC (UK) ‘COTS’ programme, the ERC grant ‘NOTES’ and ‘TOSCA’, NERC (UK), the European Space Agency, and the CEOI-ST. AGD and EHL also acknowledge support from the Royal Society and the Wolfson Foundation. PD acknowledges support from EPSRC (UK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Han, Y.J. et al. (2017). Development of Terahertz Frequency Quantum Cascade Lasers for the Applications as Local Oscillators. In: Pereira, M., Shulika, O. (eds) THz for CBRN and Explosives Detection and Diagnosis. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1093-8_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1093-8_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-024-1092-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-024-1093-8
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)