Abstract
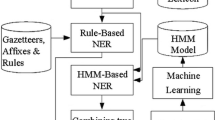
In the exploration of Chinese named entity recognition for a specific domain, the authors found that the errors caused during word segmentation and part-of-speech (POS) tagging have obstructed the improvement of the recognition performance. In order to further enhance recognition recall and precision, the authors propose an error correction approach for Chinese named entity recognition. In the error correction component, transformation-based machine learning is adopted because it is suitable to fix Chinese word segmentation and POS tagging errors and produce effective correcting rules automatically. The Chinese named entity recognition component utilizes Finite-State Cascades which are automatically constructed by POS rules with semantic constraints. A prototype system, CNERS (Chinese Named Entity Recognition System), has been implemented. The experimental result shows that the recognition performance of most named entities have significantly been improved. On the other hand, the system is also fast and reliable.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abney S. Partial Parsing via Finite-State Cascades. In Proceedings of the ESSLLI’ 96 Robust Parsing Workshop. Prague, Czech Republic, 1996.
Brill E. Transformation-Based Error-Driven Learning and Natural Language Processing: A Case Study in Part of Speech Tagging. Computational Linguistics. Vol. 21, No. 4, 1995.
Chen H.H. et al. Description of the NTU System Used for MET2. Proceedings of 7th Message Understanding Conference, Fairfax, VA, U.S.A., 1998.
Dong Z.D. and Dong Q. HowNet. http://www.keenage.com/zhiwang/e_zhiwang.html, 2000.
Hockenmaier J. and Brew C. Error-Driven Learning of Chinese Word Segmentation. Communications of COLIPS 8(1), 1998.
Kameyama M. Information Extraction across Linguistic Barriers. In AAAI Spring Symposium on Cross-Language Text and Speech Processing, 1997.
Lin X.G. et al. Dictionary of Verbs in Contemporary Chinese. Bei**g Language and Culture University Press. Bei**g China, (In Chinese), 1994.
Liu K.Y. Automatic Segmentation and Tagging for Chinese Text. The Commercial Press. Bei**g, China. (In Chinese), 2000.
Palmer D. and Burger J. Chinese Word Segmentation and Information Retrieval. In AAAI Spring Symposium on Cross-Language Text and Speech Retrieval, Electronic Working Notes, 1997.
Wilks Y. Information Extraction as a Core Language Technology. In Maria Teresa Pazienza editor, Information Extraction: A Multidisciplinary Approach to an Emerging Information Technology, LNAI 1299, pages 1–9. Springer, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yao, T., Ding, W., Erbach, G. (2002). Correcting Word Segmentation and Part-of-Speech Tagging Errors for Chinese Named Entity Recognition. In: Hommel, G., Huanye, S. (eds) The Internet Challenge: Technology and Applications. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0494-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0494-7_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-3942-0
Online ISBN: 978-94-010-0494-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive