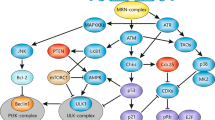
Abstract
Eukaryotic cells continuously encounter DNA damage caused by uncontrolled DNA replication and several sources of genotoxic stresses such as ultraviolet or ionizing irradiation. The cells have acquired the surveillance system, known as the DNA damage responses, to maintain genomic integrity. The DNA damage responses play an important role in sensing DNA damage, transmitting the signals to downstream targets, and coordinating various cellular responses such as cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and cellular senescence. Apoptosis is a highly regulated cell death process that controls cellular homeostasis and prevents survival of injured, damaged, or transformed cells. On the other hand, cellular senescence is not only a potent tumor-suppressive mechanism leading to permanent cell-cycle arrest but also is proposed to drive organismal aging. Recent advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate apoptosis and cellular senescence identified various key regulators. In this chapter, we will review the signaling networks underlying the induction of apoptosis and cellular senescence and their implications for cancer development and therapy. We will also discuss cellular senescence’s impact beyond the tumor-suppressive function, animal aging, and tissue homeostasis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JC, O’Loghlen A, Banito A, Raguz S, Gil J (2008) Control of senescence by CXCR2 and its ligands. Cell Cycle 7(19):2956–2959
Adams PD (2009) Healing and hurting: molecular mechanisms, functions, and pathologies of cellular senescence. Mol Cell 36(1):2–14
Ancrile B, Lim KH, Counter CM (2007) Oncogenic Ras-induced secretion of IL6 is required for tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 21(14):1714–1719
Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Childs BG, van de Sluis B, Kirkland JL, van Deursen JM (2011) Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 479(7372):232–236
Balducci L, Ershler WB (2005) Cancer and ageing: a nexus at several levels. Nat Rev Cancer 5(8):655–662
Bandyopadhyay S, Zhan R, Chaudhuri A et al (2006) Interaction of KAI1 on tumor cells with DARC on vascular endothelium leads to metastasis suppression. Nat Med 12(8):933–938
Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M et al (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444(7119):633–637
Baus F, Gire V, Fisher D, Piette J, Dulić V (2003) Permanent cell cycle exit in G2 phase after DNA damage in normal human fibroblasts. EMBO J 22(15):3992–4002
Biton S, Ashkenazi A (2011) NEMO and RIP1 control cell fate in response to extensive DNA damage via TNF-α feedforward signaling. Cell 145(1):92–103
Brown JM, Attardi LD (2005) The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer 5(3):231–237
Burkhart DL, Sage J (2008) Cellular mechanisms of tumour suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat Rev Cancer 8(9):671–682
Burstein E, Duckett CS (2003) Dying for NF-kappaB? Control of cell death by transcriptional regulation of the apoptotic machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15(6):732–737
Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Shilov A, Hultcrantz M, Pugacheva E, Chumakov P, Bergman J, Wiman KG, Selivanova G (2002) Restoration of the tumor suppressor function to mutant p53 by a low-molecular-weight compound. Nat Med 8(3):282–288
Campisi J, d’Adda di Fagagna F (2007) Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(9):729–740
Chehab NH, Malikzay A, Appel M, Halazonetis TD (2000) Chk2/hCds1 functions as a DNA damage checkpoint in G(1) by stabilizing p53. Genes Dev 14(3):278–288
Clarke AR, Purdie CA, Harrison DJ et al (1993) Thymocyte apoptosis induced p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362(6423):849–852
Cobrinik D (2005) Pocket proteins and cell cycle control. Oncogene 24(17):2796–2809
Collado M, Serrano M (2010) Senescence in tumours: evidence from mice and humans. Nat Rev Cancer 10(1):51–57
Coppé JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, Sun Y, Muñoz DP, Goldstein J, Nelson PS, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2008) Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PloS Biol 6(12):2853–2868
Coppé JP, Rodier F, Patil CK, Freund A, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2011) Tumor suppressor and aging biomarker p16(INK4a) induces cellular senescence without the associated inflammatory secretory phenotype. J Biol Chem 286(42):36396–36403
Cotter TG (2009) Apoptosis and cancer: the genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer 9(7):501–507
Courtois-Cox S, Jones SL, Cichowski K (2008) Many roads lead to oncogene-induced senescence. Oncogene 27(20):2801–2809
d’Adda di Fagagna F, Reaper PM, Clay-Farrace L, Fiegler H, Carr P, Von Zglinicki T, Saretzki G, Carter NP, Jackson SP (2003) A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence. Nature 426(6963):194–198
Davoli T, de Lange T (2012) Telomere-driven tetraploidization occurs in human cells undergoing crisis and promotes transformation of mouse cells. Cancer Cell 21(6):765–776
Davoli T, Denchi EL, de Lange T (2010) Persistent telomere damage induces bypass of mitosis and tetraploidy. Cell 141(1):81–93
Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A et al (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature 444(7119):638–642
D’Orazi G, Cecchinelli B, Bruno T et al (2002) Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 phosphorylates p53 at Ser 46 and mediates apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4(1):11–19
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516
Feng L, Hollstein M, XuY (2006) Ser46 phosphorylation regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and replicative senescence. Cell Cycle 5(23):2812–2819
Flores ER, Tsai KY, Crowley D, Sengupta S, Yang A, McKeon F, Jacks T (2002) p63 and p73 are required for p53-dependent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Nature 416(6880):560–564
Foster BA, Coffey HA, Morin MJ, Rastinejad F (1999) Pharmacological rescue of mutant p53 conformation and function. Science 286(5449):2507–2510
Freund A, Patil CK, Campisi J (2011) p38MAPK is a novel DNA damage response-independent regulator of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. EMBO J 30(8):1536–1548
Fumagalli M, Rossiello F, Clerici M (2012) Telomeric DNA damage is irreparable and causes persistent DNA-damage-response activation. Nat Cell Biol 14(4):355–365
Gosselin K, Martien S, Pourtier A (2009) Senescence-associated oxidative DNA damage promotes the generation of neoplastic cells. Cancer Res 69(20):7917–7925
Guney I, Sedivy JM (2006) Cellular senescence, epigenetic switches and c-Myc. Cell Cycle 5(20):2319–2323
Halazonetis TD, Gorgoulis VG, Bartek J (2008) An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development. Science 319(5868):1352–1355
Hayflick L, Moorhead PS (1961) The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 25:585–621
He L, He X, Lim LP (2007) A microRNA component of the p53 tumor suppressor network. Nature 447(7148):1130–1134
Hock AK, Vousden KH (2012) Tumor suppression by p53: fall of the triumvirate? Cell 149(6):1183–1185
Hofmann TG, Möller A, Sirma H, Zentgraf H, Taya Y, Dröge W, Will H, Schmitz ML (2002) Regulation of p53 activity by its interaction with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2. Nat Cell Biol 4(1):1–10
Horn HF, Vousden KH (2007) Co** with stress: multiple ways to activate p53. Oncogene 26(9):1306–1316
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300
** Z, El-Deiry WS (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 4(2):139–163
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3(3):221–227
Kosar M, Bartkova J, Hubackova S, Hodny Z, Lukas J, Bartek J (2011) Senescence-associated heterochromatin foci are dispensable for cellular senescence, occur in a cell type- and insult-dependent manner and follow expression of p16(ink4a). Cell Cycle 10(3):457–468
Krammer PH, Galle PR, Möller P, Debatin KM (1998) CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis in normal and malignant liver, colon, and hematopoietic cells. Adv Cancer Res 75:251–273
Krtolica A, Parrinello S, Lockett S, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2001) Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial cell growth and tumorigenesis: a link between cancer and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(21):12072–12077
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH (1997) Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature 387(6630):299–303
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Douma S, van Doorn R, Desmet CJ, Aarden LA, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS (2008) Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell 133(6):1019–1031
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS (2010) The essence of senescence. Genes Dev 24(22):2463–2479
Lahav G, Rosenfeld N, Sigal A, Geva-Zatorsky N, Levine AJ, Elowitz MB, Alon U (2004) Dynamics of the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop in individual cells. Nat Genet 36(2):147–150
Lapenko O, Prives C (2006) Transcriptional regulation by p53: one protein, many possibilities. Cell Death Differ 13(6):951–961
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88(3):323–331
Levine AJ, Oren M (2009) The first years of p53: growing evermore complex. Nat Rev Cancer 9(10):749–758
Liu H, Fergusson MM, Castilho RM (2007) Augmented Wnt signaling in a mammalian model of accelerated aging. Science 317(5839):803–806
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA, Jacks T (1993) p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature 362(6423):847–849
Mao Z, Ke Z, Gorbunova V, Seluanov A (2012) Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases. Aging (Albany NY) 4(6):431–435
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter KM, Green DR, Cotter TG (1994) BCR-ABL maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death. Blood 83(5):1179–1187
Meek DW, Anderson CW (2009) Posttranslational modification of p53: cooperative integrators of function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(6):a000950
Munro J, Barr NI, Ireland H, Morrison V, Parkinson EK (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce a senescence-like state in human cells by a p16-dependent mechanism that is independent of a mitotic clock. Exp Cell Res 295(2):525–538
Narita M, Nũnez S, Heard E, Narita M, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW (2003) Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 113(6):703–716
Narita M, Narita M, Krizhanovsky V, Nuñez S, Chicas A, Hearn SA, Myers MP, Lowe SW (2006) A novel role for high-mobility group a proteins in cellular senescence and heterochromatin formation. Cell 126(3):503–514
Navarro CL, Cau P, Lévy N (2006) Molecular bases of progeroid syndromes. Hum Mol Genet 15(Spec No 2):R151–R161
Oda K, Arakawa H, Tanaka T et al (2000) p53AIP1, a potential mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis, and its regulation by Ser-46-phosphorylated p53. Cell 102(6):849–862
Ohtani N, Hara E (2013) Roles and mechanisms of cellular senescence in regulation of tissue homeostasis. Cancer Sci 104(5):525–530
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR (2005) An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435(7042):677–681
Polager S, Ginsberg D (2009) p53 and E2f: partners in life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 9(10):738–748
Purvis JE, Karhohs KW, Mock C, Batchelor E, Loewer A, Lahav G (2012) p53 dynamics control cell fate. Science 336(6078):1440–1444
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Moskovits N, Bentwich Z, Oren M (2007) Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell 26(5):731–743
Rayess H, Wang MB, Srivatsan ES (2012) Cellular senescence and tumor suppressor gene p16. Int J Cancer 130(8):1715–1725
Reed JC, Green DR (2011) Apoptosis: physiology and pathology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Robles SJ, Adami GR (1998) Agents that cause DNA double strand breaks lead to p16INK4a enrichment and the premature senescence of normal fibroblasts. Oncogene 16(9):1113–1123
Rodier F, Campsi J (2011) Four faces of cellular senescence. J Cell Biol 192(4):547–556
Rodier F, Kim SH, Nijjar T, Yaswen P, Campisi J (2005) Cancer and aging: the importance of telomeres in genome maintenance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(5):977–990
Rodier F, Coppé JP, Patil CK, Hoeijmakers WA, Muñoz DP, Raza SR, Freund A, Campeau E, Davalos AR, Campisi J (2009) Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion. Nat Cell Biol 11(8):973–979
Rowland BD, Bernards R (2006) Re-evaluating cell-cycle regulation by E2Fs. Cell 127(5):871–874
Rufini A, Tucci P, Celardo I, Melino G (2013) Senescence and aging: the critical roles of p53. Oncogene 32(43):5129–5143
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, Vousden KH (2000) Role of NF-kappaB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 404(6780):892–897
Sadaie M, Salama R, Carroll T et al (2013) Redistribution of the Lamin B1 genomic binding profile affects rearrangement of heterochromatic domains and SAHF formation during senescence. Genes Dev 27(16):1800–1808
Sayan AE, Sayan BS, Gogvadze V, Dinsdale D, Nyman U, Hansen TM, Zhivotovsky B, Cohen GM, Knight RA, Melino G (2008) p73 and caspase-cleaved p73 fragments localize to mitochondria and augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 27(31):4363–4372
Sedelnikova OA, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura AJ, Georgakilas AG, Bonner WM (2010) Role of oxidatively induced DNA lesions in human pathogenesis. Mutat Res 704(1–3):152–159
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D, Lowe SW (1997) Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell 88(5):593–602
Shah PP, Donahue G, Otte GL et al (2013) Lamin B1 depletion in senescent cells triggers large-scale changes in gene expression and the chromatin landscape. Genes Dev 27(16):1787–1799
Shay JW, Pereira-Smith OM, Wright WE (1991) A role for both RB and p53 in the regulation of human cellular senescence. Exp Cell Res 196(1):33–39
Siliciano JD, Canman CE, Taya Y, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB (1997) DNA damage induces phosphorylation of the amino terminus of p53. Genes Dev 11(24):3471–3481
Sparmann A, Bar-Sagi D (2004) Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6(5):447–458
Sykes SM, Mellert HS, Holbert MA, Li K, Marmorstein R, Lane WS, McMahon SB (2006) Acetylation of the p53 DNA-binding domain requires apoptosis induction. Mol Cell 24(6):841–851
Taira N, Nihira K, Yamaguchi T, Miki Y, Yoshida K (2007) DYRK2 is targeted to the nucleus and controls p53 via Ser46 phosphorylation in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Mol Cell 25(5):725–738
Takahashi A, Ohtani N, Yamakoshi K, Iida S, Tahara H, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Ide T, Saya H, Hara E (2006) Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a-Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence. Nat Cell Biol 8(11):1291–1297
Takahashi A, Imai Y, Yamakoshi K et al (2012) DNA damage signaling triggers degradation of histone methyltransferases through APC/C(Cdh1) in senescent cells. Mol Cell 45(1):123–131
Tanaka T, Ohkubo S, Tatsuno I, Prives C (2007) hCAS/CSE1L associates with chromatin and regulates expression of select p53 target genes. Cell 130(4):638–650
Tang Y, Luo J, Zhang W, Gu W (2006) Tip60-dependent acetylation of p53 modulates the decision between cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Cell 24(6):827–839
Toledo F, Wahl GM (2006) Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat Rev Cancer 6(12):909–923
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B et al (2004) In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303(5659):844–848
Vousden KH, Prives C (2009) Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell 137(3):413–431
Wiebusch L, Hagemeier C (2010) p53- and p21-dependent premature APC/C-Cdh1 activation in G2 is part of the long-term response to genotoxic stress. Oncogene 29(24):3477–3489
Yang Y, Ludwig RL, Jensen JP et al (2005) Small molecule inhibitors of HDM2 ubiquitin ligase activity stabilize and activate p53 in cells. Cancer Cell 7(6):547–559
Ye C, Zhang X, Wan J, Chang L, Hu W, Bing Z, Zhang S, Li J, He J, Wang J, Zhou G (2013) Radiation-induced cellular senescence results from a slippage of long-term G2 arrested cells into G1 phase. Cell Cycle 12(9):1424–1432
Yonish-Rouach E, Resnitzky D, Lotem J, Sachs L, Kimchi A, Oren M (1991) Wild-type p53induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature 352(6333):345–347
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Keiko Kono for critically reading the manuscript and all of the members of Nakanishi’s laboratory for useful discussions during the preparation of this manuscript. We also regret not being able to cite all the major contributions to this field and those colleagues whose work we should have cited but inadvertently did not. M.N. was supported by a Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas, “Cell Fate Control”; Scientific Research (A); and Challenging Exploratory Research from MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Johmura, Y., Nakanishi, M. (2016). Molecular Insights into the Regulation of Apoptosis and Cellular Senescence and Their Implications for Cancer. In: Hanaoka, F., Sugasawa, K. (eds) DNA Replication, Recombination, and Repair. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55873-6_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55873-6_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55871-2
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55873-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)