Abstract
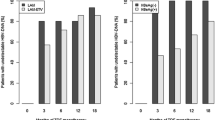
Chronic HBV infection is a major worldwide problem and a leading cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Lamivudine (LAM) therapy has expanded treatment options to include patients unable or unwilling to be treated with alfa interferon. However, YMDD mutations in hepatitis B virus (HBV) polymerase emerge in 16-32% of chronic hepatitis B patients after one year of LAM therapy, increasing to 69% at five years. The YMDD mutant results in clinical resistance in some patients (abnormal serum aminotransferases and elevated serum HBV DNA). Adefovir Dipivoxil (ADV) is a nucleotide analogue with potent in vivo and in vitro activity against both wild-type and LAM resistant HBV. Placebo controlled studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of 10mg ADV with respect to changes in HBV DNA (Roche PCR), serum aminotransferases, HBeAg seroconversion and liver histology after 48 weeks of treatment. These studies have included naïve HBV patients, those with LAM resistance, HIV co-infected and peri-organ transplant patients. In all, over 1600 patients have been treated with ADV 10mg per day, with 256 for over 96 weeks. HBV DNA decreased by a median of 3.5 to 4 log 10.
These biochemical and serologic improvements were also seen in peritransplant patients and in patients co-infected with HBV and HIV. In LAM resistant patients, ADV was efficacious with a 4 log10 decrease in serum HBV DNA noted. Rare ADV resistant mutants have been found in 4 patients. Discontinuation of ADV led to a “flare” in serum ALT in 25% of patients. Side effects were minimal. Abnormal renal function was only noted in those patients with pre-existing renal dysfunction and in peri-transplant patients. This has led to renal dosing guidelines for patients with impaired renal function.
In summary ADV 10mg per day is safe and efficacious in the treatment of chronic HBV infection, leading to decrease in HBV DNA with concomitant improvement in liver biochemistry and histology. It may be used in naïve patients as well as those resistant to LAM and decompensated patients with end-stage liver disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Dienstag J, et al. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1256–63.
Schaim S, et al. Gut 2000;46:562–8.
Schiff ER, et al. Hepatology 2001;34:446A.
Lai CL, et al. N Engl J Med 1998;339:61–8.
Mutimer D, et al. Gut 2000;46:107–13.
Leung NW, et al. Hepatology 2001;33:1527–32.
Marcellin P, et al. N Engl J Med 2003;348:808–16.
Hadziyannis SJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2003;348:800–7.
Yang H, et al. Hepatology 2001;34:316A.
Perrillo A, et al. Hepatology 2001;34:349A
Benhamou Y, et al. Lancet 2001;358:718–23.
Peters M, et al. J Hepatol 2002;36:6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer Japan
About this paper
Cite this paper
Peters, M. (2004). New Antiviral Therapy: Adefovir Dipivoxil for HBV. In: Omata, M., Okita, K. (eds) Therapy for Viral Hepatitis and Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-53977-3_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-53977-3_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-67975-2
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-53977-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive