Zusammenfassung
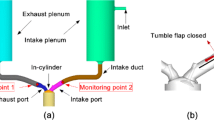
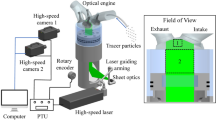
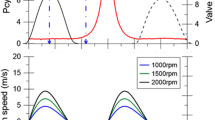
Due to increasingly strict emission regulations, improving and optimizing the combustion process is one of the main research focuses of internal combustion engine development. Combustion instability is a significant parameter, which affects the emission level, and it is reflected by cycle-to-cycle variation. Therefore, understanding the reasons for cycle-to-cycle variation is crucial for the internal combustion design. This paper investigates the causes of cycle-to-cycle variation of a spark-ignition engine through the 3D large eddy simulations done by CONVERGE v3.0. The analysis focuses on the mechanism and consequences of intake tumble flow variation. The variation of tumble ratio between cycles is found to cause fluctuation in turbulent kinetic energy, which will result in different combustion processes. Moreover, according to the results the tumble variation is attributed to the random turbulent eddies in a specific area between the cylinder head and inflow. Comparing tumble variations under different engine specifications, it is found that reducing the size of this area e.g., by changing cylinder head geometry or delaying intake valve opening, contributes to the smaller tumble variation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Informationen zu aktuellen Abgastests https://bmdv.bund.de/SharedDocs/DE/Artikel/StV/Strassenverkehr/informationen-zu-wltp-tests.html
Berckmüller, M., Tait, N.P., Greenhalgh, D.A.: The influence of local fuel concentration on cyclic variability of a lean burn stratified-charge engine. SAE transactions pp. 1151–1176 (1997)
De Soete, G.: Propagation behaviour of spark ignited flames in the early stages. In: International Conference on Combustion in Engineering, vol. 1, p. 93 (1983)
Enaux, B., Granet, V., Vermorel, O., Lacour, C., Pera, C., Angelberger, C., Poinsot, T.: Les study of cycle-to-cycle variations in a spark ignition engine. Proceedings of the combustion Institute 33(2), 3115–3122 (2011)
Chen, C., Ameen, M.M., Wei, H., Iyer, C., Ting, F., Vanderwege, B., Som, S.: Les analysis on cycle-to-cycle variation of combustion process in a disi engine. Tech. rep., SAE Technical Paper (2019)
Ge, H., Zhao, P.: Numerical investigation of the spark plug orientation effects on flame kernel growth. Tech. rep., SAE Technical Paper (2019)
Pischinger, S., Heywood, J.B.: How heat losses to the spark plug electrodes affect flame kernel development in an si-engine. SAE transactions pp. 53–73 (1990)
Goryntsev, D., Sadiki, A., Klein, M., Janicka, J.: Large eddy simulation based analysis of the effects of cycle-to-cycle variations on air-fuel mixing in realistic disi ic-engines. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 32(2), 2759–2766 (2009)
Heywood, J.B.: Internal combustion engine fundamentals. McGraw-Hill Education (2018)
Stone, R.: Introduction to internal combustion engines, vol. 3. Springer (1999)
Vermorel, O., Richard, S., Colin, O., Angelberger, C., Benkenida, A., Veynante, D.: Towards the understanding of cyclic variability in a spark ignited engine using multi-cycle les. Combustion and flame 156(8), 1525–1541 (2009)
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Peng, Z., Ladommatos, N.: Analysis of tumble and swirl motions in a four-valve si engine. SAE Transactions pp. 2226–2241 (2001)
Matsuda, M., Yokomori, T., Shimura, M., Minamoto, Y., Tanahashi, M., Iida, N.: Development of cycle-to-cycle variation of the tumble flow motion in a cylinder of a spark ignition internal combustion engine with miller cycle. International Journal of Engine Research 22(5), 1512–1524 (2021)
Xu, L., Hu, P., Luo, F.: Study on the influence of masking on the high tumble intake ports of gdi engine by three-dimensional simulation. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, vol. 252, p. 032202. IOP Publishing (2019)
Granet, V., Vermorel, O., Lacour, C., Enaux, B., Dugué, V., Poinsot, T.: Large-eddy simulation and experimental study of cycle-to-cycle variations of stable and unstable operating points in a spark ignition engine. Combustion and Flame 159(4), 1562–1575 (2012)
Convergent Science : CONVERGE CFD MANUAL SERIES v3.0. Convergent Science (2021)
Large Eddy Simulation (LES) 2: Turbulent Kinetic https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QKDFTCUh7zU
Salih, A.: Kelvin-helmholtz instability. Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapurm (2010)
Leung, P.T., Gibson, C.H.: Turbulence and fossil turbulence in oceans and lakes. Journal of Cosmology 21, 9427–9450 (2013)
Versteeg, H.K., Malalasekera, W.: An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Pearson education (2007)
Arcoumanis, C., Hu, Z., Vafidis, C., Whitelaw, J.: Tumbling motion: a mechanism for turbulence enhancement in spark-ignition engines. SAE transactions pp. 375–391 (1990)
Wurms, R.: Einfluss einlassseitig erzeugter Ladungsbewegung auf das Betriebsverhalten von Vierventil-Ottomotoren. na (1994)
Correlation Coefficient – Types, Formulas and Examples https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/correlation-coefficient
Acknowledgements
The paper is the scientific result of the FVV research project “Modelling Turbulence” (Project Nr. 1435). The research project was carried out in the framework of the industrial collective research programme (IGF/CORNET no. 286 EN). It was supported by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) through the AiF (German Federation of Industrial Research Associations eV) based on a decision taken by the German Bundestag, Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) and the Science for a moving society (funding no. 6014351). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support received from the FVV eV and from all those involved in the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Der/die Autor(en), exklusiv lizenziert an Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Feng, Y., Mirsch, N., Grill, M., Kulzer, A.C., Günther, M., Pischinger, S. (2023). Numerical Investigation on the Mechanism of Tumble Caused Cycle-to-Cycle Variation of High-Tumble Spark-Ignition Engine. In: Kulzer, A.C., Reuss, HC., Wagner, A. (eds) 23. Internationales Stuttgarter Symposium. ISSYM 2023. Proceedings. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42236-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42236-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-658-42235-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-658-42236-3
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)