Abstract
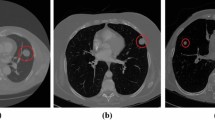
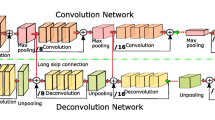
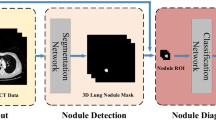
Lung cancer represents one of the most common and lethal types of cancerous pathologies and lung nodules are an early indicator for pulmonary cancer. Hence, a precise and reliable segmentation of lung nodules could enhance early diagnosis and therapy and thus, increase patients’ survival rates. This work proposes a modified 3D-Res2Unet, combining an Unet-style neural network architecture with residual blocks and attention mechanisms. This network was tested on the publicly available LUNA16 CT dataset and achieved on average 91.27 ± 6.49 %. Therefore, the proposed method indicates state-of-the-art performance and could represent an important tool for early diagnosis of lung cancer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34.
Kamble B, Sahu SP, Doriya R. A review on lung and nodule segmentation techniques. Advances in Data and Information Sciences: Proceedings of ICDIS 2019. 2020:555–65.
Carvalho Filho AO de, Sampaio WB de, Silva AC, Paiva AC de, Nunes RA, Gattass M. Automatic detection of solitary lung nodules using quality threshold clustering, genetic algorithm and diversity index. Artif Intell Med. 2014;60(3):165–77.
Pezzano G, Ripoll VR, Radeva P. CoLe-CNN: context-learning convolutional neural network with adaptive loss function for lung nodule segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;198:105792.
**ao Z, Liu B, Geng L, Zhang F, Liu Y. Segmentation of lung nodules using improved 3D-UNet neural network. Symmetry (Basel). 2020;12(11):1787.
Keetha NV, Annavarapu CSR et al. U-Det: a modified U-Net architecture with bidirectional feature network for lung nodule segmentation. ar**v preprint ar**v:2003.09293. 2020.
Huang X, Sun W, Tseng TLB, Li C, Qian W. Fast and fully-automated detection and segmentation of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT scans using deep convolutional neural networks. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. 2019;74:25–36.
Khosravan N, Bagci U. Semi-supervised multi-task learning for lung cancer diagnosis. 2018 40th Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE. 2018:710–3.
LUng Nodule Analysis 2016 (LUNA16). https://luna16.grand- challenge.org/Home/. Accessed: 2010-09-30.
Armato III SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys. 2011;38(2):915–31.
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. CoRR. 2015;abs/1505.04597.
Gao SH, Cheng MM, Zhao K, Zhang XY, Yang MH, Torr P. Res2Net: a new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2021;43(2):652–62.
Glorot X, Bengio Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings. 2010:249–56.
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O. 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Der/die Autor(en), exklusiv lizenziert an Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tummala, P., Hille, G., Saalfeld, S. (2023). Automatic Lung Nodule Segmentation in CT Imaging using an Improved 3D-Res2Unet. In: Deserno, T.M., Handels, H., Maier, A., Maier-Hein, K., Palm, C., Tolxdorff, T. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2023. BVM 2023. Informatik aktuell. Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-41657-7_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN: 978-3-658-41656-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-658-41657-7
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)