Abstract
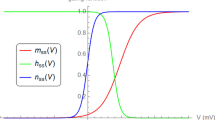
A short description will be given of the voltage clamp experiments on the myelinated nerve fibre. This technique allows measurements of the membrane currents associated to step changes of the membrane potential. An analysis of the membrane currents, with the fibre in solutions of various compositions, shows that the ionic currents during step polarizations are passive currents; i.e. the ions move as charged particles in free diffusion in an electric field. The ionic currents can therefore be described by the membrane permeability and the ionic concentrations both sides the membrane. The sodium permeability and the potassium permeability of the membrane depend on membrane potential and on time. These specific permeability changes have been described in a quantitative form. A solution of the equations describing the voltage clamp currents predicts an action potential very similar to the action potential recorded from the myelinated nerve fibre. The analysis follows the main lines of the squid fibre voltage clamp analysis made by Hodgkin and Huxley. A reference list is given at the end of this communication covering the major bulk of the original papers on the problem.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennet, M. R.: An analysis of the surface fixed-charge theory of the squid giant axon membrane. Biophys. J. 7, 151–164 (1967).
Cole, K. S., and J. W. Moore: Potassium ion current in the squid giant axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys. J. 1, 1–14 (1960).
Dodge, F. A.: Ionic permeability changes underlying nerve excitation. Biophysics of physiological and pharmacological actions, p. 112–143. Washington: Amer. Ass. Adv. Sci. 1961.
Dodge, F. A., and B. Frankenhaeuser: Membrane currents in isolated frog nerve fibre under voltage clamp conditions. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 143, 76–90 (1958).
Dodge, F. A., and B. Frankenhaeuser: Sodium currents in the myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus leavis investigated with the voltage clamp technique. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 148, 188–200 (1959).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: The hypothesis of saltatory conduction. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 17, 27–32 (1952).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (1) A method for recording resting and action potentials in the isolated myelinated frog nerve fibre. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 135, 550–559 (1957).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (2) The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fibre. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 245–260 (1957).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: Steady state inactivation of sodium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 148, 671–676 (1959).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (1) Quantitative description of sodium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 151, 491–501 (1960).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (2) Sodium permeability in toad nerve and in squid nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 152, 159–166 (1960).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (1) Delayed currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis investigated with voltage clamp technique. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 40–45 (1962).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (2) Instantaneous potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 46–53 (1962).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (3) Potassium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 54–61 (1962).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (1) A quantitative description of potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 424–430 (1963).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: (2) Inactivation of the sodium-carrying mechanism in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 445–451 (1963).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: Computed action potential in nerve from Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 180, 780–787 (1965).
Frankenhaeuser, B. and A. L. Hodgkin: The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 218–244 (1957).
Frankenhaeuser, B. and A. F. Huxley: The action potential in the myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 171, 302–315 (1964).
Frankenhaeuser, B. and L. E. Moore: (1) The effect of temperature on the sodium and potassium permeability changes in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 431–437 (1963).
Frankenhaeuser, B. and L. E. Moore: (2) The specificity of the initial current in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Voltage clamp experiments. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 438–444 (1963).
Frankenhaeuser, B. and A. B. Vallbo: Accommodation in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. Acta physiol. scand. 63, 1–20 (1965).
Hille, B.: Common mode of action of three agents that decrease the transient change in sodium permeability in nerves. Nature (Lond.) 210, 1220–1222 (1966).
Hodgkin, A. L., and A. F. Huxley: (1) Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 449–472 (1952).
Hodgkin, A. L., and A. F. Huxley: (2) The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 473–496 (1952).
Hodgkin, A. L., and A. F. Huxley: (3) The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 497–506 (1952).
Hodgkin, A. L., and A. F. Huxley: (4) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 500–544 (1952).
Hodgkin, A. L., and B. Katz: Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axons of Loligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 116, 424–448 (1952).
Hodgkin, A. L., and B. Katz: The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 108, 37–77 (1949).
Huxley, A. F., and R. Stämpfli: Evidence for saltatory conduction in peripheral myelinated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 108, 315–339 (1949).
Huxley, A. F., and R. Stämpfli: Direct determination of membrane resting potential and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 112, 476–495 (1951).
Koppenhöfer, E.: Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf die Membranströme Ran vierscher Schnürringe von Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 293, 34–55 (1967).
Narahashi, T., N. C. Anderson, and J. W. Moore: Tetrodotoxin does not block excitation from inside the nerve membrane. Science 153, 765–767 (1966).
Narahashi, T., J. W. Moore, and W. R. Scott: Tetrodotoxin blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axons. J. gen. Physiol. 47, 965–974 (1964).
Stämpfli, R.: Bau und Funktion isolierter markhaltiger Nervenfasern. Ergebn. Physiol. 47, 69–165 (1952).
Stämpfli, R.: Conduction and transmission in the nervous system. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 25, 493–522 (1963).
Tasaki, I.: Nervous Transmission. Springfield: Thomas 1953.
Vallbo, A. B.: Accommodation related to inactivation of the sodium permeability in single myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. Acta physiol. scand. 61, 429–444 (1964).
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1969 Springer-Verlag Berlin · Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Frankenhaeuser, B. (1969). Ionic Currents in the Myelinated Nerve Fibre. In: Passow, H., Stämpfli, R. (eds) Laboratory Techniques in Membrane Biophysics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-87259-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-87259-4_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-04592-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-87259-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive