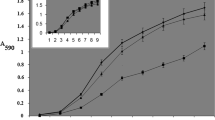
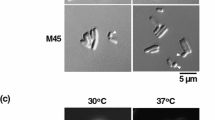
Abstract
We investigated the role of the DnaK (HSP70) ehaperone In metabolism of Escherichia coli by analyzing cellular defects caused by deletion of the dnaK gene (ΔdnaK52). ΔdnaK52 mutants are cold sensitive as well as temperature sensitive and thus possess a very narrow temperature range for growth. At intermediate (30°C) temperature, ΔdnaK52mutants display severe defects in major cellular processes such as cell division, chromosome segregation, replication of low copy number plasmids and regulation of heat shock gene expression that lead to poor growth and genetic instability of the cells. These results indicate important functions of DnaK in cellular metabolism of E. coli at a wide range of growth temperatures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardwell, JCA and Craig, EA, (1984) Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-indueible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 848–852.
Bukau, B and Walker, GC, (1989a) Cellular defects caused by deletion of the Escherichia coli dnaK gene indicate roles for heat shock protein in normal metabolism. J. Bacteriol., 171: 2337–2346.
Bukau, B and Walker, GC, (1989b) ΔdnaK52 mutants of Escherichia coli have defects in chromosome segregation and plasmid maintenance at normal growth temperatures. J. Bacteriol., 171: 6030–6038.
Bukau, B and Walker, GC, Mutations altering heat shock specific subunit of RNA polymerase suppress major celltuar defects of E. coli mutants lacking the DnaK chaperone. EMBO J., in press.
Bukau, B, Donnelly, CE and Walker, GC, (1989) DnaK and GroE proteins play roles in E. coli metabolism at low and intermediate temperatures as well as at high temperatures, p. 27–36. In Pardue, ML, Feramiseo, JR and Lindquist, S, eds., Stress Induced Proteins. Alan. R Liss, Inc., New York.
Chiang, H-L, Terlecky, SR, Plant, CP and Dice, JF, (1989) A role for a 70- kilodalton heat shock protein in lysosomal degradation of intracellular proteins. Science, 246: 382–385.
Echols, H, (1986) Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science, 233: 1050–1056.
Funnell, BE, (1988) Mini-Pi plasmid partitioning: excess ParB protein destabilizes plasmids containing the centromereparS. J. Baeteriol., 170: 954–960.
Grossman, AD, Straus, DB, Walter, WA and Gross, CA (1987) σ32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev., 1: 179–184.
Hirota, Y, Ryter, A and Jacob, F, (1968) Thermosensitive mutants of E. coli affected in the processes of DNA synthesis and cellular division. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 33: 677–694.
Itikawa, H and Ryu, J-I, (1979) Isolation and characterization of a temperature- sensitive dnaK mutant of Escherichia coli B. J. Baeteriol., 138: 339–344.
Liberek, K, Georgopoulos, C and Zylicz, M, (1988) Role of the Escherichia coli DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins in the initiation of bacteriophage X DNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85: 6632–6636.
Lindquist, Sand Craig, EA, (1988) The heat-shock proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 22: 631–677.
Morimoto, R I, Tissieres, A and Georgopoulos, C, eds. (1990) Stress Proteins in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor monograph Series Vol. 19, Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y
Sakakibara, Y, (1988) The dnaK gene of Escherichia coli functions in initiation of chromosome replication. J. Baeteriol., 170: 972–979.
Sell, SM, Eisen, C, Ang, D, Zylicz, M and Georgopoulos, C, (1990) Isolation and characterization of dnaJ null mutants of Escherichia coli J. Bacteriol., 172: 4827–4835.
Sternberg, N and Austin, S, (1983) Isolation and characterization of PI minireplieons, λ-P1:5R and λ,-P1:5L. J. Bacteriol., 153: 800–812.
Straus, DB, Walter, WA and Gross, CA (1987) The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of σ32. Nature, 329: 348–351.
Straus, DB, Walter, WA and Gross, CA, (1988) Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev., 2: 1851–1858.
Tilly, K, McKittrick, N, Zylicz, M and Georgopoulos, C, (1983) The dnaK protein modulates the heat shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell, 34: 641–646.
Tilly, K, Spence, J and Georgopoulos, C, (1989) Modulation of stability of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory factor σ32. J. Bacteriol., 171: 1585–1589.
Tilly, K and Yarmolinsky, M, (1989) Participation of Escherichia coli heat shock proteins DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE in PI plasmid replication. J. Bacteriol., 171: 6025–6029.
Zylicz, M, Ang, D, Liberek, Kand Georgopoulos, C, (1989) Initiation of lambda DNAreplication with purified host- and baeteriophage-encoded proteins: the role of the dnaK, dnaJ and grpE heat shock proteins. EMBO J., 8: 1601–1608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bukau, B., Walker, G.C. (1991). E. coli Mutants Lacking the dnaK Heat Shock Gene: Identification of Cellular Defects and Analysis of Suppressor Mutations. In: Maresca, B., Lindquist, S. (eds) Heat Shock. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-76679-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-76679-4_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-76681-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-76679-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive