Abstract
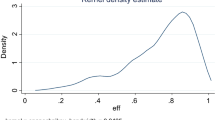
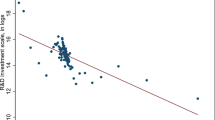
With the development of IT industry, Chinese IT firms have become listed on overseas stock markets one after another. Decision-makers are mainly concerned about firms’ capacity and efficiency of raising funds overseas. In order to assess their performances, IT firms are defined as a two-stage production process. The first one is the operational process and the other is the market financing process. This paper aims to evaluate and analyze the operational efficiency and market efficiency of 28 Chinese IT firms listed on NASDAQ from 2008 to 2011 using the advanced DEA method. The study shows that the inefficiency mainly results from the market financing stage. Decomposition of the technical efficiency indicates that it is not the scale but the pure technical inefficiency or the week capacity of raising funds overseas lowered the market efficiency. Therefore, IT firms should cautiously choose financing by listing overseas under the current international economic downturn.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Golany B, Halek R, Klopp G, Schmitz E, Thomas D (1986) Two phase data envelopment analysis approaches to policy evaluation and management of army recruiting activities, Research report CCS#532, Center for Cybernetic Studies. The University of Texas at Austin, Texas
Han-tao Liu (2004) To measure the efficiency of commercial banks in China: the application of DEA method (in Chinese). Econ Sci 26(6):48–58
Hong-mei Tan (2010) DEA model based on information technology in China case study of performance evaluation of listed companies (in Chinese). Master’s thesis, **hua University, Sichuan
Jian-hua Zhang (2003) DEA method on efficiency study of Chinese commercial banks and the positivist analysis from 1997 to 2001 (in Chinese). J Financ 46(3):11–25
Kao C, Hwang SN (2011) Decomposition of technical and scale efficiencies in two-stage production systems. Eur J Oper Res 211:515–519
Lin-bo ** (2003) The development of information technology industry and the implementation of a leap from universal access to universal service (in Chinese). Manag World 19(6):24–38
Lovell CAK, Walters LC, Wood LL (1994) Stratified models of education production using modified DEA and regression analysis. Expert Syst Appl 27:329–351
Ning Wang, Zhi Li (2006) The application of DEA to the research of efficiency of commercial banks in China (in Chinese). Contemp Econ Manag 28(1):67–72
Noulas AG, Hatzigayios T, Lazaridis J, Lyroudi K (2001) Non-parametric production frontier approach to the study of efficiency of non-life insurance companies in Greece. J Financ Manag Anal 14:19–26
Rangan N, Gawbowski R, Aly HY, Pasurka C (1988) The technical efficiency of U.S. banks. Econ Lett 28:37–55
Sathye M (2003) Efficiency of banks a develo** country: the case of India. J Bank Financ 148(3):662–671
Schinnar AP, Gould EK, Delucia N, Rothbard AB (1990) Organizational determinants of efficiency and effectiveness in mental health partial care programs. Health Serv Res 25:387–420
Seiford LM, Zhu J (1999) Profitability and marketability of the top 55 US commercial banks. Manag Sci 45(9):1270–1288
Sexton TR, Lewis HF (2003) Two-stage DEA: an application to major league baseball. J Prod Anal 19:227–249
Sherman G (1985) Bank branch operating efficiency: evaluation with data envelopment analysis. J Bank Financ 9(2):297–315
Wang CH, Gopal R, Zionts S (1997) Use of data envelopment analysis in assessing information technology impact on firm performance. Ann Oper Res 73:191–213
**ang Li (2009) Research on DEA-based methods of information technology on performance evaluation of listed companies (in Chinese). Master’s thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Zhejiang
**ang Zhao (2010) The measurement of bank branches efficiency and analysis of influence factors, based on the empirical research of super efficiency DEA and Tobit model (in Chinese). Econ Sci 32(1):37–55
**ao-min Zhang, Zhi-ying Liu (2007) An analysis of the efficiency of listed companies of information technology in China (in Chinese). Sci Technol Econ 1:15–19
Yu Wei, Li Wang (2000) The non-parametric approach to the measurement of efficiency: the case of China commercial banks (in Chinese). J Financ Res 43(3):88–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ge, H., Li, Md., Gai, Y. (2013). Capacity and DEA Efficiency of Listed Chinese IT Firms Overseas. In: Qi, E., Shen, J., Dou, R. (eds) Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40063-6_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40063-6_49
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-40062-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-40063-6
eBook Packages: Business and EconomicsBusiness and Management (R0)