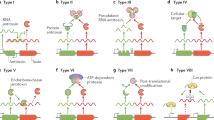
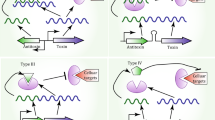
Abstract
A few of the bacterial type II TA systems, primarily those involved in translational inhibition, occur widely throughout the archaeal domain. Using a bioinformatic approach, the frequency and distribution of these diverse TA loci were examined within completed genomes of 124 archaea that are distributed fairly evenly throughout the major archaeal phyla. Results for the frequency and diversity of TA loci are summarised for archaea isolated from environmental niches generally characterised by extreme conditions including high temperature, high salt concentrations, high pressures, extremes of pH or strictly anaerobic conditions. No clear correlations were found between the number of TA loci present and either the genome size or particular environmental conditions. Multiple TA loci tend to be concentrated in variable genomic regions where the occurrence of intra- or inter-genomic gene transfer are most prevalent. For members of the Sulfolobales which are uniformly rich in TA loci, a case is made for some TA systems facilitating maintenance of important genomic regions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brügger, K., Redder, P., She, Q., Confalonieri, F., Zivanovic, Y., & Garrett, R. A. (2002). Mobile elements in archaeal genomes. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 206, 131–141.
Christensen, S. K., & Gerdes, K. (2003). RelE toxins from bacteria and archaea cleave mRNAs on translating ribosomes which are rescued by tmRNA. Molecular Microbiology, 48, 1389–1400.
Cooper, C. R., Daugherty, A. J., Tachdjian, S., Blum, P. H., & Kelly, R. M. (2009). Role of vapBC toxin-antitoxin loci in the thermal stress response of Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochemical Society Transactions, 37, 123–126.
Dienemann, C., Bøggild, A., Winther, K. S., Gerdes, K., & Brodersen, D. (2011). Crystal structure of VapBC toxin-antitoxin complex from Shigella flexneri reveals a hetero-octameric DNA-binding assembly. Journal of Molecular Biology, 414, 713–722.
Eddy, S. R. (2011). Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Computational Biology, 7, 10.
Filée, J., Siguier, P., & Chandler, M. (2007). Insertion sequence diversity in archaea. Microbiological and Molecular Biological Reviews, 71, 121–157.
Gadelle, D., Filee, J., Buhler, C., & Forterre, P. (2003). Phylogenomics of type II DNA topoisomerases. BioEssays, 25, 232–242.
Garrett, R. A., Vestergaard, G., & Shah, S. A. (2011). Archaeal CRISPR-based immune systems: exchangeable functional modules. Trends in Microbiology, 19, 549–556.
Gerdes, K. (2000). Toxin-antitoxin modules may regulate synthsis of macromolecules during nutritional stress. Journal of Bacteriology, 182, 561–572.
Gerdes, K., Christensen, S. K., & Lobner-Olesen, A. (2005). Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3, 371–382.
Gribaldo, S., Poole, A. M., Daubin, V., Forterre, P., & Brochier-Armanet, C. (2010). The origin of eukaryotes and their relationship with the archaea: are we at a phylogenomic impasse? Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8, 743–752.
Guo, L., Brügger, K., Liu, C., Shah, S. A., Zheng, H., Zhu, Y., et al. (2011). Genome analyses of Icelandic strains of Sulfolobus islandicus: Model organisms for genetic and virus-host interaction studies. Journal of Bacteriology, 193, 1672–1680.
Jørgensen, M. G., Pandey, D. P., Jaskolska, M., & Gerdes, K. (2009). HicA of Escherichia coli defines a novel family of translation-independent mRNA transferases in bacteria and archaea. Journal of Bacteriology, 191, 1191–1199.
Kletzin, A. (2007). General characteristics and important model organisms. In R. Cavicchioli (Ed.), Molecular and Cellular Biology (pp. 14–92). USA: ASM press.
Kurland, C. G., Collins, L. J., & Penny, D. (2006). Genomics and the irreducible nature of eukaryotic cells. Science, 312, 1011–1014.
Maezato, Y., Daugherty, A., Dana, K., Soo, E., Cooper, C., Tachdjian S., et al. (2011) VapC6, a ribonucleolytic toxin regulates thermophilicity in the crenarchaeote Sulfolobus solfataricus. RNA, 17, 1381–1392.
Magnuson, R. D. (2007). Hypothetical functions of toxin-antitoxin systems. Journal of Bacteriology, 189, 6089–6092.
Maisonneuve, E., Shakespeare, L. J., Jørgensen, M. G., & Gerdes, K. (2011). Bacterial persistence by RNA endonucleases. Proceedings of National Academic of Sciences USA, 108, 13206–13211.
Makarova, K. S., Grishin, N. V., & Koonin, E. V. (2009a). The HicAB cassette, a putative novel, RNA targeting toxin-antitoxin system in archaea and bacteria. Bioinformatics, 22, 2581–2584.
Makarova, K. S., Wolf, Y. I., & Koonin, E. V. (2009b). Comprehensive comparative-genomic analysis of type 2 toxin-antitoxin systems and related mobile stress response systems in prokaryotes. Biology Direct, 4, 19.
McKenzie, J. L., Duyvestyn, J. M., Smith, T., Bendak, K., Mackay, J., Cursons, R. et al. (2012). Determination of ribonuclease sequence-specificity using Pentaprobes and mass spectrometry. RNA, 18, 1267–1278
Melderen, L. V. (2010). Toxin-antitoxin systems: why so many, what for? Current Opinion in Microbiology, 13, 781–785.
Neubauer, C., Gao, Y. G., Andersen, K. R., Dunham, C. M., Kelley, A. C., Hentschel, J., et al. (2009). The structural basis for mRNA recognition and cleavage by the ribosome-dependent endonuclease RelE. Cell, 139, 1084–1095.
Pandey, D. P., & Gerdes, K. (2005). Toxin-antitoxin loci are highly abundant in free-living but lost from host-associated prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 966–976.
Pedersen, K., Christensen, S. K., & Gerdes, K. (2002). Rapid induction and reversal of a bacteriostatic condition by controlled expression of toxins and antitoxins. Molecular Microbiology, 45, 501–510.
Porter, K., Russ, B. E., & Dyall-Smith, M. L. (2007). Virus-host interactions in salt lakes. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 10, 418–424.
Prangishvili, D., Forterre, P., & Garrett, R. A. (2006). Viruses of the archaea: A unifying view. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 11, 837–848.
Reno, M. L., Held, N. L., Fields, C. J., Burke, P. V., & Whitaker, R. J. (2009). Sulfolobus islandicus pan-genome. Proceedings of National Academic of Sciences, USA, 106, 8605–8610.
Rodriguez-Fonseca, C., Amils, R., & Garrett, R. A. (1995). Fine structure of the peptidyl transferase centre on 23 S-like rRNAs deduced from chemical probing of antibiotic-ribosome complexes. Journal of Molecular Biology, 247, 224–235.
Snyder, J. C., Bateson, M. M., Lavin, M., & Young, M. J. (2010). Use of cellular CRISPR (clusters of regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) spacer-based microarrays for detection of viruses in environmental samples. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 76, 7251–7258.
Valentine, D. L. (2007). Adaptations to energy stress dictate the ecology and evolution of archaea. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 5, 316–323.
Wilbur, J. S., Chivers, P. T., Mattison, K., Potter, L., Brennan, R. G., & So, M. (2005). Neisseria gonorrheae FitA interacts with FitB to bind DNA through its ribbon-helix-helix motif. Biochemistry, 44, 12515–12524.
Winther, K. S., & Gerdes, K. (2011). Enteric virulence associated protein VapC inhibits translation by cleavage of initiator tRNA. Proceedings of National Academic of Sciences, USA, 108, 7403–7407.
Yamashiro, K., & Yamagishi, A. (2005). Characterization of the DNA gyrase from the thermoacidophilic archaeon Thermoplasma acidophilum. Journal of Bacteriology, 187, 8531–8536.
You, X.-Y., Liu, C., Wang, S.-Y., Jiang, C.-Y., Shah, S. A., Prangishvili, D., et al. (2011). Genomic studies of Acidianus hospitalis W1 a host for studying crenarchaeal virus and plasmid life cycles. Extremophiles, 15, 487–497.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shah, S.A., Garrett, R.A. (2013). Archaeal Type II Toxin-Antitoxins. In: Gerdes, K. (eds) Prokaryotic Toxin-Antitoxins. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33253-1_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33253-1_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-33252-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-33253-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)