Abstract
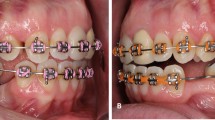
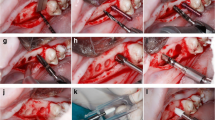
Introduction This study was designed to investigate how the factors including the healing time, implantation location, inserting method and bone density play the important roles in the stability of mini-implant anchorage (MIA), and to evaluate the effects of using the mini-implants in the dental clinic. Materials and Methods Eighteen adult Beagle dogs implanted Aarhus MIAs were chosen to establish the animal experimental model and four vital factors including the healing time, implantation location, inserting method and bone density were considered. The stability of MIAs in different groups was evaluated by super sclerous tissues slice technique, pull-out test and immunohistochemistry. Meanwhile, MIAs were used in clinical therapy for closing extraction space and intruding lower incisors, compared with conventional anchorage methods. Results and Discussion All the MIAs with different healing time (immediate, 2 weeks or 4 weeks loading) provided sufficient anchorage for tooth movement, while the 2- week-loading group showed a relatively better performance. MIAs implanted in the mandible expressed a significantly higher osseointegration ratio and pull-out strength than those in the maxilla. The MIAs implanted close to an extraction wound had more active bone remodeling than the control group. In both self-tap** and pilot-drilling ways, the MIAs showed enough stability though their osseointegration ratio were obviously different. The clinical application of MIA took a distinctive advantage over the conventional methods in such occasions as extraction space closing and tooth intruding. The healing time, implantation location, inserting method and bone density have significant effects on the osseointegration ratio at the interface between MIA and bone, thus the stability of MIA. However, application of MIA as a powerful tool in orthodontic treatment, especially in some complicated cases, widens the scope of the treatment and brings a new prospect of the orthodontic therapy.
This research supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China No.30470436 and No.10572160
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, Z. et al. (2013). Basic and Clinical Biomechanical Study on Microscrew. In: Long, M. (eds) World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering May 26-31, 2012, Bei**g, China. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 39. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_519
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29305-4_519
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-29304-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-29305-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)