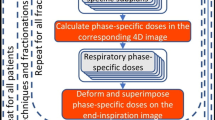
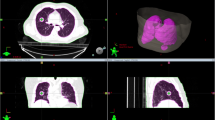
Abstract
Hypo-fractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) employs precisely-conforming high-level radiation dose delivery to improve tumor control probabilities and sparing of healthy tissue. However, the delivery precision and conformity of SBRT renders dose accumulation particularly susceptible to organ motion, and respiratory-induced motion in the abdomen may result in significant displacement of lesion targets during the breathing cycle. Given the maturity of the technology, sensitivity of dose deposition to respiratory-induced organ motion represents a significant factor in observed discrepancies between predictive treatment plan indicators and clinical patient outcome statistics and one of the major outstanding unsolved problems in SBRT. Techniques intended to compensate for respiratory-induced organ motion have been investigated, but very few have yet reached clinical practice. To improve SBRT, it is necessary to overcome the challenge that uncertainties in dose deposition due to organ motion present. This requires incorporating an accurate prediction of the effects of the random nature of the respiratory process on SBRT dose deposition for improved treatment planning and delivery of SBRT. We introduce a means of characterizing the underlying day-to-day variability of patient breathing and calculate the resulting stochasticity in dose accumulation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timmerman, R., Forster, K., Chinsoo Cho, L.: Extracranial stereotactic radiation delivery. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 15, 202–207 (2005)
Lujan, A., Larsen, E., Balter, J., Ten Haken, R.: A method for incorporating organ motion due to breathing into 3D dose calculations. Med. Phys. 26, 715–720 (2003)
Brandner, E., Wu, A., Chen, H., Heron, D., Kalnicki, S., Komanduri, K., Gerszten, K., Burton, S., Ahmed, I., Shou, Z.: Abdominal organ motion measured using 4D CT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 65, 554–560 (2006)
Wu, Q., Thongphiew, D., Wang, Z., Chankong, V., Yin, F.: The impact of respiratory motion and treatment technique on stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver cancer. Med. Phys. 35(4), 1440–1451 (2008)
Keall, P., Kini, V., Vedam, S., Mohan, R.: Potential radiotherapy improvements with respiratory gating. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 25, 1–6 (2005)
Hanley, J., Debois, M., Raben, A., et al.: Deep inspiration breath-hold technique for lung tumors: The potential value of target immobilization and reduced lung density in dose escalation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 36(1), 188 (1996)
Neicu, T., Berbeco, R., Wolfgang, J., Jiang, S.: Synchonized moving aperture radiation therapy (SMART): Improvement of breathing pattern reproducibility using respiratory coaching. Phys. Med. Biol. 51, 617–636 (2006)
Boldea, V., Sharp, G., Jiang, S., Sarrut, D.: 4D-CT lung motion estimation with deformable registration: Quantification of motion nonlinearity and hysteresis. Med. Phys. 35(3), 1008–1018 (2008)
Ford, E., Mageras, G., Yorke, E., Ling, C.: Respiration-correlated spiral ct: A method of measuring respiratory-induced anatomic motion for radiation treatment planning. Med. Phys. 30, 88–97 (2003)
Vedam, S., Keall, P., Kini, V., Mostafavi, H., Shukla, H., Mohan, R.: Acquiring a four-dimensional computed tomography dataset using an external respiratory signal. Phys. Med. Biol. 48(1), 45–62 (2003)
Foskey, M., Davis, B., Goyal, L., Chang, S., Chaney, E., Strehl, N., Tomei, S., Rosenman, J., Joshi, S.: Large deformation three-dimensional image registration in image-guided radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 5869–5892 (2005)
Keall, P., Joshi, S., Vedam, S., Siebers, J., Kini, V., Mohan, R.: Four-dimensional radiotherapy planning for DMLC-based respiratory motion tracking. Med. Phys. 32, 942–951 (2005)
Beddar, A., Kainz, K., Briere, T., Tsunashima, Y., Pan, T., Prado, K., Mohan, R., Gillin, M., Krishnan, S.: Correlation between internal fiducial tumor motion and external marker motion for liver tumors imaged with 4D-CT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 67(2), 630–638 (2007)
Ionascu, D., Jiang, S., Nishloka, S., Shirato, H., Berbeco, R.: Internal-external correlation investigations of respiratory induced motion of lung tumors. Med. Phys. 34(10), 3893–3903 (2007)
Pevsner, A., Davis, B., Joshi, S., et al.: Evaluation of an automated deformable image matching method for quantifying lung motion in respiration-correlated CT images. Med. Phys. 33(2), 369–376 (2006)
Wijesooriya, K., Weiss, E., Dill, V., Dong, L., Mohan, R., Joshi, S.: Quantifying the accuracy of automated structure segmentation in 4D CT images using a deformable image registration algorithm. Med. Phys. 35(4), 1251–1260 (2008)
McLachlan, G., Peel, D.: Finite Mixture Models. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (2000)
Dempster, A., Laird, N., Rubin, D.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B. Met. 39(1), 1–38 (1977)
Pearson, K.: On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. 2(6), 559–572 (1901)
**u, D., Hesthaven, J.: High-order collocation methods for differential equations with random inputs. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 27(3), 1118–1139 (2005)
**u, D.: Efficient collocational approach for parametric uncertainty analysis. Comm. Comput. Phys. 2(2), 293–309 (2007)
**u, D., Karniadakis, G.: The Wiener-Askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 24, 619–644 (2002)
Golub, G., Welsh, J.: Calculation of Gauss quadrature rules. Math. Comput. 10, A1–A10 (1969)
Press, W., Teukolsky, S., Vetterling, W., Flannery, B.: Gaussian Quadratures and Orthogonal Polynomials. In: Numerical recipes in C: The art of scientific computing, 2nd edn., pp. 147–161. Cambridge University Press, New York (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Geneser, S.E., Kirby, R.M., Wang, B., Salter, B., Joshi, S. (2009). Incorporating Patient Breathing Variability into a Stochastic Model of Dose Deposition for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. In: Prince, J.L., Pham, D.L., Myers, K.J. (eds) Information Processing in Medical Imaging. IPMI 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5636. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02498-6_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02498-6_57
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02497-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02498-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)