Abstract
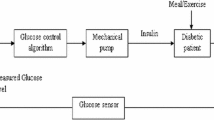
A robust H∞ controller was developed to deliver insulin via a mechanical pump in Type I diabetic patients. A fundamental nonlinear diabetic patient model was linearized and then reduced to a third-order linear form for controller synthesis. H∞ control was applied for the insulin delivery to prevent the hyperglycemic levels in Type I diabetic patient. Uncertainty in the nonlinear model was characterized by up to ±40% variation in eight physiological parameters. A sensitivity analysis identified the three parameter set having the most significant effect on glucose and insulin dynamics over the frequency range of interest [0.02 0.2](rad/min). This uncertainty was represented in the frequency domain and incorporated in the controller design. The controller performance was assessed in terms of its ability to track a normoglycemic set point(81.1 mg/dL) in response to a 50 g meal disturbance. In the nominal continuous-time case, controller maintained glucose concentrations within ± 3.3 mg/dL of set point. A controller tuned to accommodate uncertainty yielded a maximum deviation of 17.6 mg/dL for the worst-case parameter variation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellazi, R., Nucci, G., and Cobelli C (2001). The subcutaneous route to insulin-dependent diabetes therapy. IEEE Eng. In Medicine and Biol, Magazine, 20(1), 54–64.
Bergman, R., Phillips, L., and cabal, C.(1981). Physiologic evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in man. J. Clinic Investigation, 68, 1456–1467.
Bellazi, R., Nucci, G., and Cobelli C (2001). The subcutaneous route to insulin-dependent diabetes therapy. IEEE Eng. In Medicine and Biol, Magazine, 20(1), 54–64.
Bergman, R., Phillips, L., and cabal, C.(1981). Physiologic evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in man. J. Clinic Investigation, 68, 1456–1467.
Doyle, J.C., Glover, K., Khargonekar, P.P., and Fracis B.A.(1989). State space solutions tostandard H 2 and H ∞ control problems. IEEE Trans. On Automatic Control, 34, 831–847.
Erzen, F.C., Birol, G., and Cinar. A. (2000), Simulation studies on the dynamics of diabetes mellitus. Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Bio-Informatics and Biomedical Eng. 232–235.
Femat R and Ruiz-Velaquez E., (1999), Blood glucose regulation an output feedback approach, Proc. Int. Conf. Control Appl., vol.2, 1290–1293.
Gahinet, P., and Apkarian, P.(1994). A linear matrix inequality approach to H ∞ control. Int. J. Robust control, 4, 421–448.
Halim, M., Carson, E.R., Andreassen, S., Hejelsen, O., and Hovorka, R. (1993). The role of a diabetic advisory system (dias) in the management of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc. Int Conf. IEEE Eng. In Medicine and Biology Soc., 610–611.
Lehmann E.D., and Deutsch, T. (1998). Compartmental models for glycaemic prediction and decision-support in clinical diabetes care: promise and reality. Computer Methods and programs in Biomedicine, 56, 193–204.
Lehmann, E.D., and Deutsch, T. (1992). A physiological model of glucose-insulin interaction in type I diabetes mellitus. J. of Biomedical Engineering, 14, 235–242.
Lenart P.J. and Parker R.S. (2001) Modeling exercise effects in type I diabetic patients, Proc.15th Triennial World Congress IFAC,Barcelona, Spain 21–26 July 2002.
Maurer A.C., (1979) The therapy of diabetes, Amer. Scientist, 67, 422–431.
Pacini, G and cobeli, C.(1990) Estimation of Beta-cell secretion and insulin hepatic extraction by the minimal modeling technique. Computational Methods Programs in Biomedicine. 32, 241–248.
Parker R.S., (1999) Model-based analysis and control for biosystems, Ph.D. Thesis, University of delware,delware.
[Parker R.S., Doyle III, F.J. and Peppas, N.A.(1999). A model-based algorithm for blood glucose control in type I diabetes patients. IEEE Trans. Biomed.Eng., 46(2), 148–157.
Parker R.S., Doyle III F.J., and Peppas N.A.(2000). Robust H∞ glucose control in diabetes using a physiological model. AICHE J., 46(12), 2537–2549.
Parker R.S., Doyle III F.J., and Peppas N.A. (2001). The intravenous route to blood glucose control, IEEE Eng. in Med. and Biol., 20, 65–73.
Ruiz-Velaquez, E., Femat, R. Campos-delgado, D.U.(2004) Blood glucose contreol for type I diabetes mellitus: a robust tracking H∞ problem, Control Engineering Practice, Vol.12 pp 1179–1195.
J.T. Sorensen, “A physiologic model of glucose metabolism in man and its use to design and access improved insulin therapies for diabetes,” Ph.D.Thesis, dept chem. Eng.,Massachusetts Inst. Tecnol. (MIT). Cambridge, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kamath, S., George, V.I., Vidyasagar, S. (2008). Blood Glucose Control In Type I Diabetics: An Output Feedback Approach. In: Abu Osman, N.A., Ibrahim, F., Wan Abas, W.A.B., Abdul Rahman, H.S., Ting, HN. (eds) 4th Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biomedical Engineering 2008. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 21. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69139-6_165
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69139-6_165
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-69138-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-69139-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)