Abstract
The dynamic properties of crossing and veering in coupled structures have been studied both numerically and analytically, but they are difficult to investigate using Finite Element Analysis because of the change in the topological arrangement due to the different configuration.
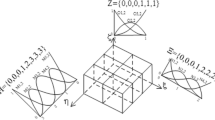
Isogeometric Analysis, recently developed method for numerical simulation, could overcome some of the drawbacks of the change in the configuration such as remeshing, coupling between the nodes of the different models, need of a fine mesh to allow small change in the configuration to be comparable to the mesh size.
The key of this method is to avoid meshing and using the same basis functions used by the geometry, namely Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS), to define the discretization of a Finite Element model. Other advantages are the possibility of increasing the order of the functions to obtain smooth stress field across the element interfaces.
An experimental test-rig composed by beams and masses, which allow different configuration and dynamic coupling as well, is used as test case to validate the accuracy of the results with respect to both experimental data and classical Finite Element Analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leissa W (1974) On a curve veering aberration. J Appl Math Phys (ZAMP) 25:99–111
Chen X, Kareem A, Matsumoto M (2001) Multimode coupled flutter and buffeting analysis of long span bridges. J Wind Eng Ind Aerod 89:649–664
Chan Y, Inman DJ (2010) Management of the variability of vibration response levels in mistuned bladed discs using robust design concepts. Part 1. Parameter design. Mech Syst Signal Pr 24:2777–2791
Bae JS, Inman DJ, Lee I (2004) Effects of structural nonlinearity on subsonic aeroelastic characteristics of an aircraft wing with control surface. J Fluid Struct 19:747–763
Khodaparast H, Mottershead JE, Badcock K (2010) Propagation of structural uncertainty to lineat aeroelastic stability. J Fluid Struct 88: 223–236
Tang D, Dowell E (2010) Aeroelastic response of aircraft with freeplay structural nonlinearity. In: Proceedings of 2nd aircraft structural design conference, London
Maeda T, Baburaj V, Ito Y, Koga T (1998) Flexural-torsional coupling effect on vibrational characteristics of angle-ply laminates. J Sound Vib 210(3):351–365
du Bois JL, Adhikari S, Lieven NA (2007) Experimental and numerical investigation of mode veering in a stressed structure. In: Proceedings of 25th IMAC, Orlando, FL
Hughes TJR, Cottrell JA, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(39–41):4135–4195
Cottrell JA, Hughes TJR, Reali A (2007) Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric structural analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(41–44):4160–4183
Temizer I, Wriggers P, Hughes TJR (2011) Contact treatment in isogeometric analysis with NURBS. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200 (9–12):1100–1112
Jia L (2011) Isogeometric contact analysis: geometric basis and formulation for frictionless contact. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200 (5–8):726–741
Temizer I, Wriggers P, Hughes TJR (2012) Three-dimensional mortar-based frictional contact treatment in isogeometric analysis with NURBS. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 209–212:115–128
De Lorenzis L, Temizer I, Wriggers P, Zavarise G (2011) A large deformation frictional contact formulation using NURBS-based isogeometric analysis. Int J Numer Meth Eng 87(13):1278–1300
Matzen ME, Cichosz T, Bischoff M (2013) A point to segment contact formulation for isogeometric, NURBS-based finite elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 255:27–39
Wall WA, Frenzel MA, Cyron C (2008) Isogeometric structural shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(33–40):2976–2988
Manh ND, Evgrafov A, Gersborg AR, Gravesen J (2011) Isogeometric shape optimization of vibrating membranes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(13–16):1343–1353
Qian X, Sigmund O (2011) Isogeometric shape optimization of photonic crystals via Coons patches. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200 (25–28):2237–2255
Qian X (2010) Full analytical sensitivities in NURBS based isogeometric shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199 (29–32):2059–2071
Bazilevs Y, Calo VM, Cottrell JA, Evans JA, Hughes TJR, Lipton S, Scott MA, Sederberg TW (2010) Isogeometric analysis using T-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(5–8):229–263
Scott MA, Li X, Sederberg TW, Hughes TJR (2012) Local refinement of analysis-suitable T-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 213–216:206–222
Nitsche J (1971) Uber ein variationsprinzip zur losung von dirichlet-problemen bei verwendung von teilraumen, die keinen randbedingungen unterworfen sind. Abh Math Sem Univ Hamburg 36:9–15
Imregun M, Visser WJ (1991) A review of model updating techniques. Shock Vib Digest 23(1):9–20
Mottershead JE, Friswell MI (1993) Model updating in structural dynamics: a survey. J Sound Vibr 167(2):347–375
Kim KO, Anderson WJ, Sandstorm RE (1983) Non-linear inverse perturbation method in dynamic analysis. AIAA J 21(9):1310–1316
Lin RM, Lim MK, Du H (1995) Improved inverse eigensensitivity method for structural analytical model updating. Trans ASME J Vibr Acoust 117:192–198
Bonisoli E, Fasana A, Garibaldi L, Marchesiello S (2002) Sensitivity analysis and damage location over the Z24 bridge. In: ONERA, Structural health monitoring, Paris, pp. 1007–1015
Bonisoli E, Delprete C, Esposito M, Mottershead JE (2011) Structural dynamics with coincident eigenvalues: modelling and testing. In: Proceedings of the 29th IMAC, vol 3(6). Detroit, MI, pp. 325–337
Piegl LA, Tiller W (1996) The NURBS book. Springer, Berlin
Fritz A, Hüeber S, Wohlmuth BI (2004) A comparison of mortar and Nitsche techniques for linear elasticity. CALCOLO 41(3):115–137
Bazilevs Y, Hughes TJR (2007) Weak imposition of Dirichlet boundary conditions in fluid mechanics. Comput Fluids 36(1):12–16
Nguyen VP, Kerfriden P, Bordas S (2013) Isogeometric cohesive elements for two and three dimensional composite delamination analysis. Compos Sci Technol http://arxiv.org/abs/1305.2738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 The Society for Experimental Mechanics, Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tornincasa, S., Bonisoli, E., Kerfriden, P., Brino, M. (2014). Investigation of Crossing and Veering Phenomena in an Isogeometric Analysis Framework. In: Allemang, R. (eds) Topics in Modal Analysis II, Volume 8. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04774-4_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04774-4_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-04773-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-04774-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)