Abstract
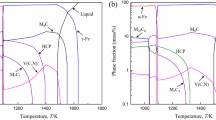
The morphology of carbides in AISI M35 high-speed steel electroslag remelting ingot, as well as decomposition mechanism of the carbides at high temperature were investigated by thermodynamic calculations, microscopy analyses, and phase analyses. The calculation results indicated that the main types carbides formed in steel during solidification were MC and M2C. Through observation, it was found that there were lots of network eutectic carbides in the electroslag ingot, and the size of carbides at the center was larger than that at the edge. The micro morphologies of carbides in the ingot mainly had two types: a lath-like shape and a brain one, and both phases were identified as M2C. They could be decomposed and formed new phases MC and M6C at high temperatures. The decomposition of M2C carbides occurred obviously with the increasing holding temperature, especially at 1,423 to 1,473 K. Which were more easily broken and deformed in the subsequent working.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang W, Pan F, Tang A (2011) Decomposition of the coarse primary carbides in the M2 high speed steels containing silicon. Rare Met Mater Eng S3:38–42
Luo YW, Guo HJ, Sun XL (2020) Effects of nitrogen on the morphology and evolution of M2C eutectic carbides in Fe-Mo-W-Co-Cr-VC alloy. JOM 72:326–332
**ao ZX, Li HP, Feng JH (2018) Microstructural homogeneity of electroslag remelting M2 high speed steel ingot. J Iron Steel Res 30(07):529–535
Zhou B, Shen Y, Chen J (2011) Breakdown behavior of eutectic carbide in high speed steel during hot compression. J Iron Steel Res Int 18(1):41–48
Zhou XF, Zheng ZX, Zhang WC (2020) Effect of pre-deformation on decomposition and spheroidization of M2C carbide in high-speed steel. Metall Mater Trans A 51:3552–3564
Zhou XF, Zheng ZX, Zhang WC (2020) Deformation-induced carbide transformation in M2 high-speed steel. Metall Mater Trans A 51:568–573
Narahari PS, Rajasekhar K, Chatterjee M (2013) Influence of composition and processing on properties of stainless steels. Adv Mater Res 794:117–123
Chen K, Cheng SC, Zhang JZ (2012) The effect of large Nb containing MC carbides on the high-temperature properties of LF2 alloy. Mech Eng Mater 36(3):18–21
Deng YK (2002) High speed tool steel. Metallurgical Industry Press, Bei**g
Zhou B, Shen L, Chen J (2010) Evolving mechanism of eutectic carbide in As-cast AISI M2 high-speed steel at elevated temperature. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Sci) 15(04):463–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liang, W., Li, J., Li, Jh. (2024). Formation and Decomposition Mechanism of Carbides in AISI M35 High-Speed Steel Produced by ESR. In: TMS 2024 153rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings. TMS 2024. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50349-8_122
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50349-8_122
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-50348-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-50349-8
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)