Abstract
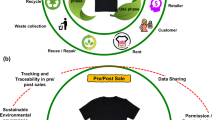
STVgoDigital Fashion Ecosystem 4.0 Project aims to support the Next Generation Fashion Ecosystem. The main goal of this project is to develop a digital ecosystem that brings together the main stakeholders of the textile and clothing industries, to promote an environment that offers greater interaction and customization promoting new business and production models to fulfill current market demands in terms of customization and sustainability. To support the Next-Generation Fashion Ecosystem, the STVgoDigital PPS3 project is develo** an Open Platform for Fashion and the Microfactory solution. The Open Platform for Fashion supports clothing customization. The microfactory being developed allows the production of customized products sold through the platform, allowing to adjust a small factory easily and sustainably produce micro or small series of products, but it can also be replicated in other scenarios or industries.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Le, The future of digitally printed textiles. AATCC Rev. 19(1), 32–37 (2019)
M. Koszewska, Circular economy in textiles and fashion—The role of a consumer, in Circular Economy in Textiles and Apparel, (2019), pp. 183–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-102630-4.00009-1
M.H. To, K. Uisan, Y.S. Ok, D. Pleissner, C.S.K. Lin, Recent trends in green and sustainable chemistry: Rethinking textile waste in a circular economy. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 20, 1–10 (2019)
M. Stenton, Cultivated fashion: Exploring the commercial viability of bioengineered fashion and textile products, in Expanding Communities of Sustainable Practice, 62 (2018)
S. Rashid, M.S. Islam, Potential of rainwater harvesting and reusing industrial effluent in a textile industry (Doctoral dissertation, Department of Civil and Environment Engineering, Islamic University of Technology (IUT), Board Bazar, Gazipur, Bangladesh, 2021)
P. Dutta, M.R. Rabbi, M.A. Sufian, S. Mahjebin, Effects of textile dyeing effluent on the environment and its treatment: A review
X. Chen, H.A. Memon, Y. Wang, I. Marriam, M. Tebyetekerwa, Circular Economy and sustainability of the clothing and textile Industry. Mater. Circ. Econ. 3(1), 1–9 (2021)
S. Moazzem, F. Daver, E. Crossin, L. Wang, Assessing environmental impact of textile supply chain using life cycle assessment methodology. J. Text. Inst. 109(12), 1574–1585 (2018)
K. Niinimäki, G. Peters, H. Dahlbo, P. Perry, T. Rissanen, A. Gwilt, The environmental price of fast fashion. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 1(4), 189–200 (2020)
L. Lara, I. Cabral, J. Cunha, Ecological approaches to textile dyeing: A review. Sustainability 14(14), 8353 (2022)
A.N. Riordain, Wastewater, fast fashion and the water convention 1992. Plassey Law Rev. 2, 34 (2022)
R. Nayak (ed.), Sustainable technologies for fashion and textiles (Woodhead Publishing, 2019)
F.B. Alam, A. Hossain, Conservation of water resource in textile and apparel industries. IOSR J. Polym. Text. Eng. 5(5), 11–14 (2018)
A. Cattermole, How the circular economy is changing fashion. AATCC Rev. 18(2), 37–42 (2018)
Ellen MacArthur Foundation, A new textiles economy: Redesigning fashion’s future (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, 2017)
M. Stenton, Cultivated fashion: Exploring the commercial viability of bioengineered fashion and textile products (Expanding Communities of Sustainable Practice, 2018), p. 62
E. MacArthur, Beyond plastic waste. Science 358(6365), 843–843 (2017)
D. Dissanayake, D. Weerasinghe, Towards circular economy in fashion: Review of strategies, barriers and enablers. Circ Econ Sustain 2(1), 25–45 (2021)
N. Remy, E. Speelman, S. Swartz, Style that’s sustainable: A new fast-fashion formula (McKinsey Global Institute, 2016)
L. Polat, A. Erkollar, Industry4.0 vs. Society 5.0, in The International Symposium for Production Research, (Springer, Cham, 2020, September), pp. 333–345
G. Marzano, A. Martinovs, Teaching industry4.0, in Society. Integration. Education. Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference, vol. 2, (2020, May), pp. 69–76
L.D. Evjemo, T. Gjerstad, E.I. Grøtli, G. Sziebig, Trends in smart manufacturing: Role of humans and industrial robots in smart factories. Curr. Robot. Rep. 1(2), 35–41 (2020)
S. Grabowska, Smart factories in the age of Industry4.0. Management systems in production engineering (2020)
D.R. Sjödin, V. Parida, M. Leksell, A. Petrovic, Smart factory implementation and process innovation: A preliminary maturity model for leveraging digitalization in manufacturing moving to smart factories presents specific challenges that can be addressed through a structured approach focused on people, processes, and technologies. Res-Technol Manag 61(5), 22–31 (2018)
B. Adams, K. Judd, Data is the new gold–development players mine a new seam. Global Policy Watch 19, 28 (2017)
A. Stăncioiu, The fourth industrial revolution ‘Industry4.0’. Fiabilitate Şi Durabilitate 1(19), 74–78 (2017)
A. Schumacher, S. Erol, W. Sihn, A maturity model for assessing Industry4.0 readiness and maturity of manufacturing enterprises. Procedia Cirp 52, 161–166 (2016)
P. Bansal, The corporate challenges of sustainable development. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 16(2), 122–131 (2002)
I.A.O. Fraunhofer, A.G. Ingenics, Industrie 4.0–Eine Revolution der Arbeitsgestaltung. Wie Automatisierung und Digitalisierung Unsere Produkte Verändern Warden (2014)
N. Davis, What is the fourth industrial revolution, in World Economic Forum, vol. 19, (2016, January)
K.A. Demir, G. Döven, B. Sezen, Industry 5.0 and human-robot co-working. Procedia Comput. Sci. 158, 688–695 (2019)
T. Economist, The world’s most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data (New York, Economist, 2017)
C. Costa, N. Azoia, C. Silva, E. Marques, Textile industry in a changing world: Challenges of sustainable development. U. Porto J. Eng. 6(2), 86–97 (2020)
V. Petrovic, M. Pesic, D. Joksimovic, A. Milosavljevic, Digitization in the textile Industry-4.0 industrial revolution in clothing production
M. Hartmann, B. Halecker, Management of innovation in the industrial internet of things, in ISPIM Conference Proceedings, (The Inter-national Society for Professional Innovation Management (ISPIM), 2015), p. 1
S.F. Kabir, S. Chakraborty, S.A. Hoque, K. Mathur, Sustainability assessment of cotton-based textile wet processing. Clean Technol. 1(1), 232–246 (2019)
L. Chen, F. Caro, C.J. Corbett, X. Ding, Estimating the environmental and economic impacts of widespread adoption of potential technology solutions to reduce water use and pollution: Application to China’s textile industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 79, 106293 (2019)
M. Ghoreishi, A. Happonen, M. Pynnönen, Exploring Industry4.0 technologies to enhance circularity in textile industry: Role of internet of things, in Twenty-First International Working Seminar on Production Economics, (2020, February), p. 16
J. Hawkes, The fourth pillar of sustainability. Culture’s essential role in public planning (2001)
M. Ghoreishi, A. Happonen, M. Pynnönen, Exploring Industry4.0 technologies to enhance circularity in textile industry: Role of internet of things, in Twenty-first International Working Seminar on Production Economics (2020, February), p. 16
M. Revelli, A. Paidakaki, Networking and housing advocacy in the homelessness sector: A path towards social sustainability? A study of the Housing First Europe Hub. Eur J Homelessness 16(2), 65 (2022)
A. Rojko, Industry4.0 concept: Background and overview. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 11(5), 77 (2017)
S. Plitsos, P.P. Repoussis, I. Mourtos, C.D. Tarantilis, Energy-aware decision support for production scheduling. Decis. Support Syst. 93, 88–97 (2017)
A. Cunha, J.P. Mendonça, M. Catarino, H. Costa, R. Nogueira, Sustainable manufacturing: The impact of collaboration on SMEs, in 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), (IEEE, 2018, September), pp. 630–636
2018. Learning in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, BBNTtimes. https://www.bbntimes.com/en/society/learning-in-the-fourthindustrial-revolution
J.D. Contreras, J.I. Garcia, J.D. Pastrana, Develo** of Industry4.0 applications. Int. J. Online Eng. 13(10) (2017)
F. Zezulka, P. Marcon, I. Vesely, O. Sajdl, Industry4.0–An Introduction in the phenomenon. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49(25), 8–12 (2016)
S.W. Lin, B. Murphy, E. Clauer, U. Loewen, R. Neubert, G. Bachmann, M. Pai, M. Hankel, Architecture alignment and interoperability: An industrial internet consortium and plattform industrie 4.0 joint whitepaper. White Paper, Industrial Internet Consortium (2017)
M. Karrenbauer, S. Ludwig, H. Buhr, H. Klessig, A. Bernardy, H. Wu, C. Pallasch, A. Fellan, N. Hoffmann, V. Seelmann, M. Taghouti, Future industrial networking: from use cases to wireless technologies to a flexible system architecture. atAutomatisierungstechnik 67(7), 526–544 (2019)
Sensirion, SPS30 – PM2.5 Sensor for HVAC and air quality applications SPS30 [online] (n.d.). sensirion.com. Available at: https://sensirion.com/us/products/catalog/SPS30/. Accessed 19 Mar 2022
Microchip.com. 2022 [online]. Available at: https://www.microchip.com/en-us/product/PIC18F27K42. Accessed 3 May 2022
Acknowledgements
This work was developed in the framework of STVgoDIGITAL project (no 46086), which was co-financed by Portugal 2020, under the Operational Program for Competitiveness and Internationalization (COMPETE 2020) through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cunha, A. et al. (2023). Next-Generation Fashion Ecosystem: A STVgoDigital Approach. In: da Silva Portela, C.F. (eds) Sustainable, Innovative and Intelligent Societies and Cities. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30514-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30514-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-30513-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-30514-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)