Abstract
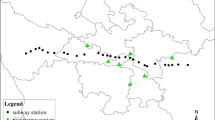
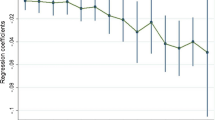
With China’s continuous urbanization and industrialization, the emissions in Chinese cities have become increasingly serious. Chinese government has set a goal to reach carbon peak and achieve carbon neutrality, endeavoring to gradually realize net-zero carbon dioxide (CO2) emission. Moreover, the new transport technology has also been fast developed, represented by the quick expansion of the high-speed rail (HSR) system. Based on the Air Quality Index (AQI) of 286 Chinese cities over the 2016–2019 period, this paper first adopts the spatial auto-correlation analysis to quantify the spatio-temporal characteristics of Chinese cities’ AQI. Then, a spatial difference-in-differences (SDID) model is estimated to shed light on how Chinese cities’ air quality can be affected by HSR. Our paper identifies apparent spatio-temporal distribution patterns in Chinese cities’ air quality. Our empirical results that the HSR opening can help reduce emissions to improve the city’s air quality. Moreover, HSR opening in the adjacent city can also improve one city’s air quality (i.e., the neighboring effect). We also highlight and verify the mechanism of such a positive HSR impact on the city’s air quality. First, as a cleaner transport mode, HSR helps divert traffic from other more polluting modes (i.e., positive direct “transport substitution effect”). HSR also helps promote the city’s tertiary industry, leading to fewer emissions (i.e., positive indirect “industrial structure effect”). Our heterogeneous analyses further demonstrate that HSR is more effective to improve the air quality in eastern and western regions. But the neighboring effect is only obvious in eastern China as the cities are closer to each other in terms of economic relations and geographic locations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The ecological environment [Internet]: Environmental air quality index of technical specifications (trial). http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201203/t20120302_224166.shtml (2012). Accessed 29 Feb 2012
Auffhammer, M., Kellogg, R.: Clearing the air? The effects of gasoline content regulation on air quality. Am. Econ. Rev. 101(6), 2687–2722 (2011)
Cao, J., Wang, X., Zhong, X.H.: Have traffic restrictions improved air quality in Bei**g? Econ. Q. 13(03), 1091–1126 (2014)
The ecological environment[Internet]: China mobile source environmental management report (2020). http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk15/202008/t20200810_793252.html (2020). Accessed 10 Aug 2020
Zheng, S., Kahn, M.E.: Mitigating the cost of bullet trace market integration and mitigation of megacity growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110(14), E1248–E1253 (2013)
Zhang, J.: High-speed railway construction and county economic development – a study based on satellite light data. Econ. Q. 16(04), 1533–1562 (2017)
Mohring, H.: Optimization and scale economies in urban bus transport. Am. Econ. Rev. 62(4), 591–604 (1972)
Lan, B.X., Zhang, L.: Revenue Management Model of High-speed Railway Passenger Dedicated Line. Chin. J. Manage. Sci. 17(04), 53–59 (2009)
Xu, Y.T., Liu, X.Z., Wang, Z.B.: Spatio-temporal distribution of air quality in Chinese cities based on AQI index. J. Guangxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.). 37(01), 187–196 (2019)
Guo, Y.M., Lin, X.Q., Bian, Y.: Spatio-temporal evolution of air quality in urban agglomerations in China and its influencing factors. Ecol. Econ. 35(11), 167–175 (2019)
Niu, H.M., Tu, J.J., Yao, Z., Ha, L., Li, J.B.: Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of air quality in Chinese cities. Henan Sci. 34(08), 1317–1321 (2016)
Yan, S., Cao, H., Chen, Y., Wu, C., Hong, T., Fan, H.: Spatial and temporal characteristics of air quality and air pollutants in 2013 in Bei**g. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23(14), 13996–14007 (2016)
Chen, W.W., Liu, Y., Wu, X.W., Bao, Q.Y., Gao, Z.T., Zhang, X.L., et al.: Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of air quality and causes of heavy pollution in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. 40(11), 4810–4823 (2019)
Fang, C., Liu, H., Li, G., Sun, D., Miao, Z.: Estimating the impact of urbanization on air quality in China using spatial regression models. Sustainability 7(11), 15570–15592 (2015)
Zhang, X.M., Luo, S., Li, Z.F., Jia, L., Zhai, H.M., Wang, L.M.: Study on influencing factors of spatial pattern of air quality in China. J. **nyang Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Edn.). 33(01), 83–88 (2020)
Dai, Y.H., Zhou, W.X.: Temporal and spatial correlation patterns of air pollutants in Chinese cities. PLoS ONE 12(8), e0182724 (2017)
Zhao, L.X., Zhao, R.: Study on the relationship between economic growth, energy intensity and air pollution. Soft Sci. 33(6), 60–66+78 (2019)
Fang, J.: Impacts of high-speed rail on urban smog pollution in China: a spatial difference-in-difference approach. Sci. Total Environ. 777, 146153 (2021)
Lin, X.Q., Wang, D.: Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and socio-economic driving forces of city’s air quality in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 71(08), 1357–1371 (2016)
Li, M.S., Ren, X.X., Yu, Y., Zhou, L.: Spatial and temporal distribution of PM_(2.5) pollution in Chinese mainland. China Environ. Sci. 36(03), 641–650 (2016)
Jia, R., Shao, S., Yang, L.: High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: a spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Economics. 99, 105271 (2021)
Zhang, X.P., Lin, M.H.: Analysis of the regional differences of air pollution in Chinese cities and the socio-economic influencing factors: A comparative study of two air quality indexes. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 37(01), 39–50 (2020)
Griffin, P.W., Hammond, G.P., McKenna, R.C.: Industrial energy use and decarbonisation in the glass sector: a UK perspective. Adv. Appl. Energy. 3, 100037 (2021)
Wang, L.: Panel data analysis of correlation between automobile consumption and air pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 24(S2), 462–466 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.en.2016.01.004
Shang, W.L., Chen, J., Bi, H., Sui, Y., Chen, Y.: Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on user behaviors and environmental benefits of bike sharing: a big data analysis. Appl. Energy 285, 116429 (2021)
Chi, J.Y., Zhang, Y., Yan, S.Y.: City’s air quality is affected by the level of urban economic development: a case study in China. Econ. Manag. 28(05), 26–31 (2014)
Bi, H., Shang, W.L., Chen, Y., Wang, K., Yu, Q., Sui, Y.: GIS aided sustainable management for urban road transport systems with a unifying queuing and neural network model. Appl. Energy 116818 (2021)
Gray, N., McDonagh, S., O’Shea, R., Smyth, B., Murphy, J.D.: Decarbonising ships, planes and trucks: an analysis of suitable low-carbon fuels for the maritime, aviation and haulage sectors. Adv. Appl. Energy 1, 100008 (2021)
Li, Y., Chiu, Y., Lin, T.Y.: Energy and environmental efficiency in different Chinese regions. Sustainability 11(4), 1216 (2019)
Jiang, L., Zhou, H.F., Bai, L., Wang, Z.J.: Dynamic change characteristics of city’s air quality index (AQI) in China. Econ. Geogr. 38(09), 87–95 (2018)
Wang, B.H., Wang, S.: An empirical study on influencing factors of city’s air quality in China: based on the analysis of panel data of 31 major cities in China. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. 18(06), 29–33 (2015)
Jiao, J., Wang, J., Zhang, F., **, F., Liu, W.: Roles of accessibility, connectivity and spatial interdependence in realizing the economic impact of high-speed rail: evidence from China. Transp. Policy 91, 1–15 (2020)
Zhang, A., Wan, Y., Yang, H.: Impacts of high-speed rail on airlines, airports and regional economies: a survey of recent research. Transp. Policy 81, A1–A19 (2019)
Liu, S., Wan, Y., Ha, H.K., Yoshida, Y., Zhang, A.: Impact of high-speed rail network development on airport traffic and traffic distribution: evidence from China and Japan. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 127, 115–135 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Yu, D.H., Sun, T.: Impact of the opening of high-speed railway on green restructuring of urban production system. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 29(07), 41–49 (2019)
Zhu, S.J., Yin, S.S., Zhong, T.L.: Does the opening of high-speed rail curb urban pollution? J. Econ. Manag. 33(03), 52–57 (2019)
Qin, B.T., **e, R.B., Ge, L.M.: Study on the relationship between FDI, economic growth and environmental pollution–based on the analysis and test of China’s provincial panel data. J. Guangxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 33(02), 81–96 (2020)
Yu, K., Strauss, J., Liu, S., Li, H., Kuang, X., Wu, J.: Effects of railway speed on aviation demand and CO2 emissions in China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 94, 102772 (2021)
Park, Y., Ha, H.K.: Analysis of the impact of high-speed railroad service on air transport demand. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 42(2), 95–104 (2006)
Zhang, H., Feng, F.: Green high-speed rail: Will it reduce smog pollution? Acta Ecol. Sin. 6(03), 114–147 (2019)
Beaudoin, J., Lin, L.C.Y.C.: Is public transit's “green” reputation deserved? : Evaluating the effects of transit supply on air quality. University of California at Davis Working Paper (2016)
Chen, P., Lu, Y., Wan, Y., et al.: Assessing carbon dioxide emissions of high-speed rail: the case of Bei**g-Shanghai corridor. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 97, 102949 (2021)
Lalive, R., Luechinger, S., Schmutzler, A.: Does expanding regional train service reduce air pollution? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 92, 744–764 (2018)
Li, H., Strauss, J., Liu, L.: A panel investigation on China’s carbon footprint. Sustainability 11(7), 2011 (2019)
Ren, T.X, Lin, J.Y.: Spatial spillover effect of high-speed rail on urban economic growth: evidence from 277 core cities. Math. Stat. Manag. 1–16 (2021)
Zheng, C.L., Zhang, J.T.: The impact of high-speed railway opening on urban innovation quality: An empirical study based on PSM-DID model. Techn. Econ. 40(02), 28–35 (2021)
Liu, J., Huang, X.F., Chen, J.: High-speed railway and high quality urban economic development: an empirical study based on the data of prefectural cities. Contemp. Finance Econ. 01, 14–26 (2021)
Beck, T., Levine, R., Levkov, A.: Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 65(5), 1637–1667 (2010)
Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., et al.: Parameters identification of photovoltaic models using a differential evolution algorithm based on elite and obsolete dynamic learning. Appl. Energy 314, 118877 (2022)
Yang, Z., Shang, W., Zhang, H., Garg, H., Han, C.: Assessing the green distribution transformer manufacturing process using a cloud-based fuzzy multi-criteria framework. Appl. Energy 118687 (2022)
Zhai, G.Y.: Overview of data analysis based on python. Gansu Sci. Technol. Rev. 47(11), 5–7+26 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, Q., Li, H., Shang, Wl., Wang, K. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Chinese Cities’ Air Quality and the Impact of High-Speed Rail to Promote Carbon Neutrality. In: Pagliara, F. (eds) Socioeconomic Impacts of High-Speed Rail Systems. IW-HSR 2022. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26340-8_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26340-8_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26339-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26340-8
eBook Packages: Economics and FinanceEconomics and Finance (R0)