Abstract
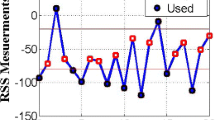
With the rapid development of vehicle intelligence, the in-vehicle network is no longer a traditional closed network. External devices can be connected through Bluetooth, WiFi or OBD interfaces, so that attackers can remotely attack vehicles through these channels. Hence we create one-time pads to protect the in-vehicle network. Intelligent connected vehicle (ICV) is an information physical system, thus finding a suitable entropy source from its physical properties to extract true random numbers as a one-time pad can well ensure the security of ICV. During the driving process of ICV, the driving decision will change in real time, and these changes will directly act on the generator of the vehicle’s power system, causing the voltage to change in real time. Therefore, we observe that the on-board power voltage of ICV is a very useful source of entropy. We propose a scheme to extract random numbers from the voltage entropy source. First, we filter the weak periodicity in the voltage signal using wavelet variations. After obtaining the non-periodic voltage signal, we fuse the high voltage time interval with it as a second entropy source to improve the extraction efficiency of the random numbers. Secondly, we build Markov chains by analysing the partial autocorrelation coefficient of the quantized bits of one trace. Finally, we extract perfect random numbers from the Markov chain by using cascaded XOR and hash function. Extensive realistic experiments are conducted to validate our scheme.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y., Luo, Q., Liu, J., Guo, H., Kato, N.: TSP security in intelligent and connected vehicles: challenges and solutions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 26(3), 125–131 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/MWC.2019.1800289
Aliwa, E., Rana, O., Perera, C., et al.: Cyberattacks and countermeasures for in-vehicle networks. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 54(1), 1–37 (2021)
Hu, Q., Luo, F.: Review of secure communication approaches for in-vehicle network. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 19(5), 879–894 (2018)
Liming, K., Haifeng, Y., Chunyi, C., et al.: Extraction of true random number based on atmospheric turbulence light flicker. Appl. Opt. 40(03), 165–172 (2019)
Herrero-Collantes, M., Garcia-Escartin, J.C.: Quantum random number generators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 89(1), 015004 (2017)
Clerk, A.A., Devoret, M.H., Girvin, S.M., et al.: Introduction to quantum noise, measurement, and amplification. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82(2), 1155 (2010)
Vizioli, L., Moeller, S., Dowdle, L., et al.: Lowering the thermal noise barrier in functional brain map** with magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–15 (2021)
Avaroğlu, E., Tuncer, T., Özer, A.B., et al.: A novel chaos-based post-processing for TRNG. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1), 189–199 (2015)
Sunar, B., Martin, W.J., Stinson, D.R.: A provably secure true random number generator with built - in tolerance to active attacks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 56(1), 109–119 (2007)
Rukhin, A., et al.: A statistical test suite for random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications. NIST Special Publication 800–22 Revision 1a, April 2010. https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-22r1a
Wu, H., Yin, Z., **e, J., et al.: Design and implementation of true random number generators based on semiconductor superlattice chaos. Microelectron. J. 114, 105119 (2021)
Baran, M.E., El-Markabi, I.M.: A multiagent-based dispatching scheme for distributed generators for voltage support on distribution feeders. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 22(1), 52–59 (2007)
Zhang, D.: Wavelet transform. In: Fundamentals of Image Data Mining. TCS, pp. 35–44. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17989-2_3
Liang, F., Song, Q., Qiu, P.: An equivalent measure of partial correlation coefficients for high-dimensional gaussian graphical models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 110(511), 1248–1265 (2015)
Csiszár, I., Shields, P.C.: The consistency of the BIC Markov order estimator. Ann. Stat. 28(6), 1601–1619 (2000)
Su, F., Wu, J., He, S.: Set pair analysis-Markov chain model for groundwater quality assessment and prediction: a case study of **’an city, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 25(1–2), 158–175 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Srivastava, A.: Accurate temperature estimation using noisy thermal sensors for Gaussian and non-Gaussian cases. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 19(9), 1617–1626 (2010)
Guo, X., Shu, Y., Kim, G.H., et al.: Pseudorandom orbiting stroke for freeform optics postprocessing. Opt. Eng. 58, 092608 (2019)
Li, Z., Cai, J., Chang, Y.: Determining the complexity of FH/SS sequence by approximate entropy. IEEE Trans. Commun. 57(3), 812–820 (2009)
Sýs, M., Říha, Z.: Faster randomness testing with the NIST statistical test suite. In: Chakraborty, R.S., Matyas, V., Schaumont, P. (eds.) SPACE 2014. LNCS, vol. 8804, pp. 272–284. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12060-7_18
Zhonghui, L., Chunyi, C., Haifeng, Y., et al.: Study on extraction of true random numbers based on propagated laser speckle in atmospheric turbulence. Infrared Laser Eng. 48(12), 1205005–1205005 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chu, J., Han, M., Ma, S. (2023). Extracting Random Secret Key Scheme for One-Time Pad Under Intelligent Connected Vehicle. In: Xu, Y., Yan, H., Teng, H., Cai, J., Li, J. (eds) Machine Learning for Cyber Security. ML4CS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13656. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20099-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20099-1_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20098-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20099-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)