Abstract
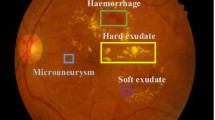
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is one of the most common retinal diseases caused by gene defects, which can lead to night blindness or complete blindness. Accurate diagnosis and lesion identification are significant tasks for clinicians to assess fundus images. However, due to some limitations, it is still challenging to design a method that can simultaneously diagnose and accomplish lesion identification so that the accurate lesion identification can promote the accuracy of diagnosis. In this paper, we propose a method based on weakly-supervised lesion-aware and consistency regularization to detect RP and generate lesion attention map (LAM). Specifically, we extend global average pooling to multiple scales, and use multi-scale features to offset the gap between semantic information and spatial information to generate a more refined LAM. At the same time, we regularize LAMs with different affine transforms for the same sample, and force them to produce more accurate predictions and reduce the overconfidence of the network, which can enhance LAM to cover lesions. We use two central datasets to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model. We train the proposed model in one dataset and test it in the other dataset to verify the generalization performance. Experimental results show that our method achieves promising performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hartong, D.T., Berson, E.L., Dryja, T.P.: Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 368, 1795–1809 (2006)
Cicinelli, M.V., Marchese, A., Bordato, A., Manitto, M.P., Bandello, F., Parodi, M.B.: Reviewing the role of ultra-widefield imaging in inherited retinal dystrophies. Ophthalmol. Ther. 1–15 (2020)
Olthoff, C.M., Schouten, J.S., van de Borne, B.W., Webers, C.A.: Noncompliance with ocular hypotensive treatment in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension: an evidence-based review. Ophthalmology 112, 953–961, e957 (2005)
Nagasato, D., et al.: Hayashi: deep neural network-based method for detecting central retinal vein occlusion using ultrawide-field fundus ophthalmoscopy. J. Ophthalmol. 2018 (2018)
Masumoto, H., et al.: Accuracy of a deep convolutional neural network in detection of retinitis pigmentosa on ultrawide-field images. PeerJ 7, e6900 (2019)
Litjens, G., et al.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Liao, W., Zou, B., Zhao, R., Chen, Y., He, Z., Zhou, M.: Clinical interpretable deep learning model for glaucoma diagnosis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24, 1405–1412 (2019)
Wang, Z., Yin, Y., Shi, J., Fang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Zoom-in-net: deep mining lesions for diabetic retinopathy detection. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10435, pp. 267–275. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_31
Zhao, R., Liao, W., Zou, B., Chen, Z., Li, S.: Weakly-supervised simultaneous evidence identification and segmentation for automated glaucoma diagnosis. In: AAAI, pp. 809–816 (2019)
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: CVPR, pp. 2921–2929 (2016)
Tang, M., Perazzi, F., Djelouah, A., Ayed, I.B., Schroers, C., Boykov, Y.: On Regularized losses for weakly-supervised CNN segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11220, pp. 524–540. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01270-0_31
Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Kan, M., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Self-supervised equivariant attention mechanism for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 12275–12284 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Masahiro, K.: masumoto RP data normal optos (2018). https://figshare.com/articles/masumoto_RP_data_normal_optos/7403825
Masahiro, K.: masumoto RP data RP optos (2018). https://figshare.com/articles/masumoto_RP_data_RP_optos/7403831
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: ICLR (2015)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: CVPR, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61871274, 61801305 and 81571758), National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2020A1515010649 and No. 2019A1515 111205), Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Popular High Performance Computers (No. 2017B030314073), Guangdong Laboratory of Artificial-Intelligence and Cyber-Economics (SZ), Shenzhen Peacock Plan (Nos. KQTD2016053112051497 and KQTD2015033016104926), Shenzhen Key Basic Research Project (Nos. JCYJ201908 08165209410, 20190808145011259, JCYJ20180507184647636, GJHZ20190822095 414576 and JCYJ20170302153337765, JCYJ20170302150411789, JCYJ2017030214 2515949, GCZX2017040715180580, GJHZ20180418190529516, and JSGG2018050 7183215520), NTUT-SZU Joint Research Program (No. 2020003), Special Project in Key Areas of Ordinary Universities of Guangdong Province (No. 2019KZDZX1015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, B. et al. (2020). Weakly-Supervised Lesion-Aware and Consistency Regularization for Retinitis Pigmentosa Detection from Ultra-Widefield Images. In: Fu, H., Garvin, M.K., MacGillivray, T., Xu, Y., Zheng, Y. (eds) Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis. OMIA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12069. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63419-3_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63419-3_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63418-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63419-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)