Abstract
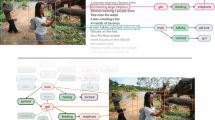
We propose Localized Narratives, a new form of multimodal image annotations connecting vision and language. We ask annotators to describe an image with their voice while simultaneously hovering their mouse over the region they are describing. Since the voice and the mouse pointer are synchronized, we can localize every single word in the description. This dense visual grounding takes the form of a mouse trace segment per word and is unique to our data. We annotated 849k images with Localized Narratives: the whole COCO, Flickr30k, and ADE20K datasets, and 671k images of Open Images, all of which we make publicly available. We provide an extensive analysis of these annotations showing they are diverse, accurate, and efficient to produce. We also demonstrate their utility on the application of controlled image captioning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amodei, D., et al.: Deep speech 2: end-to-end speech recognition in English and Mandarin. In: ICML (2016)
Anderson, P., Fernando, B., Johnson, M., Gould, S.: SPICE: semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In: ECCV (2016)
Anderson, P., et al.: Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: CVPR (2018)
Antol, S., et al.: VQA: visual question answering. In: ICCV (2015)
Benenson, R., Popov, S., Ferrari, V.: Large-scale interactive object segmentation with human annotators. In: CVPR (2019)
Bigham, J.P., et al.: VizWiz: nearly real-time answers to visual questions. In: Proceedings of the 23nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (2010)
Changpinyo, S., Pang, B., Sharma, P., Soricut, R.: Decoupled box proposal and featurization with ultrafine-grained semantic labels improve image captioning and visual question answering. In: EMNLP-IJCNLP (2019)
Chen, X., et al.: Microsoft COCO captions: data collection and evaluation server. ar**v (2015)
Cirik, V., Morency, L.P., Berg-Kirkpatrick, T.: Visual referring expression recognition: what do systems actually learn? In: NAACL (2018)
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cucchiara, R.: Show, control and tell: a framework for generating controllable and grounded captions. In: CVPR (2019)
Dai, D.: Towards cost-effective and performance-aware vision algorithms. Ph.D. thesis, ETH Zurich (2016)
Damen, D., et al.: The EPIC-KITCHENS dataset: collection, challenges and baselines. IEEE Trans. PAMI (2020)
Dogan, P., Sigal, L., Gross, M.: Neural sequential phrase grounding (seqground). In: CVPR (2019)
Google cloud speech-to-text API. https://cloud.google.com/speech-to-text/
Graves, A., Mohamed, A.R., Hinton, G.: Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: ICASSP (2013)
Gygli, M., Ferrari, V.: Efficient object annotation via speaking and pointing. In: IJCV (2019)
Gygli, M., Ferrari, V.: Fast object class labelling via speech. In: CVPR (2019)
Harwath, D., Recasens, A., Surís, D., Chuang, G., Torralba, A., Glass, J.: Jointly discovering visual objects and spoken words from raw sensory input. In: ECCV (2018)
Honnibal, M., Montani, I.: spaCy 2: natural language understanding with Bloom embeddings, convolutional neural networks and incremental parsing (2017). spacy.io
Hudson, D.A., Manning, C.D.: GQA: a new dataset for real-world visual reasoning and compositional question answering. In: CVPR (2019)
Johnson, J., Karpathy, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Densecap: fully convolutional localization networks for dense captioning. In: CVPR (2016)
Kahneman, D.: Attention and effort. Citeseer (1973)
Kalchbrenner, N., et al.: Efficient neural audio synthesis. In: ICML (2018)
Kazemzadeh, S., Ordonez, V., Matten, M., Berg, T.: Referitgame: referring to objects in photographs of natural scenes. In: EMNLP (2014)
Kim, D.J., Choi, J., Oh, T.H., Kweon, I.S.: Dense relational captioning: triple-stream networks for relationship-based captioning. In: CVPR (2019)
Krause, J., Johnson, J., Krishna, R., Fei-Fei, L.: A hierarchical approach for generating descriptive image paragraphs. In: CVPR (2017)
Krishna, R., et al.: Visual genome: connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. IJCV 123(1), 32–73 (2017)
Kruskal, J.B., Liberman, M.: The symmetric time-war** problem: from continuous to discrete. In: Time Warps, String Edits, and Macromolecules - The Theory and Practice of Sequence Comparison, chap. 4. CSLI Publications (1999)
Kuznetsova, A., et al.: The Open Images Dataset V4: Unified image classification, object detection, and visual relationship detection at scale. ar**v preprint ar**v:1811.00982 (2018)
Lin, C.Y.: ROUGE: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Text Summarization Branches Out (2004)
Lin, T.Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: ECCV (2014)
Liu, C., Mao, J., Sha, F., Yuille, A.: Attention correctness in neural image captioning. In: AAAI (2017)
Lu, J., Yang, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D.: Neural baby talk. In: CVPR (2018)
Malinowski, M., Rohrbach, M., Fritz, M.: Ask your neurons: a neural-based approach to answering questions about images. In: ICCV (2015)
Mao, J., Huang, J., Toshev, A., Camburu, O., Yuille, A.L., Murphy, K.: Generation and comprehension of unambiguous object descriptions. In: CVPR (2016)
Mehri, S., et al.: Samplernn: an unconditional end-to-end neural audio generation model. In: ICLR (2017)
Oord, A.V.D., et al.: Wavenet: a generative model for raw audio. ar**v 1609.03499 (2016)
Oviatt, S.: Multimodal interfaces. In: The Human-Computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies and Emerging Applications (2003)
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.J.: Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: ACL (2002)
Plummer, B.A., Wang, L., Cervantes, C.M., Caicedo, J.C., Hockenmaier, J., Lazebnik, S.: Flickr30k entities: collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models. IJCV 123(1), 74–93 (2017)
Ravanelli, M., Parcollet, T., Bengio, Y.: The Pytorch-Kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In: ICASSP (2019)
Reed, S.E., Akata, Z., Mohan, S., Tenka, S., Schiele, B., Lee, H.: Learning what and where to draw. In: NeurIPS, pp. 217–225 (2016)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: NeurIPS (2015)
Rohrbach, A., Hendricks, L.A., Burns, K., Darrell, T., Saenko, K.: Object hallucination in image captioning. In: EMNLP (2018)
Selvaraju, R.R., et al.: Taking a HINT: leveraging explanations to make vision and language models more grounded. In: ICCV (2019)
Sharma, P., Ding, N., Goodman, S., Soricut, R.: Conceptual captions: a cleaned, hypernymed, image alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning. In: ACL (2018)
Tan, F., Feng, S., Ordonez, V.: Text2scene: generating compositional scenes from textual descriptions. In: CVPR (2019)
Vaidyanathan, P., Prud, E., Pelz, J.B., Alm, C.O.: SNAG : spoken narratives and gaze dataset. In: ACL (2018)
Vasudevan, A.B., Dai, D., Van Gool, L.: Object referring in visual scene with spoken language. In: CVPR (2017)
Vedantam, R., Lawrence Zitnick, C., Parikh, D.: CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation. In: CVPR (2015)
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., Erhan, D.: Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: CVPR (2015)
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., Erhan, D.: Show and tell: lessons learned from the 2015 MSCOCO image captioning challenge. IEEE Trans. PAMI 39(4), 652–663 (2016)
Website: Localized Narratives Data and Visualization (2020). https://google.github.io/localized-narratives
Wu, S., Wieland, J., Farivar, O., Schiller, J.: Automatic alt-text: computer-generated image descriptions for blind users on a social network service. In: Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (2017)
Xu, K., et al.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: ICML (2015)
Yan, S., Yang, H., Robertson, N.: ParaCNN: visual paragraph generation via adversarial twin contextual CNNs. ar**v (2020)
Yin, G., Liu, B., Sheng, L., Yu, N., Wang, X., Shao, J.: Semantics disentangling for text-to-image generation. In: CVPR (2019)
Yin, G., Sheng, L., Liu, B., Yu, N., Wang, X., Shao, J.: Context and attribute grounded dense captioning. In: CVPR (2019)
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., Hockenmaier, J.: From image descriptions to visual denotations: new similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. TACL 2, 67–78 (2014)
Yu, J., Li, J., Yu, Z., Huang, Q.: Multimodal transformer with multi-view visual representation for image captioning. ar**v 1905.07841 (2019)
Zhao, Y., Wu, S., Reynolds, L., Azenkot, S.: The effect of computer-generated descriptions on photo-sharing experiences of people with visual impairments. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 1 (2017)
Zhou, B., Zhao, H., Puig, X., Fidler, S., Barriuso, A., Torralba, A.: Semantic understanding of scenes through the ADE20K dataset. IJCV 127(3), 302–321 (2019)
Zhou, L., Kalantidis, Y., Chen, X., Corso, J.J., Rohrbach, M.: Grounded video description. In: CVPR (2019)
Ziegler, Z.M., Melas-Kyriazi, L., Gehrmann, S., Rush, A.M.: Encoder-agnostic adaptation for conditional language generation. ar**v (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pont-Tuset, J., Uijlings, J., Changpinyo, S., Soricut, R., Ferrari, V. (2020). Connecting Vision and Language with Localized Narratives. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, JM. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2020. ECCV 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12350. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58557-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58558-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)