Abstract
We propose a compressive spectral collocation method for the numerical approximation of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). The approach is based on a spectral Sturm-Liouville approximation of the solution and on the collocation of the PDE in strong form at randomized points, by taking advantage of the compressive sensing principle. The proposed approach makes use of a number of collocation points substantially less than the number of basis functions when the solution to recover is sparse or compressible. Focusing on the case of the diffusion equation, we prove that, under suitable assumptions on the diffusion coefficient, the matrix associated with the compressive spectral collocation approach satisfies the restricted isometry property of compressive sensing with high probability. Moreover, we demonstrate the ability of the proposed method to reduce the computational cost associated with the corresponding full spectral collocation approach while preserving good accuracy through numerical illustrations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
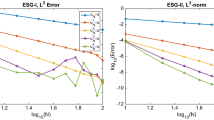
The substantial independence of the OMP recovery cost with respect to s for the full approach depends on two factors: the particular implementation of OMP in the package OMP-Box and the normalization step \(\widetilde {A} = A M^{-1}\) in Algorithm 1. In fact, in order to speed up the OMP iteration, the function omp of OMP-Box used to produce these results takes \(\widetilde {A}^T\widetilde {A}\) as input. When A is N × N, the cost of computing the matrices \(\widetilde {A}\) and \(\widetilde {A}^T\widetilde {A}\) is independent of s and it turns out to be consistently larger than the cost of OMP itself. As a result, the effect of s on the overall computational cost is negligible. The same remark holds for Fig. 4.
References
Adcock, B.: Univariate modified fourier methods for second order boundary value problems. BIT Numer. Math. 49(2), 49–280 (2009)
Adcock, B.: Multivariate modified Fourier series and application to boundary value problems. Numer. Math. 115(4), 511–552 (2010)
Adcock, B., Brugiapaglia, S., Webster, C.G.: Compressed sensing approaches for polynomial approximation of high-dimensional functions. In: Compressed Sensing and its Applications, pp. 93–124. Springer, Cham (2017)
Alberti, G.S., Santacesaria, M.: Infinite dimensional compressed sensing from anisotropic measurements (2017). Preprint. ar**v:1710.11093
Bouchot, J.-L., Rauhut, H., Schwab, C.: Multi-level compressed sensing Petrov-Galerkin discretization of high-dimensional parametric PDEs (2017). Preprint. ar**v:1701.01671
Brugiapaglia, S.: COmpRessed SolvING: sparse approximation of PDEs based on compressed sensing. PhD thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Italy (2016)
Brugiapaglia, S., Micheletti, S., Perotto, S.: Compressed solving: a numerical approximation technique for elliptic PDEs based on compressed sensing. Comput. Math. Appl. 70(6), 1306–1335 (2015)
Brugiapaglia, S., Nobile, F., Micheletti, S., Perotto, S.: A theoretical study of COmpRessed SolvING for advection-diffusion-reaction problems. Math. Comput. 87(309), 1–38 (2018)
Candès, E.J., Romberg, J., Tao, T.: Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
Canuto, C., Hussaini, M.Y., Quarteroni, A.M., Zhang, T.A.: Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics. Springer Science & Business Media, New York (2012)
Chkifa, A., Dexter, N., Tran, H., Webster, C.G.: Polynomial approximation via compressed sensing of high-dimensional functions on lower sets. Math. Comput. 87(311), 1415 (2018)
Daubechies, I., Runborg, O., Zou, J.: A sparse spectral method for homogenization multiscale problems. Multiscale Model. Simul. 6(3), 711–740 (2007)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Doostan, A., Owhadi, H.: A non-adapted sparse approximation of PDEs with stochastic inputs. J. Comput. Phys. 230(8), 3015–3034 (2011)
Foucart, S., Rauhut, H.: A Mathematical Introduction to Compressive Sensing. Birkhäuser, Basel (2013)
Gottlieb, D., Orszag, S.A.: Numerical Analysis of Spectral Methods: Theory and Applications, vol. 26. SIAM, Philadelphia (1977)
Guermond, J.-L.: A finite element technique for solving first-order PDEs in L p. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(2), 714–737 (2004)
Guermond, J.-L., Popov, B.: An optimal L 1-minimization algorithm for stationary Hamilton-Jacobi equations. Commun. Math. Sci. 7(1), 211–238 (2009)
Iserles, A., Nørsett, S.P.: From high oscillation to rapid approximation I: modified Fourier expansions. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 28(4), 862–887 (2008)
Iserles, A., Nørsett, S.P.: From high oscillation to rapid approximation III: multivariate expansions. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 29(4), 882–916 (2009)
Jokar, S., Mehrmann, V., Pfetsch, M.E., Yserentant, H.: Sparse approximate solution of partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60(4), 452–472 (2010). Special Issue: NUMAN 2008
Krahmer, F., Ward, R.: Stable and robust sampling strategies for compressive imaging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(2), 612–622 (2014)
Lavery, J.E.: Nonoscillatory solution of the steady-state inviscid Burgers’ equation by mathematical programming. J. Comput. Phys. 79(2), 436–448 (1988)
Lavery, J.E.: Solution of steady-state one-dimensional conservation laws by mathematical programming. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 26(5), 1081–1089 (1989)
Mackey, A., Schaeffer, H., Osher, S.: On the compressive spectral method. Multiscale Model. Simul. 12(4), 1800–1827 (2014)
Mathelin, L., Gallivan, K.A.: A compressed sensing approach for partial differential equations with random input data. Commun. Comput. Phys. 12(4), 919–954 (2012)
Peng, J., Hampton, J., Doostan, A.: A weighted ℓ 1-minimization approach for sparse polynomial chaos expansions. J. Comput. Phys. 267, 92–111 (2014)
Rauhut, H., Schwab, C.: Compressive sensing Petrov-Galerkin approximation of high-dimensional parametric operator equations. Math. Comput. 86(304), 661–700 (2017)
Rubinstein, R., Zibulevsky, M., Elad, M.: Efficient implementation of the K-SVD algorithm using batch orthogonal matching pursuit. Technical report, Computer Science Department, Technion (2008)
Schaeffer, H., Caflisch, R., Hauck, C.D., Osher, S.: Sparse dynamics for partial differential equations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110(17), 6634–6639 (2013)
Temlyakov, V.N.: Nonlinear methods of approximation. Found. Comput. Math. 3(1), 33 (2003)
Tran, G., Ward, R.: Exact recovery of chaotic systems from highly corrupted data. Multiscale Model. Simul. 15(3), 1108–1129 (2017)
Yang, X., Karniadakis, G.E.: Reweighted ℓ 1 minimization method for stochastic elliptic differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 248, 87–108 (2013)
Zhang, T.: Sparse recovery with orthogonal matching pursuit under RIP. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 57(9), 6215–6221 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada through grant number 611675 and the Pacific Institute for the Mathematical Sciences (PIMS) through the program “PIMS Postdoctoral Training Centre in Stochastics”. Moreover, the author gratefully acknowledge Ben Adcock and the anonymous reviewer for providing helpful comments on the first version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 National Technology & Engineering Solutions of Sandia, and The Editor(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Brugiapaglia, S. (2020). A Compressive Spectral Collocation Method for the Diffusion Equation Under the Restricted Isometry Property. In: D'Elia, M., Gunzburger, M., Rozza, G. (eds) Quantification of Uncertainty: Improving Efficiency and Technology. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol 137 . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48721-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48721-8_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-48720-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-48721-8
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)