Abstract
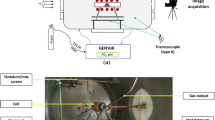
The effect of alumina ceramics surface roughness on the wetting characteristics of liquid lead was investigated by the sessile drop method. The surface 3D appearance and surface roughness of the alumina substrate were measured by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). The interface micrographs of lead and alumina substrates were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that as the alumina substrate surface roughness increases, the contact angle of the lead drop increases, the drop height increases, the contact diameter decreases, and the adsorption work decreases. An obvious pinning effect was observed during the wetting process, and the potential mechanism of the wetting behavior was described on the basis of Wenzel equation. This work provides a theoretical basis for the application of alumina ceramics in the lead industry.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu P, Coyle TW, Pershin L, Mostaghimi J (2018) Superhydrophobic ceramic coating: Fabrication by solution precursor plasma spray and investigation of wetting behavior. J Colloid Interface Sci 523:35–44
Wu M, He X, Ren S, Qin M, Qu X (2009) Effect of various Ni plating layers and aging on microstructure and shear strength of Sn–2.5 Ag–2.0 Ni solder joint. Surf Coat Technol 203:3011–3018
Protsenko P, Terlain A, Traskine V, Eustathopoulos N (2001) The role of intermetallics in wetting in metallic systems. Scr Mater 45:1439–1445
Cong XS, Shen P, Wang Y, Jiang Q (2014) Wetting of polycrystalline SiC by molten Al and Al–Si alloys. Appl Surf Sci 317:140–146
Sangghaleh A, Halali M (2009) Effect of magnesium addition on the wetting of alumina by aluminium. Appl Surf Sci 255:8202–8206
Wang J, Matsuda N, Shinozaki N, Miyoshi N, Shiraishi T (2015) Effect of SUS316L stainless steel surface conditions on the wetting of molten multi-component oxides ceramic. Appl Surf Sci 327:470–477
Singh AK, Singh JK (2017) Fabrication of durable super-repellent surfaces on cotton fabric with liquids of varying surface tension: low surface energy and high roughness. Appl Surf Sci 416:639–648
Liang Y, Shu L, Natsu W, He F (2015) Anisotropic wetting characteristics versus roughness on machined surfaces of hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials. Appl Surf Sci 331:41–49
Riahi S, Niroumand B, Moghadam AD, Rohatgi PK (2018) Effect of microstructure and surface features on wetting angle of a Fe-3.2 wt% CE cast iron with water. Appl Surf Sci 440:341–350
Ma GF, Li ZK, Ye H, He CL, Zhang HF, Hu ZQ (2015) Wetting and interface phenomena in the molten Sn/CuFeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy system. Appl Surf Sci 356:460–466
Yuan ZF, Mukai K, Huang WL (2002) Surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten silicon at different oxygen potentials. Langmuir 18:2054–2062
Yuan ZF, Mukai K, Takagi K, Ohtaka M, Huang WL, Liu QS (2002) Surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten tin determined with the sessile drop method at different oxygen partial pressures. J Colloid Interface Sci 254:338–345
Zou X, Zhao D, Sun J, Wang C, Matsuura H (2018) An integrated study on the evolution of inclusions in EH36 shipbuilding steel with Mg addition: from casting to welding. Metall Mater Trans B 49:481–489
Volceanov E, Volceanov A, Stoleriu Ş (2007) Assessment on mechanical properties controlling of alumina ceramics for harsh service conditions. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:759–762
Yuan ZF, Fan J, Li J, Ke J, Mukai K (2004) Surface tension of molten bismuth at different oxygen partial pressure with the sessile drop method. Scandinavian J Metall 33:338–346
Wenzel RN (1936) Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. J Ind Eng Chem 28:988–994
Kumar G, Prabhu KN (2007) Review of non-reactive and reactive wetting of liquids on surfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 133:61–89
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1738101) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. FRF-TP-18-007A1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qi, Z., Yuan, Z.F. (2020). Effect of Alumina Ceramics Surface Condition on the Wetting of Liquid Lead. In: Siegmund, A., Alam, S., Grogan, J., Kerney, U., Shibata, E. (eds) PbZn 2020: 9th International Symposium on Lead and Zinc Processing. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37070-1_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37070-1_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-37069-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-37070-1
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)