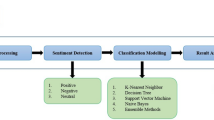
Abstract
The mounting global interest of users in social media portals has reinforced research in knowledge discovery domains to mine useful information from the publicly available user-generated big data. Uncertainty is often linked with the online content, mostly owing to the diverse, noisy, or unstructured data which might be imprecise or vague. Determining appropriate features that could yield enhanced sentiment predictive accuracy becomes a tedious and an arduous task which motivates for automating the sentiment classification predictive task. The empirical study is investigated on the tweets fetched from two standard Twitter datasets namely SemEval 2016 & SemEval 2017. Consequently, we propose the use of swarm based feature selection for enhancing classifier efficiency. The proposed feature selection using PSO outperforms baseline ensemble learning algorithm trained using conventional tf-idf. An average 8.5% improvement in accuracy with 33% reduction in feature set is obtained by implementing particle swarm optimization.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Natural Language Toolkit: https://www.nltk.org/.
References
Kumar, A., Abraham, A.: Opinion mining to assist user acceptance testing for open-beta versions. J. Inf. Assur. Secur. 12(4), 146–153 (2017)
Kumar, A., Joshi, A.: Ontology driven sentiment analysis on social web for government intelligence. In: Proceedings of the Special Collection on eGovernment Innovations in India, pp. 134–139. ACM (2017)
Kumar, A., Dogra, P., Dabas, V.: Emotion analysis of Twitter using opinion mining. In: Contemporary Computing, 8th International Conference on IC3, pp. 285–290. IEEE (2015)
Kumar, A., Sebastian, T.M.: Machine learning assisted sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Science & Engineering, ICCSE, pp. 123–130 (2012)
Kumar, A., Jaiswal, A.: Systematic literature review of sentiment analysis on twitter using soft computing techniques. Concur. Comput. Pract. Exp. (2019). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5107
Allahyari, M., Pouriyeh, S., Assefi, M., Safaei, S., Trippe, E.D., Gutierrez, J.B., Kochut, K.: A brief survey of text mining: classification, clustering and extraction techniques. In: Proceedings of KDD Bigdas, pp. 0–13 (2017)
Kumar, A., Jaiswal, A.: Empirical study of twitter and tumblr for sentiment analysis using soft computing techniques. In: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 1, pp. 1–5 (2017)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends® Inf. Retr. 2(1–2), 1–135 (2017)
Sharma, S.K., Hoque, X., Chandra, P.: Sentiment predictions using deep belief networks model for odd-even policy in Delhi. Int. J. Synth. Emot. (IJSE) 7(2), 1–22 (2016)
Kumar, A., Sebastian, T.M.: Sentiment analysis on twitter. IJCSI Int. J. Comput. Sci. 9(4), 372–378 (2012)
Kumar, A., Sebastian, T.M.: Sentiment analysis: a perspective on its past, present and future. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 4(10), 1–14 (2012)
Kumar, A., Khorwal, R., Chaudhary, S.: A survey on sentiment analysis using swarm intelligence. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 9(39), 1–7 (2016)
Kumar, A., Jaiswal, A., Garg, S., Verma, S., Kumar, S.: Sentiment analysis using cuckoo search for optimized feature selection on kaggle tweets. Int. J. Inf. Retr. Res. 9, 1–15 (2019)
Shahana, P.H., Omman, B.: Evaluation of features on sentimental analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 46, 1585–1592 (2015). Elsevier
Dave, K., Lawrence, S., Pennock, D.M.: Mining the peanut gallery: opinion extraction and semantic classification of product reviews. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on World Wide Web, Hungary, pp. 19–528 (2003)
Basari, A.S.H., Hussin, B., Ananta, I.G.P., Zeniarja, J.: Opinion mining of movie review using hybrid method of support vector machine and particle swarm optimization. Procedia Eng. 53, 453–462 (2013). Elsevier
da Silva, N.F.F., et al. Tweet sentiment analysis with classifier ensembles. Decis. Support Syst. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2014.07.003
Wang, G., et al.: Sentiment classification: the contribution of ensemble learning. Decis. Support Syst. (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.08.002
Wan, Y., Gao, Q.: An ensemble sentiment classification system of twitter data for airline services analysis. In: IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1318–1325 (2015)
Kanakaraj, M., Guddeti, R.M.R.: Performance analysis of ensemble methods on Twitter sentiment analysis using NLP techniques. In: IEEE International Conference on Semantic Computing, pp. 169–170 (2015)
**a, R., Xu, F., Yu, J., Qi, Y., Cambria, E.: Polarity shift detection, elimination and ensemble: a three-stage model for document-level sentiment analysis. Inf. Process. Manag. 52(1), 36–45 (2016)
Gupta, D.K., Reddy, K.S., Ekbal, A.S.: PSO-ASent: feature selection using particle swarm optimization for aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Biemann, C., Handschuh, S., Freitas, A., Meziane, F., Métais, E. (eds.) Natural Language Processing and Information Systems, NLDB 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9103. Springer, Cham (2015)
Catal, C., Nangir, M.: A sentiment classification model based on multiple classifiers. Appl. Soft Comput. 50, 135–141 (2017)
Akhtar, M.S., Gupta, D., Ekbal, A., Bhattacharyya, P.: Feature selection and ensemble construction: a two-step method for aspect based sentiment analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 125, 116–135 (2017)
Fouad, M.M., Gharib, T.F., Mashat, A.S.: Efficient Twitter sentiment analysis system with feature selection and classifier ensemble. In: Hassanien, A., Tolba, M., Elhoseny, M., Mostafa, M. (eds.) The International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications (AMLTA2018), AMLTA 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol. 723. Springer, Cham (2018)
Jain, D., Kumar, A., Sangwan, S.R., Nguyen, G.N., Tiwari, P.: A particle swarm optimized learning model of fault classification in webapps. IEEE Access 7, 18480–18489 (2019). IEEE, 2894871. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019
Rosenthal, S., Farra, N., Nakov, P., SemEval-2017 task 4: Sentiment analysis in Twitter. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), pp. 502–518. Association of Computational Linguistics (2017)
SemEval-2017 Task 4: Sentiment Analysis in Twitter. http://alt.qcri.org/semeval2017/task4/. Accessed 2 Jan 2018
Sulis, E., Farías, D., Rosso, P., Patti, V., Ruffo, G.: Figurative messages and affect in Twitter. Knowl. Based Syst. 108(C), 132–143 (2016)
Omar, N., Jusoh, F., Ibrahim, R., et al.: Review of feature selection for solving classification problems. J. Inf. Syst. Res. Innov. 3, 64–70 (2013)
Omar, N., Othman, M.S.: Particle swarm optimization feature selection for classification of survival analysis in cancer. Int. J. Innov. Comput. 2(1), 1–7 (2013)
Shi, Y., Eberhart, R.C.: A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference Evolutionary Computation, Anchorage, AK, USA, pp. 69–73 (1998)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.C.. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference Neural Networks, Perth, pp. 1942–1948 (1995)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.C.: A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, pp. 39–43 (1995)
Athanasiou, V., Maragoudakis, M.: A novel, gradient boosting framework for sentiment analysis in languages where NLP resources are not plentiful: a case study for modern Greek. Algorithms 10(34), 1–21 (2017)
Wijesinghe, I.: Sentiment Analysis (2015)
Geurts, P., Ernst, D., Wehenkel, L.: Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 63, 3–42 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1
Wang, X., Yang, J., Teng, X.: Feature selection based on rough sets and particle swarm optimization. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 28(4), 459–471 (2007)
Aghdam, M.H., Heidari, S.: Feature selection using particle swarm optimization in text categorization. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 5(4), 231–238 (2015)
Kumar, A., Garg, G.: Systematic Literature Review on Context-Based Sentiment Analysis in Social Multimedia, Multimedia tools and Applications (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7346-5
Kumar, V. Dabas, P.H.: Text classification algorithms for mining unstructured data: a swot analysis. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 1–11 (2017). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-017-0072-1. ISSN (Print): 2511-2104, ISSN (Online): 2511-2112
Kumar, A., Jaiswal, A.: Swarm intelligence based optimal feature selection for enhanced predictive sentiment accuracy on twitter. Multimed. Tools Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7278-0
Kumar, A., Khorwal R.: Firefly algorithm for feature selection in sentiment analysis. In: International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Mining (ICCIDM-2016), Springer Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing (AISC) Series, vol. 556. Springer (2016)
Sharma, S.K., Hoque, X.: Sentiment predictions using support vector machines for odd-even formula in Delhi. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 9(7), 61–69 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, A., Jaiswal, A. (2020). Particle Swarm Optimized Ensemble Learning for Enhanced Predictive Sentiment Accuracy of Tweets. In: Singh, P., Panigrahi, B., Suryadevara, N., Sharma, S., Singh, A. (eds) Proceedings of ICETIT 2019. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 605. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30577-2_56
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30577-2_56
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-30576-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-30577-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)