Abstract
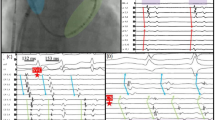
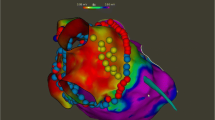
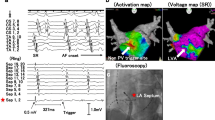
Non-pulmonary veins triggers improve the rate of freedom of AF. Most of them can be targeted with focal ablation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(10):659–66.
Suzuki S, Sagara K, Otsuka T, Kano H, Matsuno S, Takai H, et al. Usefulness of frequent supraventricular extrasystoles and a high CHADS2 score to predict first-time appearance of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111(11):1602–7.
Gladstone DJ, Dorian P, Spring M, Panzov V, Mamdani M, Healey JS, et al. Atrial premature beats predict atrial fibrillation in cryptogenic stroke: results from the EMBRACE trial. Stroke. 2015;46(4):936–41.
Kanda T, Masuda M, Fujita M, Iida O, Okamoto S, Ishihara T, et al. Comparison of the origin and coupling interval between ectopy with and without atrial fibrillation initiation. J Cardiol. 2018;71(1):59–64.
Gianni C, Mohanty S, Trivedi C, Di Biase L, Natale A. Novel concepts and approaches in ablation of atrial fibrillation: the role of non-pulmonary vein triggers. Europace. 2018;20(10):1566–76.
Santangeli P, Zado ES, Hutchinson MD, Riley MP, Lin D, Frankel DS, et al. Prevalence and distribution of focal triggers in persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13(2):374–82.
Santangeli P, Marchlinski FE. Techniques for the provocation, localization, and ablation of non-pulmonary vein triggers for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(7):1087–96.
Gokoglan Y, Mohanty S, Güneş MF, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Gianni C, et al. Pulmonary vein antrum isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: more than a decade of follow-up. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016;9(5):e003660.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Romero, J., Gomez, I.A., Grushko, M., Diaz, J.C., Natale, V., Di Biase, L. (2020). Septal Atrial Premature Contraction Induced Atrial Fibrillation. In: Natale, A., Wang, P., Al-Ahmad, A., Estes, N. (eds) Cardiac Electrophysiology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28533-3_84
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28533-3_84
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-28531-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-28533-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)