Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), are short RNA sequences involved in targeting post transcriptional gene regulation. These mature miRNAs are derived from longer sequence precursors (pre-miRNAs) (70nt-100nt in mammalian) and have been shown to integrate multiple genes into biologically networks. Previously, we have shown that pre-miRNAs can be categorized into their species of origin using sequence-based features (such as frequency of k-mer) and machine learning.
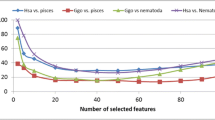
In this study, we introduce a new set of features which are extracted from the precursor sequence that based Hamming distance between k-mer and pre-miRNAs sequence. These new set of features reveal an interesting result where in some cases it outperforms the k-mer frequency.
In the Hamming distance, we consider k-mers words with k = 4 and k = 5 while in k-mer frequency we consider k = 1, 2, 3. Hamming distance allows mismatches (flexible match) while k-mer frequency require the appearance of the whole word with length k. The Hamming flexibility allows getting more accurate representation to some clades and results in improving the performance.
This study suggests that there is no one universal feature set that applicable to all microRNA clades, so one needs to examine a different set of features and apply a function that associates the best set of feature to each clade.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grey, F.: Role of microRNAs in herpesvirus latency and persistence. J. Gen. Virol. 96, 739–751 (2015)
Zhang, B., Pan, X., Cobb, G.P., Anderson, T.A.: Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev. Biol. [Internet] 289, 3–16 (2006). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012160605007645
Yousef, M., Allmer, J., Khalifa, W.: Sequence motif-based one-class classifiers can achieve comparable accuracy to two-class learners for plant microRNA detection. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. [Internet] 08, 684–94 (2015). http://www.scirp.org/journal/PaperDownload.aspx?DOI=10.4236/jbise.2015.810065
Yousef, M., Saçar Demirci, M.D., Khalifa, W., Allmer, J.: Feature selection has a large impact on one-class classification accuracy for MicroRNAs in plants. Adv. Bioinform. [Internet] 2016, 1–6 (2016). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301244460_Feature_Selection_Has_a_Large_Impact_on_One-Class_Classification_Accuracy_for_MicroRNAs_in_Plants
Saçar, M.D., Allmer, J.: Current limitations for computational analysis of miRNAs in cancer. Pak. J. Clin. Biomed. Res. 1, 3–5 (2013)
Yousef, M., Jung, S., Kossenkov, A.V., Showe, L.C., Showe, M.K.: Naive Bayes for microRNA target predictions machine learning for microRNA targets [Internet], pp. 2987–2992 (2007). http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/23/22/2987
Yousef, M., Nebozhyn, M., Shatkay, H., Kanterakis, S., Showe, L.C., Showe, M.K.: Combining multi-species genomic data for microRNA identification using a Naive Bayes classifier. Bioinformatics [Internet] 22, 1325–1334 (2006). http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/22/11/1325
Krek, A., Grün, D., Poy, M.N., Wolf, R., Rosenberg, L., Epstein, E.J., et al.: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet. 37, 495–500 (2005)
Lim, L.P., Lau, N.C., Weinstein, E.G., Abdelhakim, A., Yekta, S., Rhoades, M.W., et al.: The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 17, 991–1008 (2003)
Dang, H.T., Tho, H.P., Satou, K., Tu, B.H.: Prediction of microRNA hairpins using one-class support vector machines. In: 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE 2008, pp. 33–36 (2008)
Khalifa, W., Yousef, M., Sacar Demirci, M.D., Allmer, J.: The impact of feature selection on one and two-class classification performance for plant microRNAs. PeerJ 4, e2135 (2016) (United States)
Yousef, M., Jung, S., Showe, L.C., Showe, M.K.: Learning from positive examples when the negative class is undetermined–microRNA gene identification. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 3, 2 (2008)
Saçar Demirci, M.D., Baumbach, J., Allmer, J.: On the performance of pre-microRNA detection algorithms. Nat. Commun. 8, 330 (2017)
Yones, C.A., Stegmayer, G., Kamenetzky, L., Milone, D.H.: miRNAfe: a comprehensive tool for feature extraction in microRNA prediction. Biosystems 138, 1–5 (2015) (Elsevier Ireland Ltd.)
Peterson, S.M., Thompson, J.A., Ufkin, M.L., Sathyanarayana, P., Liaw, L., Congdon, C.B.: Common features of microRNA target prediction tools. Front. Genet. (2014)
Lai, E.C., Tomancak, P., Williams, R.W., Rubin, G.M.: Computational identification of Drosophila microRNA genes. Genome Biol. 4, R42 (2003)
Yousef, M., Levy, D., Allmer, J.: Species categorization via MicroRNAs—based on 3’UTR target sites using sequence features. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technology, Bioinformatics, vol. 4, pp. 112–118. SciTePress (2018)
Yousef, M., Khalifa, W., İlhan Erkin, A., Allmer J.: MicroRNA categorization using sequence motifs and k-mers. BMC Bioinform. [Internet] 18, 170 (2017). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1584-1
Yousef, M., Nigatu, D., Levy, D., Allmer, J., Henkel, W.: Categorization of species based on their MicroRNAs employing sequence motifs, information-theoretic sequence feature extraction, and k-mers. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process (2017)
Nigatu, D., Sobetzko, P., Yousef, M., Henkel, W.: Sequence-based information-theoretic features for gene essentiality prediction. BMC Bioinform. [Internet] 18, 473 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1884-5
Yousef, M., Khalifa, W., Acar, E., Allmer, J.: MicroRNA categorization using sequence motifs and k-mers. BMC Bioinform. 18 (2017)
Cakir, M.V., Allmer, J.: Systematic computational analysis of potential RNAi regulation in Toxoplasma gondii. In: 2010 5th International Symposium on Health Informatics and Bioinformatics (HIBIT), pp. 31–38. IEEE, Ankara, Turkey (2010)
Edgar, R.C.: Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460–2461 (2010)
Shaltout, N.A.N., El-Hefnawi, M., Rafea, A., Moustafa, A.: Information gain as a feature selection method for the efficient classification of Influenza-A based on viral hosts. In: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, pp. 625–631. Newswood Limited (2014)
Berthold, M.R., Cebron, N., Dill, F., Gabriel, T.R., Kötter, T., Meinl, T., et al.: KNIME: The Konstanz Information Miner. SIGKDD Explor. 319–326 (2008)
Xu, Q.-S., Liang, Y.-Z.: Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 56, 1–11 (2001)
Matthews, B.W.: Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. BBA—Protein Struct. 405, 442–451 (1975)
Yousef, M., Allmer, J., Khalifaa, W.: Plant MicroRNA Prediction employing Sequence Motifs Achieves High Accuracy (2015)
Tanzer, A., Stadler, P.F.: Evolution of microRNAs. Methods Mol. Biol. 342, 335–350 (2006)
Yousef, M., Nigatu, D., Levy, D., Allmer, J., Henkel, W.: Categorization of species based on their microRNAs employing sequence motifs, information-theoretic sequence feature extraction, and k-mers. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2017 (2017)
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Zefat Academic College to MY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yousef, M. (2019). Hamming Distance and K-mer Features for Classification of Pre-cursor microRNAs from Different Species. In: Benavente-Peces, C., Slama, S., Zafar, B. (eds) Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Smart Innovation, Ergonomics and Applied Human Factors (SEAHF). SEAHF 2019. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 150. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22964-1_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22964-1_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-22963-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-22964-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)