Abstract
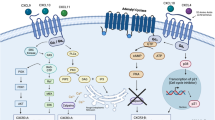
CXCR3 is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the chemokines CXCL9 (Mig), CXCL10 (IP-10), and CXCL11 (I-Tac). The murine receptor also binds CCL21. CXCR3 is expressed on activated T cells, B cells, Natural Killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, mast cells, and endothelial cells, and has now been reported on many malignant cells. There are several CXCR3 variants: CXCR3-A promotes chemotaxis and also plays a role in cell survival, CXCR3-B activation leads to inhibited DNA synthesis and apoptosis but less is known regarding the pathophysiologic role of CXCR3-alt. Melanoma, breast, and colon cancer cell lines express CXCR3, however, expression levels are not correlated with metastatic potential. Nevertheless, gene silencing of CXCR3 reduces the number of lymph node metastases from implanted melanoma or colon cancers without affecting expansion of the primary tumor implant or dissemination to the lungs. Gene silencing or antagonism of CXCR3 with a small molecular weight (m.w.) antagonist also inhibits breast cancer metastasis but in this setting, pulmonary metastases are reduced by receptor blockade. In all three histologic types, CXCR3 expression is associated with a poorer prognosis. In clear cell renal carcinoma and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia the opposite correlation is observed, where low CXCR3 is associated with shorter survival. In spite of the demonstrated contribution of tumor-expressed CXCR3 in promoting tumor metastasis in several disease settings, local overexpression of CXCR3 ligands leads to tumor inhibition in several cancer models. Antiangiogenic properties of CXCR3 ligands as well as the ability to attract CXCR3+ T lymphocytes and NK cells to the tumor contribute to the protective mechanisms. Manipulation of the CXCR3/CXCL3 axis should be considered as a potential therapeutic approach to prevent cancer progression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lazzeri E, Romagnani P. CXCR3-binding chemokines: novel multifunctional therapeutic targets. Curr. Drug Targets Immunol. Endocr Metabol Disord. 5:109–18, 2005.
Arenberg DA, Kunkel SL, Polverini PJ, Morris SB, Burdick MD, Glass MC, Taub DT, Iannettoni MD, Whyte RI, Streiter RM. Interferon-γ-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) is an angiostatic factor that inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumorigenesis and spontaneous metastases. J. Exp. Med. 184:981–992, 1996.
Shahabuddin S, Ji R, Wang P, Brailoiu E, Dun N, Yang Y, Aksoy MO, Kelsen SG. CXCR3 chemokine receptor-induced chemotaxis in human airway epithelial cells: role of p38 MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways. Am. J. Cell Physiol. 291:C34–9, 2006.
Dagan-Berger M, Feniger-Barish, Avniel S, Wald H, Galun E, Brabovsky V, Alon R, Nagler A, Ben-Baruch A, Peled A. Role of CXCR3 carboxyl terminus and third intracellular loop in receptor-mediated migration, adhesion and internalization in response to CXCL11. Blood 107:3821–31, 2006.
Lasagni L, Francalanci M, Annunziato F, Lazzeri E, Giannini S, Cosmi L, Sagrinati C, Mazzinghi B, Orlando C, Maggi E, Marra F, Romagnani S, Serio M, Romagnani, P. An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth induced by IP-10, Mig and I-TAC and acts as functional receptor for platelet factor 4. J. Exp. Med. 197:1537–1549, 2003.
Ehlert JE, Addison CA, Burdick MD, Kunkel SL, Strieter, RM. Identification and partial characterization of a variant of human CXCR3 generated by posttranscriptional exon skip**. J. Immunol. 173:6234–6240, 2004.
Sfriso P, Oliviero F, Calabrese F, Miiorin M, Faco M, Contri A, Cabrelle A, Baesso I, Cozzi F, Andretta M, Cassatella MA, Fiocco U, Todesco S, Konttinen YT, Punzi L, Agostini C. Epithelial CXCR3-B regulates chemokines bioavailability in normal, but not in Sjogren’s syndrome salivary glands. J. Immunol. 176:2581–2589, 2006.
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A Verastegui E, Zlotnik A. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–6, 2001.
Goldberg-Bittman L, Neumark E, Sagi-Assif O, Azenshtein E, Meshel T, Witz IP, Ben-Baruch, A. The expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its ligand, CXCL10, in human breast adenocarcinoma cell lines. Immunol. Lett. 92:171–8, 2004.
Goldberg-Bittman L, Sagi-Assif O, Meshel T, Nevo I, Levy-Nissenbaum O, Yron I, Witz IP, Ben-Baruch A. Cellular characteristics of neuroblastoma cells: Regulation by the ELR-- CXC chemokine CXCL10 and expression of a CXCR3-like receptor. Cytokine 29:105–17, 2005.
Jones D, Benjamin RJ, Shahsafaei A, Dorfman DM. The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is expressed in a subset of B-cell lymphomas and is a marker of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 95:627–32, 2000.
Kawada K, Sonoshita M, Sakashita H, Takabayashi A, Yamaoka Y, Manabe T, Inaba K, Minato N, Oshima M, Taketo MM. Pivotal role of CXCR3 in melanoma cell metastasis to lymph nodes. Cancer Res. 64:4010–7, 2004.
Kawada K, Hosogi H, SonoshitaM, Sakashita H, Manabe T, Shimahara Y, Sakai Y, Takabayashi A, Oshima M, Taketo MM. Chemokine receptor CXCR3 promotes colon cancer metastasis to lymph nodes. Oncogene 26:4679–4688, 2007.
Robledo MM, Bartolome RA, Longo N, Rodriguez-Frade JM, Mellado M, Longo I, van Muijen GN, Sanchez-Mateos, Teixido J. Expression of functional chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR4 on human melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276:45098–105, 2001.
Engl T, Relja B, Blumenberg C, et al. Prostate tumor CXC-chemokine profile correlates with cell adhesion to endothelium and extracellular matrix. Life Sci. 78:1784–93, 2006.
Trentin L, Agostini C, Facco M, Piazza F, Perin A, Siviero M, Gurrieri C, Galvan S, Adami F, Zambello R, Semenzato G. The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is expressed on malignant B cells and mediates chemotaxis. J. Clin. Invest. 104:115–21, 1999.
Klatte T, Seligson DB, Leppert JT, Riggs SB, Yu H, Zomorodian N, Kabbinavar FF, Strieter RM, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ. The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 179:61–66, 2008.
Ocana E, Delgado-Perez L, Campos-Caro A, Munoz J, Paz A, Franco R, Brieva JA. The prognostic role of CXCR3 expression by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Haematologica 92:349–356, 2007.
Monteagudo C, Martin JM, Jorda E, Llombart-Bosch A. CXCR3 chemokine receptor immunoreactivity in primary cutaneous malignant melanoma:correlation with clinicopathologic prognostic factors. J. Clin. Pathol. 60:596–9, 2007.
Datta D, Flaxenburg JA, Laxmanan S, Geehan C, Grimm M, Waaga-Gasser AM, Briscoe DM, and Pal S. Ras-induced modulation of CXCL10 and its receptor splice variant CXCR3-B in MDA-MB-435 and MCF-7 cells: relevance for the development of human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:9509–9518, 2006.
Walser TC, Rifat S, Ma X, Kundu N, Ward C, Goloubeva O, Johnson MG, Medina JC, Collins TL, Fulton AM. Antagonism of CXCR3 inhibits lung metastasis in a murine model of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:7701–7707, 2006.
Aksoy MO, Yang Y, Ji R, Reddy PJ, Shahabuddin S, Litvin J, Rogers TJ, Kelsen SG. CXCR3 surface expression in human airway epithelial cells:cell cycle dependence and effect on cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 290:L909–18, 2005.
Zipin-Roitman A, Meshel T, Sagi-Assif O, Shalmon B, Avivi C, Pfeffer RM, Witz IP, Ben-Baruch A. CXCL10 promotes invasion-related properties in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:3396–3405, 2007.
Shen H, Schuster R, Lu B, Waltz SE, Lentsch AB. Critical and opposing roles of the chemokine receptors CXCR2 and CXCR3 in prostate tumor growth. Prostate 66:1721–1728, 2006.
Nagpal ML, Davis J, Lin T. Overexpression of CXCL10 in human prostate LnCaP cells activates its receptor (CXCR3) expression and inhibits cell proliferation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1762:811–818, 2006.
Furuya M, Suyama T, Usui H, Kasuya Y, Nishiyama M, Tanaka N. et al. Up-regulation of CXC chemokines and their receptors: implications for proinflammatory microenvironments of ovarian carcinomas and endometriosis. Human Path. 38: 1676–1687, 2007.
Kondo T, Ito F, Nakazawa H, Horita S, Osaka Y and Toma H. High expression of chemokine gene as a favorable prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 171: 2171–5, 2004.
Kunz M, Toksoy A, Goebeler M, Engelhardt E, Brocker E, Gillitzer R. Strong expression of the lymphoattractant CXC chemokine Mig is associated with heavy infiltration of T cells in human malignant melanoma. J. Pathol. 189: 52–8, 1999.
Chu Y, Yang X, Xu W, Wang Y., Guo Q., **ong S. In situ expression of IFN-γ-inducible T cell α chemoattractant in breast cancer mounts an enhanced specific anti-tumor immunity which leads to tumor regression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 56: 1539–1549, 2007.
Winter D, Moser J, Kriehuber E, Wiesner C, Knobler R, Trautinger F, Bombosi P, Stingl, G, Petzelbauer P, Rot A, Maurer D. Down modulation of CXCR3 surface expression and function in CD8+ T cells from cutaneous T cell lymphoma patients. J. Immunol. 179: 4272–82, 2007.
**a T, O’Hara A, Araujo I, Barreto J, Carvalho E, Sapucaia JB, Ramos JC, Luz E, Pedroso C, Manrique M, Toomey NL, Brites C, Dittmer DP, Harrington, WJ. EBV microRNAs in primary lymphomas and targeting of CXCL-11 by ebv-mir-BHRF1-3. Cancer Res. 68: 1436–1442, 2008.
Tominaga M, Isashita Y, Ohta M, Shibata K, Ishio T, Ohmori N, Goto T, Sato S, Kitano S. Antitumor effects of the MIG and IP-10 genes transferred with poly [D,L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid] on murine neuroblastoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 14:696–705, 2007.
Luster AD, Leder P. IP-10, a CXC chemokine, elicits a potent thymus-dependent antitumor response in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 178:1057–1065, 1993.
Sgadari C, Angiolillo AL, Cherney BW, Pike SE, Farber JM, Koniaris LG, Vanguri P, Burd PR, Sheikh N, Gupta G, Teruya-Feldstein J, Tosato G. Interferon-inducible protein-10 identified as a mediator of tumor necrosis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. 93:13791–13796, 1996.
Feldman AL, Friedl J, Lans TE, Libutti SK, Lorang D, Miller MS, Turner EM, Hewitt SM, Alexander HR. Retroviral gene transfer of interferon-inducible protein 10 inhibits growth of human melanoma xenografts. Int. J. Cancer 99:149–153, 2002.
Pan J, Burdick MD, Belperio JA, Xue YY, Gerard C, Sharma S, Dubinett SM, and Strieter RM. CXCR3/CXCR3 ligand biological axis impairs RENCA tumor growth by a mechanism of immunoangiostasis. J. Immunol. 176:1456–1464, 2006.
Dorsey R, Kundu N, Yang Q, Tannenbaum CS, Sun H, Hamilton TA, Fulton AM. Immunotherapy with interleukin-10 depends on the CXC chemokines inducible Protein-10 and Monokine induced by IFN-γ. Cancer Res. 62: 2606–2610, 2002.
Walser TC, Ma X, Kundu N, Dorsey R, Goloubeva O, Fulton AM. Immune-mediated modulation of breast cancer growth and metastasis by the chemokine Mig (CXCL9) in a murine model. J. Immunother. 30:490–498, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Li, Y., Fulton, A.M. (2009). The CXCR3/CXCL3 Axis in Cancer. In: Fulton, A. (eds) Chemokine Receptors in Cancer. Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-267-4_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-267-4_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60327-266-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-60327-267-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)