Abstract
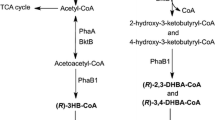
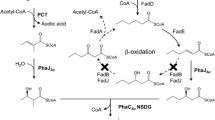
Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) consisting of 3-hydroxyalkanoates (3HAs) of 4 to 10 carbon atoms was examined in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains. When the fadA and / or fadB mutant E. coli strains harboring the plasmid containing the Pseudomonas sp. 61–3 phaC2 gene and the Ralstonia eutropha phaAB genes were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium supplemented with 2 g/L of sodium decanoate, all the recombinant E. coli strains synthesized PHAs consisting of C4, C6, C8, and C10 monomer units. The monomer composition of PHA was dependent on the E. col i strain used. When the fadA mutant E. coli was employed, PHA containing up to 63 mol% of 3-hydroyhexanoate was produced. In fadB and fad B mutant E. coli strains, 3-hydroxybutyrate (3HB) was efficiently incorporated into PHA up to 86 mol%. Cultivation of recombinant fadA and / or fadB mutant E. coli strains in LB medium containing 10 g/L of sodium gluconate and 2 g/L of sodium decanoate resulted in the production of PHA copolymer containing a very high fraction of 3HB up to 95 mol%. Since the material properties of PHA copolymer consisting of a large fraction of 3HB and a small fraction of medium-chain-length 3HA are similar to those of low-density polyethylene, recombinant E. coi strains constructed in this study should be useful for the production of PHAs suitable for various commercial applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A. J. and Dawes, E. A. (1990), Microbiol. Rev. 54, 450–472.
Doi, Y. (1990), Microbial Polyesters, VCH, New York, NY.
Lee, S. Y. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 49, 1–14.
Madison, L. L. and Huisman, G. W. (1999), Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63, 21–53.
Steinbüchel, A. and Füchtenbusch, B. (1998), Trends Biotechnol. 16, 419–427.
Lee, S. Y. (1996), Trends Biotechnol. 14, 431–438.
Steinbüchel, A.and Valentin, H. E. (1995), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 128, 219–228.
Liebergesell, M., Mayer, F., and Steinbüchel, A. (1993), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 40, 292–300.
Brandl, H., Knee, E. J., Fuller, R. C., Gross, R. A., and Renz, R. W. (1989), Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 11, 49–55.
Liebergesell, M., Hustede, E., Timm, A., Steinbüchel, A., Fuller, R. C., Lenz, R. W., and Schlegel, H. G. (1991), Arch. Microbiol. 155, 415–421.
Haywood, G. W., Anderson, A. J., Williams, G. A., Dawes, E. A., and Ewing, D. F. (1991), Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 13, 83–87.
Kato, M., Bao, H. J., Kang, C. K., Fukui, T., and Doi, Y. (1996), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 363–370.
Kobayashi, G., Shiotani, T., Shima, Y., and Doi, Y. (1994), in Biodegradable Plastics and Polymers, Doi, Y. and Fukuda, K., eds., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 410–416.
Lee, S. H., Oh, D. H., Ahn, W. S., Lee, Y., Choi, J., and Lee, S. Y. (2000), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 67, 240–244.
Steinbüchel, A. and Wiese, S. (1992), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37, 601–697.
Doi, Y., Kitamura, S., and Abe, H. (1995), Macromolecules 28, 4822–4828.
Matsusaki, H., Abe, H., and Doi, Y. (2000), Biomacromoles 1, 17–22.
Matsusaki, H., Manji, S., Taguchi, K., Kato, M., Fukui, T., Doi, Y. (1998), J. Bacteriol. 180, 6459–6467.
Matsusaki, H., Abe, H., Taguchi, K., Fukui, T., and Doi, Y. (2000), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53, 401–419.
Tsuge, T., Fukui, T., Matsusaki, H., Taguchi, S., Kobayashi, G., Ishizaki, A., and Doi, Y. (2000), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 184, 193–198.
Park, S. J., Park, J. P., and Lee, S. Y. (2002), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 214, 217–222.
Langenbach, S., Rehm, B. H. A., and Steinbüchel, A.. (1997), FEMS Microbiol. Lett.150, 303–309.
Qi, Q., Steinbüchel, A.., and Rehm, B. H. A. (1998), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 167, 89–94.
Snell, K. D., Feng, F., Zhong, L., Martin, D., and Madison, L. L. (2002),J. Bacterio1.184, 5696–5705.
Ren, Q., Sierro, N., Witholt, B., and Kessler, B. (2000), J. Bacteriol. 182, 2978–2981.
Park, S. J., Park, J. P., Lee, S. Y., and Doi, Y. (2003), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 33, 62–70.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., and Maniatis, T. (1989), Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2ndEd., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Lee, S. Y. (1994), Biotechnol. Lett. 16, 1247–1252.
Peekhaus, N. and Conway, T. (1998), J. Bacteriol. 180, 1777–1785.
Choi, J., Lee, S. Y., and Han, K. (1998), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 4897–4903.
Braunegg, G., Sonnleitner, B., and Lafferty, R. M. (1978), Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 6, 29–37.
Taguchi, K., Aoyagi, Y., Matsusaki, H., Fukui, T., and Doi, Y. (1999), FEMS Microbiol Lett. 176, 183–190.
Campbell, J. W., Morgan-Kiss, R. M., and Cronan, J. E. Jr. (2003), Mol. Microbiol. 47, 793–805.
Park, S. J. and Lee, S. Y. (2003), J. Bacteriol. 185, 5391–5397.
Ren, Q., Sierro, N., Kellerhals, M., Kessler, B., and Witholt, B. (2000), App. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 1311–1320.
Schubert, P., Steinbüchel, A.., and Schlegel, H. G. (1988), J. Bacteriol. 170, 5837–5847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, S.J., Lee, S.Y. (2004). Biosynthesis of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyalkanoates) by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coli Strains. In: Finkelstein, M., McMillan, J.D., Davison, B.H., Evans, B. (eds) Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals Held May 4–7, 2003, in Breckenridge, CO. Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59259-837-3_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59259-837-3_29
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-9873-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-59259-837-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive