Abstract
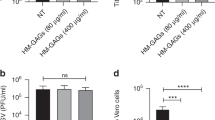
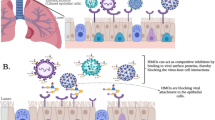
Sulfated glycolipids (SG) and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) present on the surface of colonic, vaginal epithelial, and neuroglial cells bind to HIV gpl20, suggesting that these glycoconjugates may have a role in HIV infection. The major goal of our study was to test the ability of SG and GAG from human milk to inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro. SG and GAG were purified from pooled human milk and characterized by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry. Eight different preparations of SG and one of GAG were tested for inhibition of infection. Two laboratory isolates, HIV-1Ada (macrophage-tropic virus) and HIV-1SF2 (lymphotropic virus), were used for inhibition assays using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM). Inhibition assays were performed by preincubation of serial dilutions of glycoconjugates with each virus before infecting the monolayer of cultured MDM and PBMC. After 4 days, HIV p24 antigen was quantified by enzyme immunoassay (EIA) in culture supernatants. Significant inhibition of viral infectivity was defined as >80% reduction in p24 concentration. GAG showed a low inhibitory effect (8–44%) in HIV-1 infection of PBMC. Table 1 shows the minimal amounts of the most active SG fractions, expressed as volumes of human milk from which they were extracted, that inhibit >80% HIV-1 infection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertozzi CR, Kiessling LL. Chemical glycobiology. Science 2001;291:2357–2364.
Bhat S, Mettus RV, Reddy EP, Ugen KE, Srikanthan V, Williams WV, Weiner DB. The galactosyl ceramide/sulfatide receptor binding region of HIV-1 gpl20 maps to amino acids 206–275. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 1993;9:175–181.
Furuta Y, Eriksson K, Svennerholm B, Fredman P, Horal P, Jeansson S, Vahlne A, Holmgren J, Czerkinsky C. Infection of vaginal and colonic epithelial cells by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is neutralized by antibodies raised against conserved epitopes in the envelope glycoprotein gpl20. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:12559–12563.
Harouse JM, Bhat S, Spitalnik SL, Laughlin M, Stefano K, Silberberg DH, Gonzalez-Scarano F. Inhibition of entry of HIV-1 in neural cell lines by antibodies against galactosyl ceramide. Science 1991;253:320–323.
Hirabayashi Y, Ichikawa S. In: Fukuda M, Hindsgaul O, editors. Roles of Glycolipids and Sphingolipids in Biological Membrane. The Frontiers in Molecular Biology Series. Oxford: IRL Press at Oxford University Press, 1999; pp 220–248.
Kamisago S, Iwamori M, Tai T, Mitamura K, Yazaki Y, Sugano K. Role of sulfatides in adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to gastric cancer cells. Infect Immun 1996;64:624–628.
Newburg DS. Human milk glycoconjugates that inhibit pathogens. Curr Med Chem 1999;6:117–127.
Newburg DS. Oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates in human milk: their role in host defense. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 1996;1:271–283.
Newburg DS, Linhardt RJ, Ampofo SA, Yolken RH. Human milk glycosaminoglycans inhibit HIV glycoprotein gpl20 binding to its host cell CD4 receptor. J Nutr 1995;125:419–424.
Nicoll A, Newell ML, Peckham C, Luo C, Savage F. Infant feeding and HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2000;14 Suppl 3:S57–74.
Richardson BA, John-Stewart GC, Hughes JP, Nduati R, Mbori-Ngacha D, Overbaugh J, Kreiss JK. Breast-milk infectivity in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected mothers. J Infect Dis 2003; 187:736–740.
Schneider-Schaulies J. Cellular receptors for viruses: links to tropism and pathogenesis. J Gen Virol 2000;81:1413–1429.
Schwartz SA, Nair MP. Current concepts in human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 1999;6:295–305.
Suzuki T, Sometani A, Yamazaki Y, Horiike G, Mizutani Y, Masuda H, Yamada M, Tahara H, Xu G, Miyamoto D, Oku N, Okada S, Kiso M, Hasegawa A, Ito T, Kawaoka Y, Suzuki Y. Sulphatide binds to human and animal influenza A viruses, and inhibits the viral infection. Biochem J 1996;318(Part 2):389–393
UNAIDS. AIDS Epidemic Update, December 2002.
Vos JP, Lopes-Cardozo M, Gadella BM. Metabolic and functional aspects of sulfogalactolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1994;1211:125–149.
Yahi N, Baghdiguian S, Moreau H, Fantini J. Galactosyl ceramide (or a closely related molecule) is the receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on human colon epithelial HT29 cells. J Virol 1992;66:4848–4854.
Yarema KJ, Bertozzi CR. Chemical approaches to glycobiology and emerging carbohydrate-based therapeutic agents. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1998;2:49–61.
Zopf D, Roth S. Oligosaccharide anti-infective agents. Lancet 1996;347:1017–1021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Viveros-Rogel, M., Soto-Ramirez, L., Chaturvedi, P., Newburg, D.S., Ruiz-Palacios, G.M. (2004). Inhibition of HIV-1 Infection in Vitro by Human Milk Sulfated Glycolipids and Glycosaminoglycans. In: Pickering, L.K., Morrow, A.L., Ruiz-Palacios, G.M., Schanler, R.J. (eds) Protecting Infants through Human Milk. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 554. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-4242-8_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-4242-8_69
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-3461-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4757-4242-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive