Abstract
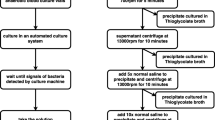
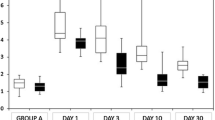
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) has been used as a reliable treatment of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) for more than 10 years.(1) However, peritonitis remains the most frequent complication and cause of failure of the method.(2) Although several useful blind schemes of antibiotic therapy have been used,(3,4) an early bacteriological diagnosis is very important for a more rational treatment. According to Vas,(5) the use of routine bacteriological techniques does not allow identification of the etiological organisms in 30–40% of cases. In addition, the use of more specialized bacteriological methods are cumbersome and expensive, thus limiting their use routinely. In the present study, we show the experience with a cytocentrifuge developed in our laboratory in order to establish an earlier bacteriological diagnosis of CAPD peritonitis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steimberg SM, Cutler SJ, Novak JW, Nolph KD. Report of the National CAPD Registry, Potomac, Emmes Corporation, 1985.
Prowant B, Nolph KD, Ryan L, Twardowski Z, Khanna R. Nephron 1986; 43: 105–109.
Williams P, Khanna R, Vas SI, Oreopoulos DG, Layne S, Pantalony D. Perit Dial Bull 1981; 1: 14–17.
Gruer LD, Turney JH, Curley J, Michael J, Adu D. Nephron 1985; 41: 279–282.
Vas SI. Perit Dial Bull 1981; 1: S11–S14.
Williams P, Pantalony D, Vas SI, Khanna R, Oreopoulos DG. Perit Dial Bull 1981; 1: 59–62.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1990 Plenum Publishing Corporation
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Durrego, P., Bellorin-Font, E., Weisinger, J.R., Paz-Martinez, V., Boissiere, M., Amair, P. (1990). Early Bacteriological Diagnosis of Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Peritonitis with the Use of a Cytocentrifuge. In: Avram, M.M., et al. Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-9555-7_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-9555-7_55
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4615-9557-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-9555-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive